Abstract
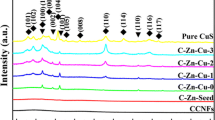
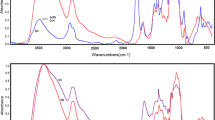
We report a simple and effective route to fabricate branched hierarchical flower-like nanostructures of ZnO on natural cotton cellulose fiber by combining electrospinning and the low-temperature hydrothermal growth technique. First, natural cotton cellulose nanofibers were prepared by electrospinning cotton cellulose /LiCl/DMAc solution. The electrospun cotton cellulose nanofibers served as flexible substrate, on which the branched, highly uniform, and dense flower-like ZnO were hydrothermally grown. The as-prepared cotton cellulose/ZnO nanocomposite fibers were characterized by SEM, HRTEM, EDS, TG, and UV-vis spectrophotometry. The modified cotton cellulose nanocomposite fibers were not only exhibiting dispersed uniformly, but also rendered excellent protection against UV radiation because of the incorporation of flower-like ZnO nanostructures. Therefore, the as-prepared nanocomposite fibers demonstrate a significant performance in ultraviolet protection and provide a potential application for ultraviolet detection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. M. Low, J. Somers, H. S. Kho, I. J. Davies, and B. A. Latella, Compos. Interface, 16, 659 (2009).
B. Surma-Slusarska, S. Presler, and D. Danielewicz, Fibres. Text. East. Eur., 16, 108 (2008).
T. A. Wheatley, Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm, 33, 281 (2007).
T. Grafe and K. Graham, Int. Nonwov. J., 12, 51 (2003).
S. Liu, L. Zhang, J. Zhou, and R. Wu, J. Phys. Chem. C, 112, 4538 (2008).
J. Zeng, S. Liu, J. Cai, and L. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. C, 114, 7806 (2010).
H. Gullapalli, V. S. M. Vemuru, A. Kumar, A. Botello-Mendez, R. Vajtai, M. Terrones, S. Nagarajaiah, and P. M. Ajayan, Small, 6, 1641 (2010).
A. Kumar, H. Gullapalli, K. Balakrishnan, A. Botello- Mendez, R. Vajtai, M. Terrones, and P. M. Ajayan, Small, 7, 2173 (2011).
E. L. Bai, L. Cen, F. L. Chen, and Y. H. Zhou, New. Chem. Mater, 40, 35 (2012).
H. F. Wang, Y. Y. Chen, and H. Lin, J. Soochow. Univ., 23 (2003).
A. Mihranyan, L. Nyholm, A. E. G. Bennett, and M. Strømme, J. Phys. Chem. B, 112, 12249 (2008).
A. Yadav, V. Prasad, A. Kathe, S. Raj, D. Yadav, C. Sundaramoorthy, and N. Vigneshwaran, B. Mater. Sci., 29, 641 (2006).
J.-H. He, Y.-Q. Wan, and L. Xu, Chaos. Soliton. Fract, 33, 26 (2007).
A. Svensson, E. Nicklasson, T. Harrah, B. Panilaitis, D. Kaplan, M. Brittberg, and P. Gatenholm, Biomaterials, 26, 419 (2005).
A. Bozzi, T. Yuranova, I. Guasaquillo, D. Laub, and J. Kiwi, J. Photoch. Photobio A, 174, 156 (2005).
A. Manekkathodi, M. Y. Lu, C. W. Wang, and L. J. Chen, Adv. Mater., 22, 4059 (2010).
C. R. Li, R. Chen, X. Q. Zhang, J. Xiong, Y. Y. Zheng, and W. J. Dong, Fiber. Polym., 12, 345 (2011).
R. Wang, J. H. Xin, X. M. Tao, and W. A. Daoud, Chem. Phys. Lett., 398, 250 (2004).
R. Wang, J. Xin, and X. Tao, Inorg. Chem., 44, 3926 (2005).
H. Lu, B. Fei, J. H. Xin, R. Wang, and L. Li, J. Colloid. Interface Sci., 300, 111 (2006).
L. E. Greene, M. Law, D. H. Tan, M. Montano, J. Goldberger, G. Somorjai, and P. Yang, Nano. Lett., 5, 1231 (2005).
P. Tonto, O. Mekasuwandumrong, S. Phatanasri, V. Pavarajarn, and P. Praserthdam, Ceram. Int., 34, 57 (2008).
C. R. Li, S. X. Shu, R. Chen, B. Chen, and W. Dong, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., DOI: 10.1002/app.39264.
Y. Li, Y. Zou, and Y. Hou, Cellulose, 18, 1643 (2011).
C. H. Ku and J. J. Wu, J. Phys. Chem. B, 110, 12981 (2006).
J. Xu, H. L. Su, J. Han, Y. Chen, W. Q. Song, Y. Gu, W. J. Moon, and D. Zhang, Appl. Phys. A-Mater., 108, 235 (2012).
B. Xu and Z. Cai, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 108, 3781 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Xie, Y., Liu, Q. et al. The formation and UV-blocking property of flower-like ZnO nanorod on electrospun natural cotton cellulose nanofibers. Fibers Polym 15, 281–285 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0281-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0281-1