Abstract
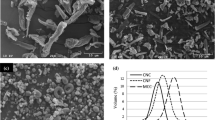
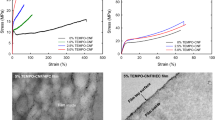
Nanocellulose was prepared by acid hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) at different hydrobromic acid (HBr) concentrations. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) composite films were prepared by the reinforcement of nanocellulose into a PVA matrix at different filler loading levels and subsequent film casting. Chemical characterization of nanocelluloses was performed for the analysis of crystallinity (Xc), degree of polymerization (DP), and molecular weight (Mw). The mechanical and thermal properties of the nanocellulose reinforced PVA films were also measured for tensile strength and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The acid hydrolysis decreased steadily the DP and Mw of MCC. The crystallinity of MCC with 1.5 M and 2.5 M HBr showed a significant increase due to the degradation of amorphous domains in cellulose. Higher crystalline cellulose showed the higher thermal stability than MCC. From X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, nanocellulose samples showed the higher peak intensity than MCC cases. Reduction of MCC particle by acid hydrolysis was clearly observed from scanning electron microscope (SEM) images. The tensile and thermal properties of PVA composite films were significantly improved with the increase of the nanocellulose loading.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Nishino, I. Matsuda, and K. Hirao, Macromolecules, 37, 7683 (2004).
S. J. Eichhorn, C. A. Baillie, N. Zafeiropoulos, L. Y. Mwaikambo, M. P. Ansell, and A. Dufresne, J. Mater. Sci., 36, 2107 (2001).
D. Fengel and G. Wegner, “Wood-Chemistry, Ultrastructure, Reactions”, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, New York, 1989.
D. Klemm, B. Heublein, H. P. Fink, and A. Bohn, Angew Chem. Int. Ed., 44, 2 (2005).
T. Zimmerman, E. Pöhler, and P. Schwaller, Adv. Eng. Mater., 12, 1156 (2005).
K. Oksmann and M. Sain, “Cellulose Nanocomposites-Processing, Characterization and Properties”, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 2006.
T. Nishino, K. Takano, and K. J. Nakamae, Polym. Sci. B, 33, 1647 (1995).
A. S. Azizi-Samir, F. Alloin, M. Paillet, and A. Dufresne, Macromolecules, 37, 4313 (2004).
H. Takagi and A. Asano, Compos. Part A, 39, 685 (2008).
R. F. Nickerson and J. A. Habrle, Ind. Eng. Chem., 39, 1507 (1947).
B. G. Ranby, Tappi, 35, 53 (1952).
V. Favier, H. Chanzy, and J. Y. Cavaille, Macromolecules, 28, 6365 (1995).
M. N. Angles and A. Dufresne, Macromolecules, 35, 2190 (2002).
A. P. Mathew, K. Oksman, and M. Sain, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 97, 2014 (2005).
K. E. Strawhwcker and E. Manias, Chem. Mater., 12, 2943 (2000).
H. Matsuyama and J. F. Young, Chem. Mater., 11, 16 (1999).
E. Tadd, A. Zeno, M. Zubris, N. Dan, and R. Tannenbaum, Macromolecules, 36, 6497 (2003).
Y. Li, K. G. Neoh, and E. T. Kang, Polymer, 45, 8779 (2004).
T. Ke and X. S. Sun, J. Polym. Environ., 11, 7 (2003).
L. Segal, J. Creely, A. Martin, and C. Conrad, Text. Res. J., 29, 786 (1959).
E. H. Immergut, B. G. Ranby, and H. Mark, Ind. Eng. Chem., 45, 2383 (1953).
A. Alemdar and M. Sain, Bioresou. Technol., 99, 1664 (2008).
S. Y. Lee, H. S. Yang, H. J. Kim, C. S. Jeong, B. S. Lim, and J. N. Lee, Compos. Struct., 65, 459 (2004).
V. Favier, R. Dendievel, G. Canova, J. Y. Cavaille, and P. Gilormini, Acta Mater., 45, 1557 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SY., Mohan, D.J., Kang, IA. et al. Nanocellulose reinforced PVA composite films: Effects of acid treatment and filler loading. Fibers Polym 10, 77–82 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-009-0077-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-009-0077-x