Abstract
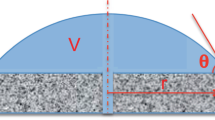
This paper presents initial work performed to develop a database of contact angles of sessile drops in reduced gravity. Currently, there is no database of wettability of sessile drops in reduced gravity. The creation of such a database is imperative for continued investigations of heat and/or mass transfer in reduced gravity and future engineering designs. In this research, liquid drops of water and ethanol were created on aluminum and PTFE substrates. The formed drops were characterized by their dimensions including contact angle, wetted perimeter and droplet shape in both normal gravity and reduced gravity. The droplets were recorded during testing with high definition video and the images obtained digitally analyzed, post-test, to determine their characteristics as a function of the experimental parameters. The Queensland University of Technology (QUT) Drop Tower Facility was utilized for the reduced gravity experimentation. For droplets with diameters above their capillary length, the changes in drop dimensions and/or wettability was observed. The Young-Laplace equation was validated to accurately predict the contact angle in reduced gravity for small droplets, however it was not adequate to describe the contact angle for larger drops (above the drops associated capillary length).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardin, J.D., Mudawar, I., Walsh, C.B., Frances, E.I.: Contact angle temperature dependence for water droplets on practical aluminum surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 40, 1017–1033 (1997)
Boyes, A.P., Ponter, A.B.: Wettability of copper and polytetrafluoroethylene surfaces with water: the influence of environmental conditions. Chem. Eng. Technol. 45, 1250–1256 (1973)
Brutin, D., Zhu, Z.Q., Rahli, O., Xie, J.C., Liu, Q.S., Tadrist, L.: Sessile drop in reduced gravity: creation, contact angle and interface. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 21, 67–76 (2009)
Brutin, D., Zhu, Z.Q., Rahli, O., Xie, J.C., Liu, Q.S., Tadrist, L.: Evaporation of ethanol drops on a heated substrate under microgravity conditions. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 22(3), 387–395 (2010)
Drelich, J.: The effect of drop (Bubble) size on contact angle at solid surfaces. J. Adhes. 63(1), 31–51 (1997)
Erbil, H.Y., Mchale, G., Newton, M.I.: Drop evaporation on solid surfaces: constant contact angle mode. Langmuir 18(7), 2636–2641 (2002)
Extrand, C.W., Kumagai, Y.: An experimental study of contact angle hysteresis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 191, 378–383 (1997)
Grandas, L.: Evaporation d’une goutte sessile: étude expérimentale des transferts de chaleur et de masse. Ph.D Thesis, Aix Marseille University (2004)
Hoorfar, M., Neuman, A.W.: Recent progress in Axisymmetric Drop Shape Analysis (ADSA). Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 121, 25–49 (2006)
Quere, D.: Wetting and roughness. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 38, 71–99 (2008)
Sodtke, C., Ajaev, V.S., Stephan, P.: Dynamic of volatile liquid droplets on heated surfaces: theory versus experiment. J. Fluid Mech. 610, 343–362 (2008)
Stalder, A.F., Kulik, G., Sage, D., Barbieri, L., Hoffmann, P.: A snake-based approach to accurate determination of both contact points and contact angles. Colloids Surf., A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 286, 1–3, 92–103 (2006)
Tarozzi, L., Muscio, A., Tartarini, P.: Experimental tests of dropwise cooling in infrared-transparent media. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 31, 857–865 (2007)
Young, T.: An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 95, 65–87 (1805)
Zhu, Z.Q., Brutin, D., Liu, Q.S., Wang, Y., Mourembles, A., Xie, J.C., Tadrist, L.: Experimental investigation of pendant and sessile evaporating drops. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 22(3), 339–345 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diana, A., Castillo, M., Brutin, D. et al. Sessile Drop Wettability in Normal and Reduced Gravity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 24, 195–202 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-011-9295-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-011-9295-0