Abstract
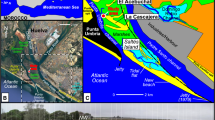
The Sele river plain is located along the western Tyrrhenian margin of the southern Apennine Chain and is confined seaward by a straight sandy coast formed during the Last Interglacial and the Holocene. The coastal plain is characterised by beach-dune ridges which interfinger landwards with lagoon and fluvio-palustrine deposits. This belt, which progressively grew up, represents the evolution of a barrier–lagoon system alternatively shifting landwards and seawards. The knowledge on the Holocene evolution of the Sele river coastal plain, along the coast of the Poseidonia-Paestum archaeological area, was improved by the drilling of two new cores and the collection of several archaeo-tephro-stratigraphic data. The area experienced the Holocene marine transgression which cut high cliffs in the travertine deposits. During the second half of the Holocene, the shoreline shifted seawards and a lagoon–beach bar system (Fossa Lupata-Laura) formed. The archaeological remains (VI cent. b.c.) and the Agnano Monte Spina tephra layer (4.1 ky BP) constrain chronologically this morpho-sedimentary system. After the VI cent. b.c., and mostly after the deposition of the 79 a.d. tephra layer, the shoreline shifted seawards and an additional beach ridge formed, while the flat area at the back (Fossa Lupata) was rapidly aggraded and dried up.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato V (2006) La risposta di alcuni tipici sistemi morfodinamici della Campania (Italia meridionale) alle variazioni climatiche oloceniche. Ph.D. thesis, pp 1–406 http://www.fedoa.unina.it
Amato V, Avagliano G, Cinque A, Cipriani M, Di Paola G, Pontrandolfo A, Rosskopf CM, Santoriello A (2009) Geomorphology and geoarchaeology of the Paestum area: modification of the physical environment in historical times. Mediterranee 112:129–135
Amorosi A, Lucchi MR, Rossi V, Sarti G (2009) Climate change signature of small-scale parasequences from Lateglacial–Holocene transgressive deposits of the Arno valley fill. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 273:142–152
Antonioli F, Anzidei M, Lambeck K, Auriemma R, Gaddi D, Furlani S, Orru` P, Solinas E, Gaspari A, Karinja S, Kovacic V, Surace L (2007) Sea-level change during the Holocene in Sardinia and in the northeastern Adriatic (central Mediterranean Sea) from archaeological and geomorphological data. Q Sci Rev 26:2463–2486
Barra D, Calderoni G, Cinque A, De Vita P, Rosskopf CM, Ermolli ER (1998) New data on the evolution of the Sele River coastal plain (southern Italy) during the Holocene. Il Quaternario 11:287–299
Barra D, Calderoni G, Cipriani M, De La Geniere’ J, Fiorillo L, Greco G, Lippi MM, Secci MM, Pescatore T, Russo B, Senatore MR, Sciarelli GT, Thorez J (1999) Depositional history and palaeogeographic reconstruction of Sele coastal plain during Magna Grecia settlement of Hera Argiva (southern Italy). Geologica Romana 35:151–166
Bartole R, Savelli C, Tramontana M, Wezel F (1984) Structural and sedimentary features in the Tyrrhenian margin of Campania, southern Italy. Mar Geol 55:163–180
Bourne A, Lowe J, Trincardi F, Asioli A, Blockley S, Wulf S, Matthews I, Piva A, Vigliotti L (2010) Distal tephra record for the last ca 105,000 years from core PRAD 1–2 in the central Adriatic Sea: implications for marine tephrostratigraphy. Q Sci Rev 29(23–24):3079–3094
Bradley RS (1999) Palaeoclimatology. International geophysic series 64. Harcourt Academic Press, p 245
Bradshaw JS (1957) Laboratory studies on the rate of growth of the foraminifer Streblus beccarii (Linne) var tepida (Cushman). J Paleontol 31(6):1138–1147
Brancaccio L, Cinque A, Belluomini G, Branca M, Delitala L (1986) Isoleucine epimerization dating and tectonic significance of upper Pleistocene sea level features of the Sele Plain (southern Italy). Zeit Geomorph N F 62(Suppl Bd):159–166
Brancaccio L, Cinque A, D’angelo G, Russo F, Santangelo N, Sgrosso I (1987) Evoluzione tettonica e geomorfologica della Piana del Sele (Campania, Appennino meridionale). Geografia Fisica e Dinamica Quaternaria 10:47–55
Brancaccio L, Cinque A, Russo F, Santangelo N, Alessio M, Allegri L, Improta S, Belluomini G, Branca M, Delitala L (1988) Nuovi dati cronologici sui depositi marini e continentali della Piana del F. Sele e della costa settentrionale del Cilento (Campania, Appennino meridionale). Atti del 74° Congresso Nazionale della Società Geologica Italiana A:55–62
Buccheri G, Bertoldo M, Coppa MG, Munno R, Pennetta M, Siani G, Valente A, Vecchione C (2002) Evoluzione sedimentaria e paleoclimatologia tardo-quaternaria della scarpata continentale del Golfo di Policastro (Mar Tirreno meridionale). Bollettino della Società Geologica Italiana 121:187–210
Calanchi N, Dinelli E (2008) Tephrostratigraphy of the last 170 ka in sedimentary successions from the Adriatic Sea. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 177:81–95
Carboni MG, Di Bella L (1997) The Plio-Pleistocene of the Anzio coast (Rome). Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana 36:135–159
Cimerman F, Langer MR (1991) Mediterranean Foraminifera. Slovenska Academia Znanosti in Umetnosti, Ljubljania, pp 1–119
Cinque A (1986) Guida alle escursioni geomorfologiche (Penisola Sorrentina, Capri, Piana del Sele e Monti Picentini). Riunione annuale del Gruppo Nazionale Geografia Fisica e Geomorfologia, Amalfi 1986. Pubbl. n. 33 del Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università Federico II di Napoli. p 119
Cinque A, Guida F, Russo F, Santangelo N (1988) Dati cronologici e stratigrafici su alcuni depositi continentali della Piana del Sele (Campania): i “Conglomerati di Eboli”. Geografia Fisica e Dinamica Quaternaria 11:39–44
D’Argenio B, Ferreri V, Violante C (1999) Travertine in the rise and decline of the ancient town of Paestum (2500–1000 BP). Eurobasin School, Event IX, Naples and Benevento, p 10
de Vita S, Orsi G, Civetta L, Carandente A, D’Antonio M, Deino A, di Cesare T, Di Vito MA, Fisher RV, Isaia R, Marotta E, Necco A, Ort M, Pappalardo L, Piochi M, Southon J (1999) The Agnano-Monte Spina eruption (4100 years BP) in the restless Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J Volcanol Geotherm Res 91:269–301
Deino AL, Orsi G, de Vita S, Piochi M (2004) The age of the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff caldera-forming eruption (Campi Flegrei caldera, Italy) assessed by 40Ar/39Ar dating method. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 133(1–4):157–170
Di Vito MA, Sulpizio R, Zanchetta G, D’Orazio M (2008) The late Pleistocene pyroclastic deposits of the Campanian Plain: new insights into the explosive activity of Neapolitan Volcanoes. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 177:19–48
Fiorini F, Vaiani SC (2001) Benthic foraminifers and transgressive-regressive cycles in the Late Quaternary subsurface sediments of the Po Plain near Ravenna (northern Italy). Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana 40:357–403
Galili E, Zvieli D, Weinstein-Evron M (2005) Holocene sea level changes and landscape evolution on the northern Carmel coast (Israel). Mediterranee 104:79–86
Guy M (1990a) La costa, la laguna e l’insediamento di Poseidonia-Paestum. In: Paestum: La città e il territorio. Quaderno di documentazione dell’Istituto della Enciclopedia Italiana Treccani, pp 67–77
Guy M (1990b) Le rivage maritime et la « lagune » de Poseidonia-Paestum. In: Livadie CA, Widemann F (Eds) Volcanologie et Archeologie. PACT 25:257–270
Insinga D, Molisso F, Lubritto C, Sacchi M, Passariello I, Morra V (2008) The proximal marine record of Somma-Vesuvius volcanic activity in the Naples and Salerno bays, Eastern Tyrrhenian Sea, during the last 3 kyrs. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 177:170–196
I.S.P.R.A. (2009) Note illustrative della Carta Geologica d’Italia alla scala 1:50.000. Foglio 486, Foce Sele. A cura di: Cinque A. Servizio Geologico Nazionale, pp 1–205
Jorissen FJ (1988) Benthic foraminifera from the Adriatic Sea: principles for phenotypic variation. Utrecht Micropalentol Bull 37:1–176
Kraft JC, Rapp G Jr, Aschenbrenner SE (1975) Late Holocene palaeogeography of the coastal plain of the Gulf of Messenia, Greece, and its relationships to archaeological settings and coastal change. Geol Soc Am Bull 86:1191–1208
Laborel J, Morhange R, Lafont R, Le Campion J, Laborel-Deguen F (1994) Biological evidence of sea level rise during the last 4500 years on the rocky coasts of continental France and Corsica. Mar Geol 120:203–223
Lambeck K, Antonioli F, Purcell A, Silenzi S (2004) Sea level change along the Italian coast for the past 10,000 years. Quat Sci Rev 23:1567–1598
Lambeck K, Anzidei M, Antonioli F, Benini A, Esposito A (2005) Sea level in Roman time in the Central Mediterranean and implications for recent change. Earth Planet Sci Lett 224:563–575
Le Bas MJ, Le Maitre RW, Streckeisen A, Zanettin B (1986) A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali–silica diagram. J Petrol 27:745–750
Leoni G, Dai Pra G (1997) Variazioni di livello del mare nel tardo Olocene lungo la costa del Lazio in base ad indicatori geoarcheologici. ENEA Tech. Rep. RT/AMB/97/8, Rome, pp 1–127
Lippmann-Baggioni M, Gars G (1984) La bordure sud des Monts Picentini: un jalon dans l’evolution neotectonique et paleoclimatique de l’Apennin Meridional. Geografia Fisica e Dinamica Quaternaria 7:49–58
Lippmann-Provansal M (1987) L’Apennin Campanien meridional (Italie). Etude Géomorphologique. Thése de Doctorat d’Etat. Univ. Aix-Marseille, p 486
Lirer L, Munno R, Petrosino P, Vinci A (1993) Tephrostratigraphy of the a.d. 79 pyroclastic deposits in perivolcanic areas of Mt. Vesuvio (Italy). J Volcanol Geotherm Res 58:133–149
Marciano R, Munno R, Petrosino P, Santangelo N, Santo A, Villa I (2008) Late Quaternary tephra layers along the Cilento coastline (southern Italy). J Volcanol Geotherm Res 177:227–243
Messerli B, Grosjean M, Hofer T, Nunez L, Pfister C (2000) From nature-dominated to human-dominated environmental changes. Quat Sci Rev 19:459–479
Morhange C, Laborel J, Hesnard A (2001) Changes of relative sea level during the past 5000 years in the ancient harbor of Marseilles. SouthFrance Palaeogeogr Palaeoclim Palaeoecol 166(3–4):319–329
Munno R, Petrosino P (2004) New constraints on the occurrence of Y-3 upper Pleistocene tephra marker layer in the Tyrrhenian sea. Il Quaternario 17(1):11–20
Munno R, Petrosino P (2007) Tephra layers in the S. Gregorio Magno lacustrine succession. J Quat Sci 22(3):247–266
Paterne M, Guichard F, Labeyrie J (1988) Esplosive activity of the south Italian volcanoes during the past 80,000 years as determined by marine tephrochronology. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 34:153–172
Pirazzoli PA (1976) Sea level variations in the northwest Mediterranean during Roman times. Science 194:519–521
Pirazzoli PA (1996) Sea-level changes. the last 20.000 years. Wiley, Chinchester, pp 1–211
Primavera M, Simone O, Fiorentino G, Caldara M (2011) The palaeoenvironmental study of Alimini Piccolo lake enables a reconstruction of Holocene sea-level changes in southeast Italy. The Holocene 21:553–563
Salvador A (1994) International stratigraphic guide: a guide to stratigraphic classification, terminology and procedure. In: The International Union of Geological Sciences and The Geological Society of America (Eds), p 156
Schmiedt G (1971) Antichi porti d’Italia. L’Universo XLVI 2:297–353
Sgarrella F, Moncharmon-Zei M (1993) Benthic foraminifera in the Gulf of Naples (Italy): systematic and autoecology. Bollettino della Società Paleontologica Italiana 32:145–264
Vita-Finzi G (1969) The mediterranean valleys: geological changes in historical times. Cambridge University Press, p 165
Wulf S, Kraml M, Brauer A, Kellerc J, Negendank FW (2004) Tephrochronology of the 100 ka lacustrine sediment record of Lago Grande di Monticchio (southern Italy). Quat Intern 122:7–30
Zanchetta G, Sulpizio R, Giaccio B, Siani G, Paterne M, Wulf S, D’Orazio M (2008) The Y-3 tephra: a stratigraphic marker for the Last Glacial successions of the Central Mediterranean Basin. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 177:145–154
Zuppetta A, Sava A (1992) Pleistocene brittle deformation in the Eboli Conglomerates (Sele plain: Campanian Apennines). Bollettino della Società Geologica Italiana 111:273–281
Aknowledgements
Authors wish to thank the Soprintendenza Archeologica of Avellino-Salerno (Paestum Office), in particular, Dr. Marina Cipriani for having kindly granted the permission for the coring within the Porta Marina archaeological area, and Dr. Alfonso Santoriello of the Salerno University (Beni Culturali Department) for the interpretation of the ceramic materials of the cores.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is an outcome of the FISR project Vulnerability of the Italian coastal area and marine Ecosystem to Climate changes and their role in the Mediterranean carbon cycles (VECTOR), subproject Vulnerability of Coastal environments to climate changes (VULCOST) on Land–sea interaction and costal changes in the Sele River plain, Campania.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amato, V., Aucelli, P.P.C., D’Argenio, B. et al. Holocene environmental evolution of the costal sector in front of the Poseidonia-Paestum archaeological area (Sele plain, southern Italy). Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 23, 45–59 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-011-0161-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-011-0161-1