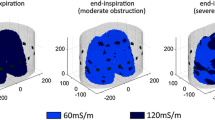
Abstract
Medically, electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a relatively inexpensive, safe, non-invasive and portable technique compared with computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In this paper, EIT_TJU_II system is developed including both the data collection system and image reconstruction algorithm. The testing approach of the system performance, including spatial resolution and sensitivity, is described through brine tank experiments. The images of the thorax physical model verify that the system can reconstruct the interior resistivity distribution. Finally, the lung ventilation functional monitoring in vivo is realized by EIT, and the visualized images indicate that the configuration and performance of EIT_TJU_II system are feasible and EIT is a promising technique in clinical monitoring application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber D C, Brown B H. Information Processing in Medical Imaging: Recent Development in Applied Potential Tomography—APT[M]. Bacharach S L ed. Nijhoff, 1986. 106–121.
Frerichs I. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) in applications related to lung and ventilation: A review of experimental and clinical activities[J]. Physical Measurement, 2000, 21(2): R1–R21.
Holder D S. Electrical Impedance Tomography Methods, History and Applications[M]. Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol and Philadelphia, 2004.
Brown B H, Barber D C, Seagar A D. Applied potential tomography: Possible clinical application[J]. Clin Phys Physiol Meas, 1985, 6: 109–121.
Brown B H. Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT): A review[J]. Med Eng Technol, 2003, 27(3): 97–108.
Barbas C S, de Matos G F, Okamoto V et al. Lung recruitment maneuvers in acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Resir Care Clin N Am, 2003, 9: 401–418.
Hinz J, Hahn G, Neumann P. End-expiratory lung impedance change enables bedside monitoring of end-expiratory lung volume change[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2003, 29: 37–43.
Nebuya S, Noshiro M, Yonemoto A et al. Study of the optimum level of electrode placement for the evaluation of absolute lung resistivity with the Mk3. 5 EIT system[J]. Physical Measurement, 2006, 27: S129–S137.
Barber D C, Brown B H. Applied potential tomography[ J]. Phy E: Sci Instrum, 1984, 17: 723–733.
Fu Feng, Dong Xiuzhen, You Fusheng et al. A dynamic reconstruction algorithm in a real-time electrical impendency tomography imaging system[J]. Beijing Biomedical Engineering, 2003, 22(2): 109–112(in Chinese).
Breckon W R, Pidcock M K. Mathematical aspects of impedance imaging[J]. Clin Phys Physiol Meas, 1987, 8(Suppl A): 77–84.
Vauhkonen M. Electrical Impedance Tomography and Prior Information[D]. Department of Physics, University of Kuopio, Finland, 1997.
Hansen P C. Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve[J]. SIAM Rev, 1992, 34(4): 561–580.
Hansen P C, O’Leary D P. The use of the L-curve in the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems[J]. SIAM J Aci Comput, 1993, 14(6): 1487–1503.
Victorino J A, Borges J B, Okamoto V N et al. Imbalances in regional lung ventilation: A validation study on electrical impedance tomography[J]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 2004, 169(7): 791–800.
Luepschen H, Meier T, Grossherr M et al. Protective ventilation using electrical impedance tomography[J]. Physiol Meas, 2007, 28: S247–S260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.60820106002, No.60532020) and Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (No.08JCYBJC03500).
CHEN Xiaoyan, born in 1973, female, doctorate student.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Wang, H., Zhao, B. et al. Lung ventilation functional monitoring based on electrical impedance tomography. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 15, 7–12 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-009-0002-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-009-0002-9