Abstract
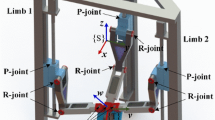
The stiffness of a novel 2(3PUS+S) parallel manipulator with two moving platforms was investigated in this study. In the stiffness evaluation, the two moving platforms of the manipulator were driven through three linear modules and the load force on the drive joint was large. The corresponding parts of the two moving platforms were divided into independent subsystems and were integrated through a stiffness modeling method of a serial system to establish the overall stiffness model of the 2(3PUS+S) parallel manipulator. During modeling, elastic deformations on the joint lever and lead screw were involved, the joint lever was simplified as a supported beam, and the axial and torsional stiffness of the lead screw were considered. Numerical analysis on the established stiffness model was validated, and virtual experiments were conducted. Results indicate that the stiffness performance of the 2(3PUS+S) parallel manipulator changes with the variation of structural parameters and moving platform positions. To ensure the minimum stiffness under the required trajectory, the length of the joint lever and the ratio of the moving platform radius to the base platform should be appropriately reduced. Comparisons between the results from the numerical analysis and virtual experiments verified the accuracy of the established stiffness model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. T. Liu, T. Huang, A. Kecskemethy, D. G. Chetwynd and Q. Li, Force/motion transmissibility analyses of redundantly actuated and overconstrained parallel manipulators, Mechanism and Machine Theory, 109 (2017) 126–138.
X. F. Fang, S. C. Zhang, Q. H. Xu, T. Y. Wang, Y. W. Liu and X. G. Chen, Optimization of a crossbar parallel machine tool based on workspace and dexterity, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 29 (8) (2015) 3297–3307.
J. X. Fu, F. Gao, W. X. Chen, Y. Pan and R. F. Lin, Kinematic accuracy research of a novel six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot with three legs, Mechanism and Machine Theory, 102 (2016) 86–102.
R. Maldonado-Echegoyen, E. Castillo-Castaneda and M. A. Garcia-Murillo, Kinematic and deformation analyses of a translational parallel robot for drilling tasks, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 29 (10) (2015) 4437–4443.
J. S. Dai, C. Gosselin and T. Huang, Stiffness analysis, motion design and reconfiguration study of parallel mechanisms and manipulators, ARCHIVE Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part C Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 230 (3) (2016) 339–340.
S. Abdolshah, D. Zanotto, G. Rosati and S. K. Agrawal, Optimizing stiffness and dexterity of planar adaptive cabledriven parallel robots, Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics-Transactions of the ASME, 9 (3) (2017) 031004.
S. Jin, J. Kim and T. Seo, Optimization of a redundantly actuated 5R symmetrical parallel mechanism based on structural stiffness, Robotica, 33 (9) (2015) 1973–1983.
Y. Lu, Z. H. Dai and N. J. Ye, Stiffness analysis of parallel manipulators with linear limbs by considering inertial wrench of moving links and constrained wrench, Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 46 (2017) 58–67.
P. Xu, B. Li, C. F. Cheung and J. F. Zhang, Stiffness modeling and optimization of a 3-DOF parallel robot in a serialparallel polishing machine, International Journal of Precision Engineering & Manufacturing, 18 (4) (2017) 497–507.
G. Cheng, P. Xu, D. H. Yang and H. G. Liu, Stiffness analysis of a 3CPS parallel manipulator for mirror active adjusting platform in segmented telescope, Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 29 (5) (2013) 302–311.
Y. Jiang, T. M. Li and L. P. Wang, Stiffness modeling of compliant parallel mechanisms and applications in the performance analysis of a decoupled parallel compliant stage, Review of Scientific Instruments, 86 (9) (2015) 095109.
B. Hu and Z. Huang, Kinetostatic model of overconstrained lower mobility parallel manipulators, Nonlinear Dynamics, 86 (1) (2016) 309–322.
H. Wang, L. S. Zhang, G. L. Chen and S. Z. Huang, Parameter optimization of heavy-load parallel manipulator by introducing stiffness distribution evaluation index, Mechanism and Machine Theory, 108 (2017) 244–259.
M. X. Wang, P. F. Wang, Y. M. Song, X. M. Zhao and T. Huang, Stiffness analysis of a 4-DOF hybrid robot, Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 47 (15) (2011) 9–16.
B. Hu, Formulation of unified Jacobian for serial-parallel manipulators, Robotics & Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 30 (5) (2014) 460–467.
Y. Lu, Z. H. Dai, N. J. Ye and P. Wang, Kinematics/statics analysis of a novel serial-parallel robotic arm with hand, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 29 (10) (2015) 4407–4416.
X. L. Shan, G. Cheng and X. Z. Liu, Application of a novel 2(3HUS+S) parallel manipulator for simulation of hip joint motion, Review of Scientific Instruments, 87 (7) (2016) 076101.
A. Rezaei, A. Akbarzadeh and M. Akbarzadeh, An investigation on stiffness of a 3-PSP spatial parallel mechanism with flexible moving platform using invariant form, Mechanism and Machine Theory, 51 (5) (2012) 195–216.
T. Huang, X. Y. Zhao and D. J. Whitehouse, Stiffness estimation of a tripod-based parallel kinematic machine, IEEE Transactions on Robotics & Automation, 18 (1) (2002) 50–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Mingxing Lin
Xianlai Shan received his Dr. Sc. Tech degree from China University of Mining and Technology in 2017. His current research interests include parallel manipulators and control of robots.
Gang Cheng received his M.S. degree in 2003 from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Dr. Sc. Tech degree in 2008 from China University of Mining and Technology. Currently, he serves as a Professor in China University of Mining and Technology. His research interests include mechanism theory and electromechanical equipment reliability.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, X., Cheng, G. Static analysis on a 2(3PUS+S) parallel manipulator with two moving platforms. J Mech Sci Technol 32, 3869–3876 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0739-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0739-y