Abstract
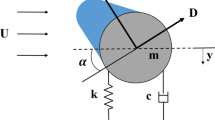
When the power transmission line (PTL) passes through a region of high mountains and heavy snowfall, maintaining the stability of the PTL and avoiding sleet jump and galloping are necessary. In this study, PTL is modeled as the mass-spring-damper system by using the multi-body dynamics analysis program, RecurDyn. The lumped mass model is compared with the finite element model based on deflection. To analyze the dynamic behavior of the PTL under icing and wind conditions, we obtained a damping coefficient for a multibody model from the free vibration test and Rayleigh damping theory. The icing cross-section of the transmission line is assumed to have ellipse and triangle shapes. The aerodynamic coefficients for each cross-section are derived by using the commercial CFD program, ANSYS Fluent. The occurrence of galloping is simulated for each shape according to the attack angle. Results indicate that the dynamic behavior of the PTL and the galloping conditions such as the icing shape, thickness, and attack angle, can be analyzed. Furthermore, the effects of each factor are evaluated. In the elliptical icing section, the effect of icing thickness is high; whereas in the triangular icing section, the wind velocity highly affects galloping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. R. Koo, Y. C. Bae, D. Y. Lee, H. S. Kim, S. M. Son and D. H. Kim, Protection method of ice and snow failure at the power transmission line, The Korea Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering, 2015 (4) (2015) 735–738.
Y. S. Kim, Study on the vibration and countermeasure of the processing transmission line, Hanyang Univ. (2008).
A. E. Davison, Dancing conductors, Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, 49 (4) (1930) 1444–1449.
J. P. Den Hartog, Transmission line vibration due to sleet, Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, 51 (4) (1932) 1074–1076.
H. M. Irvine and T. K. Caughey, The linear theory of free vibrations of a suspended cable, Proceeding of the Royal Society of London Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 341 (1626) (1974) 299–315.
J. H. Lee, Experimental study of beam and plate large deformation, Pusan Univ. (2003).
A. Alipour and F. Zareian, Study Rayleigh damping in structures; Uncertainties and treatments, Proceedings of 14th Word Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Beijing, China (2008).
CIGRE technical brochure, State of the art of conductor galloping, Task Force B2.11.06, 322 (2007).
J. P. Den Hartog, Mechanical vibration, Mcgraw-Hill, USA (1956).
S. S. Rao, Mechanical vibration fifth edition in SI units, PEARSON, USA (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Junhong Park
Jeong-Hyun Sohn is a Professor of Department of Mechanical Design Engineering at Pukyong National University since 2003. His research interests are in multibody system dynamics and coupled analysis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Sohn, J. Multibody dynamics study on galloping of power transmission line. J Mech Sci Technol 32, 3597–3602 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0710-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0710-y