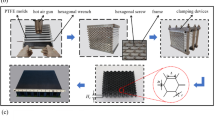
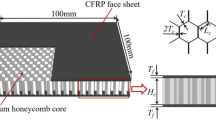
Abstract
Honeycomb sandwich composites are used as significant structural members in advanced engineering applications. Thus, it is critical to determine how they behave under impact loading, in addition to other loads. In this study, low velocity impact loading behaviors of honeycomb sandwich composites were experimentally investigated. Almost all of the design parameters of honeycomb sandwich composites were investigated. The results indicated that the core thickness of honeycomb had no effect on the strength of the composite, and the parameter influencing the impact behavior of the specimen the most was the face sheet thickness. When the face sheet thickness of the specimen was increased, the most apparent strength increase was observed in the models using carbon fiber-reinforced composite face sheets. For all face sheet types subject to impact energy of 10 Joules, the upper face sheets of 0.5 mm-thick specimens were perforated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Belouettar, A. Abbadi, Z. Azari, R. Belouettar and P. Freres, Experimental investigation of static and fatigue behaviour of composites honeycomb materials using four point bending tests, Compos. Struct., 87 (3) (2009) 265–273.
S. H. Yoon, Y. W. Kwon and L. A. Clawson, Experimental investigation on low energy impact behavior of foam cored sandwich composites, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 11 (2) (1997) 136–142.
Q. He, W. Tang, J. Zhang and X. Wang, Effects of concentrated rigid inclusions defects on the in-plane impact behavior of hexagonal honeycombs, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 31 (10) (2017) 4691–4701.
H. Yin, G. Wen, S. Hou and Q. Qing, Multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of functionally lateral graded foamfilled tubes, Mater. Des., 44 (2013) 414–428.
E. J. Herup and A. N. Palazotto, Low-velocity impact damage initiation in graphite/epoxy/Nomex honeycombsandwich plates, Compos. Sci. Technol., 57 (12) (1998) 1581–1598.
C. Y. Tan and H. M. Akil, Impact response of fiber metal laminate sandwich composite structure with polypropylene honeycomb core, Compos Part B-Eng., 43 (3) (2012) 1433–1438.
A. Akatay, M. Ö. Bora, O. Çoban, S. Fidan and V. Tuna, The influence of low velocity repeated impacts on residual compressive properties of honeycomb sandwich structures, Compos Struct., 125 (2015) 425–433.
P. M. Schubel, J. J. Luo and I. M. Daniel, Impact and post impact behavior of composite sandwich panels, Compos Part A-Appl S, 38 (3) (2007) 1051–1057.
S. A. Galehdari, M. Kadkhodayan and S. Hadidi-Moud, Low velocity impact and quasi-static in-plane loading on a graded honeycomb structure; experimental, analytical and numerical study, Aerosp. Sci. Technol., 47 (2015) 425–433.
B. O. Baba, Curved sandwich composites with layer-wise graded cores under impact loads, Compos. Struct., 159 (2017) 1–11.
Y. M. Jen, C. W. Ko and H. B. Lin, Effect of the amount of adhesive on the bending fatigue strength of adhesively bonded aluminum honeycomb sandwich beams, Int. J. Fatigue, 31 (3) (2009) 455–462.
R. Gunes and K. Arslan, Development of numerical realis-tic model for predicting low-velocity impact response of aluminium honeycomb sandwich structures, J. Sandw. Struct. Mater., 18 (1) (2016) 95–112.
R. S. Sharma, V. P. Raghupathy and G. M. Priyamvada, Investigation of low velocity impact response of aluminium honeycomb sandwich panels, APRN J. Eng. Appl. Sci., 6 (2011) 7–14.
J. K. Paik, A. K. Thayamballi and G. S. Kim, The strength characteristics of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels, Thin Wall Struct., 35 (3) (1999) 205–231.
O. Mohammadiha and H. Beheshti, Optimization of functionally graded foam filled conical tubes under axial impact loading, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 28 (5) (2014) 1741–1752.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Editor Chongdu Cho
Tolga Topkaya graduated from Department of Mechanical Engineering at Fırat University at 2007. He gained his Ph.D. degree at the same university at 2017. He is working as Research Assistant at University of Batman, Department of Mechanical Engineering since 2010. His main research fields are composites, biomechanics and adhesion and adhesives.
Murat Yavuz Solmaz received his Ph.D. degree in Mechanical Enginering from Fırat University, Turkey, in 2008. He is currently an Associate Professor at Faculty of Engineering, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Firat Univeristy in Turkey. His research interests include composite materials, sandwich composites and adhesive joints.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topkaya, T., Solmaz, M.Y. Investigation of low velocity impact behaviors of honeycomb sandwich composites. J Mech Sci Technol 32, 3161–3167 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0619-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0619-5