Abstract
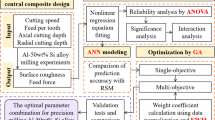
Electron beam melting (EBM) has been found to be a promising technology for producing complex shaped parts from gamma titanium aluminide alloys (γ-TiAl). The parts produced by this process are projected to have dimensions very close to the desired final shapes. However, the surface roughness of the parts produced by EBM is excessively rough. In many applications, it is necessary to improve the quality of manufactured parts using a convenient post process. This paper determines process parameters of end milling when it is used as a post process for the parts produced by EBM. Design of experiments has been used to study the effect of the selected input parameters of end milling (spindle speed, feed rate, depth of cut and coolant type) on the surface roughness of γ-TiAl parts. Response surface methodology is used to develop a predictive model for surface roughness. Effects of the selected milling process are investigated. This paper also optimizes the selected process parameters to minimize the value of the obtained surface roughness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
www.wohlersassociates.com.
G. Sauthoff, Intermetallics, Weinheim; New York (1995).
C. M. Austin, Current status of gamma Ti aluminides for aerospace applications, Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 4 (1999) 239–242.
E. A. Loria, Gamma titanium aluminides as prospective structural materials, Intermetallics, 8 (2000) 133–1345.
K. Kothari, R. Radhakrishnan, N. M. Wereley and T. S. Sudarshan, Microstructure and mechanical properties of consolidated gamma titanium aluminides, Powder Metallurgy, 50 (1) (2007) 21–7.
D. Hu, X. Wu and M. H. Loretto, Advances in optimisation of mechanical properties in cast TiAl alloys, Intermetallics, 13 (91) (2005) 4–9.
D. K. Aspinwal, R. C. Dewes and A. L. Mantle, The machining of y-TiAl intermetallic alloys, CIRP Annals -Manufacturing Technology, 54 (1) (2005) 99–104.
www.arcam.com.
K. Kothari, R. Radhakrishnan and N. M. Wereley, Advances in gamma titanium aluminides and their manufacturing techniques, Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 55 (2012) 1–16.
F. Klocke, L. Settineri, D. Lung, P. C. Priarone and M. Arft, High performance cutting of gamma titanium aluminides: Influence of lubricoolant strategy on tool wear and surface integrity, Wear, 302 (2013) 1136–1144.
P. C. Priarone, S. Rizzuti, L. Settineri and G. Vergnano, Effects of cutting angle, edge preparation, and nanostructured coating on milling performance of a gamma titanium aluminide, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 212 (2012) 2619–2628.
P. C. Priarone, S. Rizzuti, S. Ruffa and L. Settineri, Drilling experiments on a gamma titanium aluminide obtained via electron beam melting, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 69 (2013) 483–490.
A. R. C. Sharman, D. K. Aspinwall, R. C. Dewes and P. Bowen, Workpiece surface integrity considerations when finish turning gamma titanium aluminide, Wear, 249 (2001) 473–481.
S. A. Bentley, A. L. Mantle and D. K. Aspinwall, The effect of machining on the fatigue strength of a gamma titanium aluminide intertmetallic alloy, Intermetallics, 7 (1999) 967–969.
A. Beranoagirre and L. N. López de Lacalle, Topography prediction on Milling of emerging aeronautical Ti alloys, Physics Procedia, 22 (2011) 136–143.
A. Beranoagirre and L. N. López de Lacalle, Grinding of gamma TiAl intermetallic alloys, Procedia Engineering, 63 (2013) 489–498.
R. Hood, D. K. Aspinwall, S. L. Soo, A. L. Mantle and D. Novovic, Workpiece surface integrity when slot milling g-TiAl intermetallic alloy, CIRP Annals -Manufacturing Technology, 63 (2014) 53–56.
L. Zhu and Y. Chen, Study on the cutting performance and machinability of gamma titanium aluminide, Journal of Applied Sciences, 13 (18) (2013) 3774–3777.
R. Biswas, A. S. Kuar and S. Mitr, Multi-objective optimization of hole characteristics during pulsed Nd:YAG laser microdrilling of gamma-titanium aluminide alloy sheet, Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 60 (2014) 1–11.
B. Jabbaripoura, M. H. Sadeghia, M. R. Shabgardb and H. Faraji, Investigating surface roughness, material removal rate and corrosion resistance in PMEDM of y-TiAl intermetallics, Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 15 (2013) 56–68.
S. Sarkar, S. Mitra and B. Bhattacharyya, Parametric optimisation of wire electrical discharge machining of γ titanium aluminide alloy through an artificial neural network model, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 27 (2006) 501–508.
S. Mitra, G. Paul and S. S. Nagahanumaiah, Experimental study on influence of process variables on crater dimensions in micro-EDM of γ -Titanium Aluminide, AMPT (2010).
D. Clifton, A. R. Mount, D. J. Jardine and R. Roth, Electrochemical machining of gamma titanium aluminide intermetallics, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 108 (2001) 338–348.
T. Mihai, B. Alexandra, V. Aurelian, I. Nicolae, P. Alexandru and S. Alexandru, Study on processing of titanium aluminide alloy using electrical discharge machining, Applied Mechanics and Materials, 657 (2014) 311–315.
S. Biamino, A. Penna, U. Ackelid, S. Sabbadini, O. Tassa, P. Fino, M. Pavese, P. Gennaro and C. Badini, Electron beam melting of Tie48Ale2Cre2Nb alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties investigation, Intermetallics, 19 (2011) 776–781.
J. Schwerdtfeger and C. Körner, Selective electron beam melting of Tie48Ale2Nbe2Cr: Microstructure and aluminium loss, Intermetallics, 49 (2014) 29–35.
L. E. Murr, S. M. Gaytan, A. Ceylan, E. Martinez, J. L. Martinez, D. H. Hernandez, B. I. Machado, D. A. Ramirez, F. Medina, S. Collins and R. B. Wicker, Characterization of titanium aluminide alloy components fabricated by additive manufacturing using electron beam melting, Acta Materialia, 58 (2010) 1887–1894.
W. Ge, C. Guo and F. Lin, Effect of process parameters on microstructure of TiAl alloy produced by electron beam selective melting, Procedia Engineering, 81 (2014) 1192–1197.
M. Terner, S. Biamino, P. Epicoco, A. Penna, O. Hedin, S. Sabbadini, P. Fino, M. Pavese, U. Ackelid, P. Gennaro, F. Pelissero and C. Badini, Electron beam melting of high niobium containing TiAl alloy: Feasibility investigation, Steel Research Int., 83 (2012) 10.
A. R. Rastkar and B. Shokri, Surface transformation of Ti-45Al-2Nb-2Mn-1B titanium aluminide by electron beam melting, Surface & Coatings Technology, 204 (2010) 1817–1822.
P. C. Priarone, S. Ruffa, J. S. Bedolla and L. Settineri, A DoE approach to hole quality evaluation in drilling of an electron beam melted titanium aluminide, Procedia CIRP, 8 (2013) 481–486.
P. C. Priarone, S. Rizzuti, G. Rotella and L. Settineri, Tool wear and surface quality in milling of a gamma-TiAl intermetallic, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 61 (2012) 25–33.
http://www.arcam.com/wp-content/uploads/arcam-a2x.pdf.
http://www.sandvik.coromant.com/en-gb/pages/default.aspx.
A. M. A. Al-Ahmari, Prediction and optimisation models for turning operations, International Journal of Production Research, 46 (2008) 4061–4081.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abdulrahman Al-Ahmari is a dean of advanced manufacturing institute and professor of Industrial Engineering at King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. He received a Ph.D. in Manufacturing Systems Engineering from the University of Sheffield in 1998. Professor Al-Ahmari has published papers in leading journals of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering. He led a number of funded projects from different organizations in Saudi Arabia. His research interests are advanced manufacturing technologies, Petri nets, analysis and design of manufacturing systems; Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM); optimization of manufacturing operations; FMS and cellular manufacturing systems and applications of DSS in manufacturing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Ahmari, A., Ashfaq, M., Alfaify, A. et al. Predicting surface quality of γ-TiAl produced by additive manufacturing process using response surface method. J Mech Sci Technol 30, 345–352 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-1239-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-1239-y