Abstract
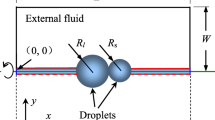
We studied the coalescence of two stationary equal-sized droplets in static vapor using a lattice Boltzmann approach. The non-ideal behavior of one-component, two-phase flow is coupled with BGK lattice Boltzmann by defining a suitable free energy function, which produces the correct equilibrium conditions of the flow. The accuracy of developed model is confirmed by calculating droplet surface tension for different conditions and comparing that with theoretical results. Finally, the coalescence process of two equal-sized drops is modeled and effective parameters on critical gap of coalescence are investigated. The results show that for two at-rest and equal-sized drops in a static flow, the critical gap of coalescence only depends on thickness of the interface, and other parameters such as droplet radius, density ratio and surface tension do not have influences on that directly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. R. Stover, C. W. Tobias and M. M. Denn, Bubble coalescence dynamics, AIChE Journal, 43 (1997) 2385–2392.
E. W. Egan and C. W. Tobias, Measurement of interfacial re-equilibration during hydrogen bubble coalescence, J. Electrochem. Soc., 141 (1994) 1118–1126.
O. A. Basaran, Nonlinear oscillations of viscous liquid drops, J. Fluid Mech., 241 (1992) 169–198.
B. K. Chi and L. G. Leal, A theoretical study of the motion of a viscous drop towards a fluid interface at low Reynolds number, J. Fluid Mech., 201 (1989) 123–146.
T. O. Oolman and H. W. Blanch, Bubble coalescence in stagnant Liquids, Chem. Eng. Commun., 43 (1986) 237–261.
S. Srivastava, P. Perlekar, L. Biferale, M. Sbragaglia and F. Toschi, Study of fluid interfaces and moving contact lines using the lattice Boltzmann method, Communications in Computational Physics, 13 (3) (2013) 725–740.
L. Biferale, P. Perlekar, M. Sbragaglia and F. Toschi, Convection in multiphase fluid flows using lattice Boltzmann methods, Physical Review Letters, 108 (10) (2012) 104502.
A. J. Briant, A. J. Wagner and J. M. Yeomans, Lattice Boltzmann simulations of contact line motion, I. Liquid-gas systems. Phys. Rev. E., 69 (2004) 031602.
M. R. Swift, E. Orlandini, W. R. Osborn and J. M. Yeomans, Lattice Boltzmann simulations of liquid-gas and binary fluid systems, Phys. Rev. E., 54 (1996) 5041–5052.
X. Shan and H. Chen, Simulation of nonideal gases and liquid-gas phase transitions by the lattice Boltzmann equation, Phys. Rev. E., 49 (1994) 2941–2948.
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz, Statistical physics, Pergamon Press (1958).
D. Jamet, O. Lebaigue, N. Coutris and J. M. Delhaye, The second gradient method for the direct numerical simulation of liquid-vapor flows with phase change, J. Comput Phys., 169 (2001) 624–651.
R. Evans, The nature of the liquid-vapour interface and other topics in the statistical mechanics of non — uniform, classical fluids, Adv. Phys., 28 (1979) 143–200.
S. Succi, The Lattice Boltzmann equation for Fluid dynamics and beyond, Oxford University Press (2001).
R. Benzi, S. Succi and M. Vergassola, The lattice Boltzmann equation: theory and applications, Physics Reports, 222 (1992) 145–197.
D. J. Holdych, D. Rovas, J. G. Georgiadis and R. O. Buckius, An improved hydrodynamics formulation for multiphase flow lattice-Boltzmann models, Int. J. Mod. Phys., C 9 (1998) 1393–1404.
A. Dupuis and J. M. Yeomans, Modeling droplets on superhydrophobic surfaces: Equilibrium states and transitions, Langmuir, 21 (2005) 2624–2629.
S. Hou, Q. Zou, S. Chen, G. Doolen and A. C. Cogley, Simulation of cavity flow by the Lattice Boltzmann method, J. Comput. Phys., 118 (1995) 329–347.
V. V. Khatavkar, P. D. Anderson and H. E. M. Meijer, On scaling of diffuse-interface models, Chemical Engineering Science, 61 (2006) 2364–2378.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Gihun Son
Ehsan Amiri Rad he is an assistant professor of Mechanical engineering at Hakim Sabzevari University. He received the B.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering from Iran University of Science and Technology in 2005 and M.Sc. in Energy Conversion from Ferdowsi University of Mashhad-Iran in 2007. His Ph.D. is from Ferdowsi University of Mashhad-Iran in 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rad, E.A. Coalescence of two at-rest equal-sized drops in static vapor of the same material: A lattice Boltzmann approach. J Mech Sci Technol 28, 3597–3603 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0821-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0821-z