Abstract
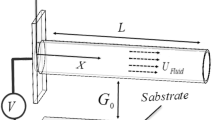
This paper deals with investigation of fluid flow on static and dynamic behaviors of carbon nanotubes under electrostatic actuation. The effects of various fluid parameters including fluid viscosity, velocity, pressure and mass ratio on the deflection and pull-in behaviors of the cantilever and doubly clamped carbon nanotubes are studied. Furthermore, the effects of temperature variation on the static and dynamic pull-in voltages of the doubly clamped carbon nanotubes are reported. The results reveal that altering the fluid parameters significantly changes the mechanical and pull-in behaviors. Hence, the proposed system can be applied properly as a nano fluidic sensor to sense the various parameters of the fluid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. He, Nanoscale flow: reliable, efficient, and promising, Thermal Science, 16 (2012) 7–8.
R. X. Chen, F. J. Liu, J. H. He and J. Fan, Silk Cocoon: “Emperor’s new clothes” for pupa: fractal nanohydrodynamical approach, Journal of Nano Research, 22 (2013) 65–70.
M. Majumder, N. Chopra, R. Andrews and B. J. Hinds, Nanoscale hydrodynamics: Enhanced flow in carbon nanotubes, Nature, 438 (2005) 44–44.
G. Hummer, Water, proton, and ion transport: from nanotubes to proteins, Molecular Physics, 105 (2007) 201–207.
M. Whitby and N. Quirke, Fluid flow in carbon nanotubes and nanopipes, Nature Nanotechnology, 2 (2007) 87–94.
L. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Ma and M. Yang, Molecular dynamics simulation of effect of liquid layering around the nanoparticle on the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids, Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 12 (2010) 811–821.
J. Lv, W. Cui, M. Bai and X. Li, Molecular dynamics simulation on flow behavior of nanofluids between flat plates under shear flow condition, Microfluidics and nanofluidics, 10 (2011) 475–480.
A. G. Arani, M. R. Bagheri, R. Kolahchi and Z. K. Maraghi, Nonlinear vibration and instability of fluid-conveying DWBNNT embedded in a visco-Pasternak medium using modified couple stress theory, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 27 (2013) 2645–2658.
H. R. Ali-Akbari, R. D. Firouz-Abadi, H. Haddadpour and M. A. Noorian, Shell-like instability of large diameter single-walled carbon nanotubes conveying fluid, Journal of mechanical Science and Technology, 26 (2012) 3389–3397.
M. Han, Thermally-driven nanoscale pump by molecular dynamics simulation, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 22 (2008) 157–165.
A. G. Arani, M. Shokravi, S. Amir and M. R. Mozdianfard, Nonlocal electro-thermal transverse vibration of embedded fluid-conveying DWBNNTs, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 26 (2012) 1455–1462.
R. D. Firouz-Abadi, M. M. Fotouhi, M. R. Permoon and H. Haddadpour, Natural frequencies and buckling of pressurized nanotubes using shear deformable nonlocal shell model, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 26 (2012) 563–573.
T. K. Lim and S. H. Rhi, Experimental study on nanofludic heat pipe hot chuck plate in semiconductor wafer baking process, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 24 (2010) 1501–1509.
J. Yoon, C. Q. Ru and A. Mioduchowski, Flow-induced flutter instability of cantilever carbon nanotubes, International Journal of Solids and Structures, 43 (2006) 3337–3349.
L. Wang and Q. Ni, On vibration and instability of carbon nanotubes conveying fluid, Computational Materials Science, 43 (2008) 399–402.
L. Wang and Q. Ni, A reappraisal of the computational modelling of carbon nanotubes conveying viscous fluid, Mechanics Research Communications, 36 (2009) 833–837.
S. D. Solares, M. Blanco and W. A. Goddard, Design of a nanomechanical fluid control valve based on functionalized silicon cantilevers: coupling molecular mechanics with classical engineering design, Nanotechnology, 15 (2004) 1405–1415.
M. Grujicic, G. Cao and W. N. Roy, Suitability of boron-nitride single-walled nanotubes as fluid-flow conduits in nano-valve applications, Applied Surface Science, 246 (2005) 149–158.
H. Y. Chen, Z. F. Liu, X. G. Gong and D. Y. Sun, Design of a one-way nanovalve based on carbon nanotube junction and C60, Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 10 (2011) 927–933.
S. Rinaldi, S. Prabhakar, S. Vengallatore and M. P. Païdoussis, Dynamics of microscale pipes containing internal fluid flow: damping, frequency shift, and stability, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 329 (2010) 1081–1088.
Y. D. Kuang, X. Q. He, C. Y. Chen and G. Q. Li, Analysis of nonlinear vibrations of double-walled carbon nanotubes conveying fluid, Computational Materials Science, 45 (2009) 875–880.
E. Ghavanloo and S. A. Fazelzadeh, Flow-thermoelastic vibration and instability analysis of viscoelastic carbon nanotubes embedded in viscous fluid, Physica E: Lowdimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 44 (2011) 17–24.
H. L. Lee and W. J. Chang, Vibration analysis of a viscousfluid-conveying single-walled carbon nanotube embedded in an elastic medium, Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 41 (2009) 529–532.
L. Wang, Q. Ni, M. Li and Q. Qian, The thermal effect on vibration and instability of carbon nanotubes conveying fluid, Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 40 (2008) 3179–3182.
M. Dequesnes, S. V. Rotkin and N. R. Aluru, Calculation of pull-in voltages for carbon-nanotube-based nanoelectromechanical switches, Nanotechnology, 13 (2002) 120–126.
G. Rezazadeh, A. Tahmasebi and M. Zubstov, Application of piezoelectric layers in electrostatic MEM actuators: controlling of pull-in voltage, Microsystem technologies, 12 (2006) 1163–1170.
M. I. Younis and A. H. Nayfeh, A study of the nonlinear response of a resonant microbeam to an electric actuation, Nonlinear Dynamics, 31 (2003) 91–117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Jaewon Chung
Mir Masoud Seyyed Fakhrabadi received the B.S. and M.S. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Tabriz, Iran, in 2007 and 2009, respectively. Also, he received his Ph.D. in Nanomechnics Engineering from University of Tehran, Iran in 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fakhrabadi, M.M.S., Rastgoo, A. & Ahmadian, M.T. Fluid-solid interaction in electrostatically actuated carbon nanotubes. J Mech Sci Technol 28, 1431–1439 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0130-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0130-6