Abstract
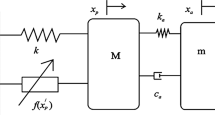
This study proposes a semi-active on-off damping controller that is a mix of three conventional ground-hook controllers for semi-active tuned mass damper systems. Three conventional ground-hook controllers are shown to be effective only in a certain frequency range. By taking advantage of all three ground-hook controllers, the mixed controller shows its better performance. More-over, we found an analytical solution of the harmonic vibration of the semi-active controlled system. The accuracy of the analytical solution and the superior performance of the proposed controller are verified by the numerical simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. T. Soong and G. F. Dargush, Passive energy dissipation systems in structural engineering, Wiley, Ltd. (UK) (1997).
G. B. Warburton, Optimal absorber parameters for various combinations of response and excitation parameters, Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 10 (1982) 381–401.
J. P. Den Hartog, Mechanical vibrations, 4th ed., McGraw-Hill, New York (1956).
S. Krenk, Frequency analysis of the tuned mass damper, Journal of Applied Mechanics, 72 (2005) 936–942.
F. Casciati and F. Marazzi, Technology of semi-active devices and applications in vibration mitigation, Wiley, UK (2006).
J. H. Koo, M. Ahmadian, M. Setareh and T. M. Murray, In search of suitable control methods for semi-active tuned vibration absorbers, Journal of Vibration and Control, 10(2) (2004) 163–174.
C. C. Lin, G. L. Lin and J. F. Wang, Protection of seismic structures using semi-active friction TMD, Earthquake Engineering And Structural Dynamics, 39 (2010) 635–659.
M. H. Chey, J. G Chase, J. B. Mander and A. J. Carr, Semiactive tuned mass damper building systems: Design, Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 39 (2010) 119–139.
J. Kang, H. S Kim and D. G. Lee, Mitigation of wind response of a tall building using semi-active tuned mass dampers, The Structural Design Of Tall And Special Buildings, 20 (2011) 552–565.
H. X. Deng and X. L. Gong, Adaptive tuned vibration absorber based on magnetorheological elastomer, Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 18 (2007) 1205–1210.
M. Setareh, J. K. Ritchey, T. M. Murray, J. H. Koo and M. Ahmadian, Semiactive tuned mass damper for floor vibration control, Journal of Structural Engineering, 133(2) (2007).
O. V. Gendelman, Targeted energy transfer in systems with external and self-excitation, Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 225 (2011) 2007–2043.
S. H. Zareh, A. Sarrafan, A. A. A. Khayyat and A. Zabihollah, Intelligent semi-active vibration control of eleven degrees of freedom suspension system using magnetorheological dampers, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 26(2) (2012) 323–334.
S. H. Zareh, M. Abbasi, H. Mahdavi and K. G. Osgouie, Semi-active vibration control of an eleven degrees af freedom suspension system using neuro inverse model of magnetorheological dampers, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 26(8) (2012) 2459–2467.
Y. J. Shin, W. H. You, H. M. Hur and J. H. Park, Semiactive control to reduce carbody vibration of railway vehicle by using scaled roller rig, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 26(11) (2012) 3423–3431.
J. J. L. Santos, R. M. Menendez and R. A. R Mendoza, Control of an automotive semi-active suspension, Mathematical Problems in Engineering, Article ID 218106 (2012) 21.
S. M. Savaresi, C. Poussot-Vassal, C. Spelta, O. Sename and L. Dugard, Semi-active suspension control, Design for Vehicles, Butterworth-Heinemann (UK) (2010).
S. Savaresi and C. Spelta, Mixed sky-hook and ADD: Approaching the filtering limits of a semi-active suspension, Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, 129(4) (2007) 382–392.
L. D. Viet, Semi-active on-off damping control of a dynamic vibration absorber using coriolis force, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 331 (2012) 3429–3436.
H. Kwakernaak and R. Sivan, Linear optimal control systems, New York, Wiley (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Ohseop Song
La Duc Viet received his B.S. and Ph.D. in Mechanics from Vietnam National University, Hanoi, Vietnam, in 2002 and 2009, respectively. He is currently a researcher at the Institute of Mechanics, Hanoi, Vietnam. His research interests include vibration control, structural dynamics, structural control, and stochastic mechanics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viet, L.D., Nghi, N.B., Hieu, N.N. et al. On a combination of ground-hook controllers for semi-active tuned mass dampers. J Mech Sci Technol 28, 2059–2064 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0109-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0109-3