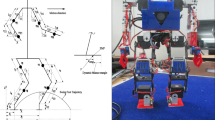
Abstract
Biped locomotion has attracted much attention in recent years. The most successful implemented methods in this area are based on two approaches, central pattern generator (CPG) and zero moment point (ZMP). Unfortunately, neither of these concepts can solely solve the movement challenge completely. In this study, we introduce a hybrid controller to combine the advantages of these methods. The proposed controller is based on two major approaches, CPG and ZMP. This hybrid controller is composed of a trajectory control system and a trajectory generator system. The trajectory control system applied to keep the robot stable uses ZMP as a real time control feedback. The trajectory generator system, which is composed of nonlinear oscillators, generates stable motions. The parameters of CPG are tuned by a new two-stage approach using differential evolution (DE) and bees algorithm (BA). Furthermore, performance of the proposed controller is verified using the robotic simulation software Webots.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. Huang, K. Yokoi, S. Kajita, K. Kaneko, H. Arai and N. Koyachi, Planning walking patterns for a biped robot, IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 17(3) (2001) 280–289.
K. Nagasaka, H. Inoue and M. Inaba, Dynamic walking pattern generation for a humanoid robot based on optimal gradient method, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Tokyo, Japan (1999) 908–913.
M. Vukobratovic and B. Borovac, Zero-moment point — thirty five years of its life, International Journal of Humanoid Robotics, 1(1) (2004) 157–173.
K. Nagasaka, Y. Kuroki, S. Suzuki, Y. Itoh and J. Yamaguchi, Integrated motion control for walking, jumping and running on a small bipedal entertainment robot, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan (2004) 3189–3914.
Y. Sakagami, R. Watanabe, C. Aoyama, S. Matsunaga, N. Higaki and K. Fujimura, The intelligent ASIMO: System overview and integration, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Saitama, Japan (2002) 2478–2483.
S. Kajita, F. Kanehiro, K. Kaneko, K. Yokoi and H. Hirukawa, The 3D linear inverted pendulum mode: A simple modeling for a biped walking pattern generation, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Hawaii, USA (2001) 239–246.
S. Kajita, F. Kanehiro, K. Kaneko, K. Fujiwara, K. Harada, K. Yokoi and H. Hirukawa, Biped walking pattern generation by using preview control of zero-moment point, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, Taipei, Taiwan (2003) 1620–1626.
K. Erbatur and O. Kurt, Natural ZMP trajectories for biped robot reference generation, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 56(3) (2009) 835–845.
T. Sato, S. Sakaino, E. Ohashi and K. Ohnishi, Walking trajectory planning on stairs using virtual slope for biped robots, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 58(4) (2011) 1385–1396.
A. J. Ijspeert, Biologically inspired artificial intelligence, Class Lecture, EPFL, Switzerland (2003).
S. Mojon, Using nonlinear oscillators to control the locomotion of a simulated biped robot, Master’s thesis, EPFL, Switzerland (2004).
W. QiDi, L. ChengJu, Z. JiaQi and C. QiJun, Survey of locomotion control of legged robots inspired by biological concept, Science in China Series F: Information Sciences, 52(10) (2009) 1715–1729.
S. Mondal, A. Nandy, P. Chakraborty and G. C. Nandi, A central pattern generator based nonlinear controller to simulate biped locomotion with a stable human gait oscillation, International Journal of Robotics and Automation, 2(2) (2011) 93–106.
K. Wolff, J. Pettersson, A. Heralic and M. Wahde, Structural evolution of central pattern generators for bipedal walking in 3D simulation, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Goteborg, Sweden (2006) 227–234.
J. J. Kim, J. W. Lee and J. J. Lee, Central pattern generator parameter search for a biped walking robot using nonparametric estimation based particle swarm optimization, International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 7(3) (2009) 447–457.
G. Taga, Y. Yamaguchi and H. Shimizu, Self-organized control of bipedal locomotion by neural oscillators in unpredictable environment, Biological Cybernetics, 65 (1991) 147–159.
L. Righetti and A. J. Ijspeert, Programmable central pattern generators an application to biped locomotion control, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, Florida, USA (2006) 1585–1590.
G. Endo, J. Nakanishi, J. Morimoto and G. Cheng, Experimental studies of a neural oscillator for biped locomotion with QRIO, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain (2005) 598–604.
K. Matsuoka, Mechanisms of frequency and pattern control in the neural rhythm generators, Journal of Biological Cybernetics, 56(5) (1987) 345–353.
NAO Humanoid Robot. Aldebaran Robotics, Paris, France, http://www.aldebaran-robotics.com.
Webots, C.L.: Commercial mobile robot simulation software. http://www.cyberbotics.com.
D. Orin, Interactive control of a six-legged vehicle with optimization of both stability and energy, Ph.D. thesis, The Ohio State University, USA (1976).
A. Goswami, Postural stability of biped robots and the foot-rotation indicator point, International Journal of Robotics Research, 18(6) (1999) 523–533.
B. Siciliano and O. Khatib, Springer handbook of robotics, Springer-Verlag, New York, USA (2008).
S. L. Hooper, Central pattern generators, John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA (2001).
A. D. Kuo, The relative roles of feedforward and feedback in the control of rhythmic movements, Motor Control, 6(2) (2002) 129–145.
J. shan, C. J. Shi and C. J. Pin, Design of central pattern generator for humanoid robot walking based on multiobjective GA, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Takamatsu, Japan (2000) 1930–1935.
H. Inada and K. Ishii, Behavior generation of bipedal robot using central pattern generator (CPG) (1st report: CPG parameter searching method by genetic algorithm), Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Las Vegas, USA (2003) 2179–2184.
S. Ok, K. Miyashita and K. Hase, Evolving bipedal locomotion with genetic programming-a preliminary report, Proc. IEEE Int. Cong. on Evolutionary Computation, Seoul, Korea (2001) 1025–1032.
Y. Nakamura, T. Mori, M. Sato and S. Ishii, Reinforement learning for a biped robot based on a CPG-actor-critic method, Neural Networks, 20(6) (2007) 723–735.
R. Storn and K. Price, Differential evolution — a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces, Journal of Global Optimization, 11(4) (1997) 341–359.
D. T. Pham, A. Ghanbarzadeh, E. Koc, S. Otri, S. Rahim and M. Zaidi, The bees algorithm — A novel tool for complex optimisation problems, Proc. of Int. Conf. on Intelligent Production Machines and Systems, Oxford, UK (2006) 454–459.
G. L. Liu, M. K. Habib, K. Watanabe and K. Izumi, Central pattern generators based on Matsuoka oscillators for the locomotion of biped robots, Artificial Life and Robotics, 12(1) (2008) 264–269.
Open dynamic enginedocumentation, http://www.ode.org.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Jong Hyeon Park
Ali Zamani received his B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from K. N. ToosiUniversity of Technology in 2008 and 2011, respectively. His research interests are in the areas of dynamics modeling, gait planning, and control of walking robots.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massah B, A., Zamani, A., Salehinia, Y. et al. A hybrid controller based on CPG and ZMP for biped locomotion. J Mech Sci Technol 27, 3473–3486 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-013-0871-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-013-0871-7