Abstract
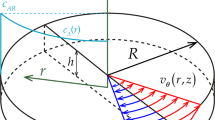
In order to investigate turbulent drag reduction (DR), a rotating disk apparatus (RDA) generating an “external flow” was designed and then polymer-induced DR efficiency of water-soluble polymers both poly (ethylene oxide) (PEO) and poly (acryl amide) (PAAM) were examined as a function of either polymer concentration or temperature. The need for a sensitive measuring system at high Reynolds numbers has stimulated the development of a high-precision computer-aided system, which is able to measure the difference between the torques for a Newtonian fluid and a dilute polymeric solution with drag reducers very accurately. Their mechanical degradation behavior in the RDA as a function of time in a turbulent flow was also analyzed using both a simple exponential decay function and a fractional exponential decay equation. The fractional exponential decay equation was found to fit the experimental data better than the simple first-order degradation exponential decay function in the case of PEO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Amarouchene and H. Kellay, Polymers in 2D turbulence: Suppression of large scale fluctuations, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89(10) (2002) 104502.
P. Tong, W. I. Goldburg, C. K. Chan and A. Sirivat, Turbulent transition by photon-correlation spectroscopy, Phys. Rev. A 37(6) (1988) 2125–2133.
A. Nakano and Y. Minoura, Effects of solvent and concentration on scission of polymers with high-speed stirring, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 19(8) (1975) 2119–2130.
A. Nakano and Y. Minoura, Relationship between hydrodynamic volume and scission of polymer-chains by high-speed stirring in several solvents, Macromolecules, 8(5) (1975) 677–680.
J. F. S. Yu; J. L. Zakin and G. K. Patterson, Mechanical degradation of high molecular-weight polymers in dilute-solution, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 23(8) (1979) 2493–2512.
E. Ruckenst, Mechanism of drag reduction, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 17(10) (1973) 3239–3240.
R. Armstrong and M. S. Jhon, A self-consistent theoretical approach to polymer induced turbulent drag reduction, Chem. Eng. Commun., 30 (1984) 99–112.
E. D. Burger, L. G. Chorn and T. K. Perkins, Studies of drag reduction conducted over a broad range of pipeline conditions when flowing Prudhoe Bay crude-oil, J. Rheol., 24(5) (1980) 603–626.
H. L. Greene, R. F. Mostardi and R. F. Nokes, Effects of drag reducing polymers on initiation of atherosclerosis, Polym. Eng. Sci., 20(7) (1980) 499–504.
C. A. Kim, D. S. Jo, H. J. Choi, C. B. Kim and M. S. Jhon, A high-precision rotating disk apparatus for drag reduction characterization, Polym. Test., 20(1) (2001) 43–48.
P. Tong, W. I. Goldburg, J. S. Huang and T. A. Witten, Anisotropy in turbulent drag reduction, Phys. Rev. Lett., 65(22) (1990) 2780–2783.
H. J. Choi, S. T. Lim, P. Y. Lai and C. K. Chan, Turbulent drag reduction and degradation of DNA, Phys. Rev. Lett., 89(8) (2002) 088302.
S. T. Lim, H. J. Choi, S. Y. Lee, J. S. So and C. K. Chan, Gamma-DNA induced turbulent drag reduction and its characteristics, Macromolecules, 36(14) (2003) 5348–5354.
S. T. Lim, S. J. Park, C. K. Chan and H. J. Choi, Turbulent drag reduction characteristics induced by calf-thymus DNA, Physica, A 350(1) (2005) 84–88.
S. A. Vanapalli, M. T. Islam and M. J. Solomon, Scission-induced bounds on maximum polymer drag reduction in turbulent flow, Phys. Fluids, 17(9) (2005) 095108.
W. Brostow; H. Ertepinar and R. P. Singh, Flow of Dilute Polymer-Solutions — Chain Conformations and Degradation of Drag Reducers, Macromolecules, 23(24) (1990) 5109–5118.
S. T. Lim, C. H. Hong, H. J. Choi, P. Y. Lai and C. K. Chan, Polymer turbulent drag reduction near the theta point, Euro. Phys. Lett., 80 (2007) 58003.
S. A. Vanapalli, S. L. Ceccio and M. J. Solomon, Universal scaling for polymer chain scission in tubulence, PNAS, 103(45) (2006) 16660–16665.
H. J. Choi, C. A. Kim, J. I. Sohn and M. S. Jhon, An exponential decay function for polymer degradation in turbulent drag reduction, Polym. Deg. Stab., 69 (2000) 341–346.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was presented at the 9th Asian International Conference on Fluid Machinery (AICFM9), Jeju, Korea, October 16–19, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, C.H., Choi, H.J. & Kim, J.H. Rotating disk apparatus for polymer-induced turbulent drag reduction. J Mech Sci Technol 22, 1908–1913 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0731-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0731-z