Abstract
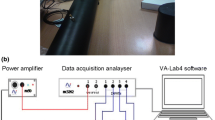
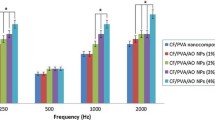
In this paper, the effects of soundproofing by polymer and carbon-nanotube (CNT) composites were investigated. The specimens for sound insulation measurement were fabricated with Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)/CNT composites. Tests showed that sound transmission loss of ABS/CNT 15 vol.% composite was higher by 21.7% (4.1 dB) than that of pure ABS specimen at a frequency of 3400 Hz. It was found that the principal factor influencing the improvement of sound insulations of ABS/CNT composites was increased stiffness by CNT additives. To demonstrate the practical applicability of polymer/CNT composites, tests were conducted for the reduction of operational noise from mechanical relay.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
T. Tokairin and T. Kitada, Study on the effect of porous fence on air quality and traffic noise level around a double-decked road structure, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 105 (2005) 121–143.
Y. Zhang, L. Wang, Y. Gao, J. Chen and X. Shi, Noise reduction in Doppler ultrasound signals using an adaptive decomposition algorithm, Medical Engineering and Physics, 29(6) (2007) 699–707.
Y. Y. Jiang, S. Yoshimura, R. Imai, H. Katsura, T. Yoshida and C. Kato, Quantitative evaluation of flow-induced structural vibration and noise in turbomachinery by full-scale weakly coupled simulation, Journal of Fluids and Structures, 23(4) (2007) 531–544.
B. Mazeaud and M. A. Galland, A multi-channel feedback algorithm for the development of active liners to reduce noise in flow duct applications, Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 21(7) (2007) 2880–2899.
H. S. Yang, D. J. Kim and H. J. Kim, Rice straw-wood particle composite for sound absorbing wooden construction materials, Bioresource Technology, 86(2) (2003) 117–121.
P. P. Narang, Material parameter selection in polyester fibre insulation for sound transmission and absorption, Applied Acoustics, 45(4) (1995) 335–358.
F. Hern’andez-Olivaresa, M. R. Bollatib, M. del Rioc and B. Parga-Landad, Development of cork-gypsum composites for building applications, Construction and Building Materials, 13(4) (1999) 179–186.
C. F. Ng and C. K. Hui, Low frequency sound insulation using stiffness control with honeycomb panels, Applied Acoustics, 69(4) (2008) 293–301
H. Zhou, B. Li and G. S., Huang, Sound absorption behavior of multiporous hollow polymer microspheres, Materials Letters, 60(29–30) (2006) 3451–3456.
B. H. Song, J. S. Boltona and Y. J. Kang, Effect of circumferential edge constraint on the acoustical properties of glass fiber materials, Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 110(6) (2001) 2902–2916.
C. J. Hwang, D. J. Lee and K. S. Chae, Time Accurate Finite Difference Method for Performance Prediction of a Silencer with Mean Flow and Nonlinear Incident Wave, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 21(1) (2007) 1–11.
F. Seybert, Two-senor methods for the measurement of sound intensity and acoustic properties in ducts, Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 83(6) (1988) 2233–2239.
K. M. Ho, Z. Yang, X. X. Zhang and P. Sheng, Measurements of sound transmission through panels of locally resonant materials between impedance tubes, Applied acoustics, 66 (2005) 751–765.
J. Y. Chung and D. A. Blaser, Transfer function method measuring in duct acoustic properties, I. Theory and II. Experiment, Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 68(3) (1980) 907–921.
F. G. Katz Brian, Method to resolve microphone and sample location errors in the two-microphone duct measurement method, Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 108(5) (2000) 2231–2237.
S. Lee, D. H. Lee, S. K. Cheong and H. T. Yong, Sound Transmission Loss Measurement of Sound Isolation Materials Using Two-Microphone Impedance Tube Method, Autumn Conference Proceedings of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers, (2002) 694–699.
W. K. Jung, S. H. Ahn and M. S. Won, Effect of Nano Particles and Ion Implantation on the Electromagnetic Shielding of Glass/Epoxy Composites, Journal of Composite Materials, 40(2) (2006) 175–188.
M. Heckl, The Tenth Sir Richard Fairly Memorial Lecture: Sound Transmission in Buildings, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 77(2) (1981) 165–189.
R. E. Jones, Intercomparisons of Laboratory Determinations of Airborne Sound Transmission Loss, Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 66(1) (1979) 148–164.
Y. Zheng, A. Zhang, Q. Chen, J. Zhang and R. Ning, Functionalized effect on carbon nanotube/epoxy nano-composites, Materials Science and Engineering: Part A, 435-436 (2006) 145–149.
Meincke, D. Kaempfer, H. Weickmann, C. Friedrich, M. Vathauer and H. Warth, Mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of carbonnanotube filled polyamide-6 and its blends with acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene, Polymer, 45(3) (2004) 739–748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JC., Hong, YS., Nan, RG. et al. Soundproofing effect of nano particle reinforced polymer composites. J Mech Sci Technol 22, 1468–1474 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0419-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0419-4