Abstract
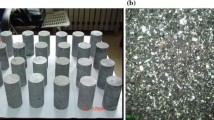
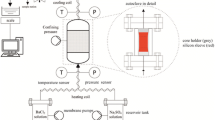
Groundwater seepage is one of the important factors which affect the physical and mechanical properties of soft rock. In this study, the permeability evolution of sandstone was investigated using water solution seepage tests with different pH values. The results show that the chemical nature of the solutions has a great influence on the evolution of the permeability coefficients of sandstone specimens. Over time, it was determined that the permeability coefficient under the solution with PH = 2 was significantly greater than those under the PH = 7 and PH = 12 solutions used in this study. During the infiltrations, the ions of H+ and OH- which were involved in the water-rock interaction made the pH value of the solution change with different degrees. After the seepage, the ions in the solutions changed significantly. The ion concentrations seeping from sandstone specimen in the acidic solution, such as Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+ (Fe2+), Al3+ and K+, were found to be much greater than in the neutral and alkaline solutions. However, the ion concentrations seeping from sandstone specimen in the neutral solution displayed little differences from those in the alkaline solution. The concentration of the Si ion in the alkaline solution was much higher than those of the acid and neutral solutions, and the concentration of the acid solution was slightly higher than that of the neutral solution. The changes in the ion concentration in the osmotic solution reflected that there had been different forms of chemical reactions between the minerals of the sandstone and the solutions. The seepage pressures also had some effects on the permeability coefficients, pH values, and concentrations of ions in the solutions. After the seepage tests, the rock microstructures were observed by the means of a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). The results show that some new holes have been formed in the sandstone specimen due to the seepage, especially in the sample with the acid solution. The internal structural changes of the sandstone are found to be the main reasons for the changes in the permeability coefficients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brantley, S. L., Kubicki, J. D., and White, A. F. (2008). Kinetics of water-rock interaction, Springer, New York, 2008.
Dunning, J., Douglas, B., Miller, M., and McDonald, S. (1994). “The role of the chemical environment in frictional deformation: Stress corrosion cracking and comminution.” Pure & Applied Geophysics, Vol. 143, Nos. 1–3, pp. 151–178, DOI: 10.1007/BF00874327.
Feng, X. T. and Ding, W. (2007). “Experimental study of limestone micro-fracturing under a coupled stress, fluid flow and changing chemical environment.” International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, Vol. 44, No. 3, pp. 437–448, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.07.012.
Feng, X. T., Liu, J., and Jing, L. (2004). “Research and application on coupled T-H-M-C processes of geological media in China -a review.” Elsevier Geo-Engineering Book Series, Vol. 2, pp. 37–48, DOI: 10.1016/S1571-9960(04)80021-1.
Groves, C. G. and Howard, A. D. (1994). “Minimum hydrochemical conditions allowing limestone cave development.” Water Resources Research, Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 607–615, DOI: 10.1029/93WR02945.
Heggheim, T., Madland, M. V., Risnes, R., and Austad, T. (2005). “A chemical induced enhanced weakening of chalk by seawater.” Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, Vol. 46, No. 3, pp. 171–184, DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2004.12.001.
Izadi, G. and Elsworth, D. (2015). “The influence of thermal-hydraulicmechanical-and chemical effects on the evolution of permeability, seismicity and heat production in geothermal reservoirs.” Geothermics, Vol. 53, pp. 385–395, DOI: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.08.005.
Karfakis, M. G. and Akram, M. (1993). “Effects of chemical solutions on rock fracturing.” International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, Vol. 30, No. 7, pp. 1253–1259, DOI: 10.1016/0148-9062(93)90104-L.
Li, N., Zhu, Y. M., Su, B., and Gunter, S. (2003). “A chemical damage model of sandstone in acid solution.” International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, Vol. 40, No. 2, pp. 243–249, DOI: 10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00132-6.
Liao, Q. L., Li, X., Li, S. D., and Hou, Z. S. (2003). “The effect of waster-rock interaction on the development and evolvement of the landslide 102 on the Chuan-Zang Highway.” Journal of Engineering Geology, Vol. 11, No. 4, pp. 390–395, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2003.04.010. (in Chinese)
Liu, J., Sheng, J. C., Polak, A., Elsworth, D., Yasuhara, H., and Grader, A. (2006). “A fully-coupled hydrological–mechanical–chemical model for fracture sealing and preferential opening.” International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, Vol. 43, No. 1, pp. 23–36, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2005.04.012.
Min, K. B., Rutqvist, J., and Elsworth, D. (2009). “Chemically and mechanically mediated influences on the transport and mechanical characteristics of rock fractures.” International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences. Vol. 46, No. 1, pp. 80–89, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.04.002.
Polak, A., Elsworth, D., Liu, J., and Grader, A. S. (2004). “Spontaneous switching of permeability changes in a limestone fracture with net dissolution.” Water Resources Research, Vol. 40, No. 3, pp. 383–391, DOI: 10.1029/2003WR002717.
Sheng, J., Li, F., Yao, D., Huang, Q., Song, H., and Zhan, M. (2012). “Experimental study of seepage properties in rocks fracture under coupled hydro-mechano-chemical process.” Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, Vol. 31, No. 5, pp. 1016–1025, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.05.019. (in Chinese)
Tenthorey, E., Cox, S. F., and Todd, H. F. (2003). “Evolution of strength recovery and permeability during fluid–rock reaction in experimental fault zones.” Earth & Planetary Science Letters, Vol. 206, No. 1, pp. 161–172, DOI: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)01082-8.
Xie, S. Y., Shao, J. F., and Xu, W. Y. (2011). “Influences of chemical degradation on mechanical behaviour of a limestone.” International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, Vol. 48, No. 5, pp.741–747, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.04.015.
Yao, H. Y., Feng, X. T., Cui, Q., and Zhou, H. (2009). “Meso-mechanical experimental study of meso-fraeturing process of limestone under coupled chemical corrosion and water pressure.” Rock and Soil Mechanics, Vol. 30, No. 1, pp. 59–66, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.01.009. (in Chinese)
Zhang, G. J., Xu, W. Y., and Lai, M. (2003). “Leaching of solution rock and permeability study under karst-engineering geological condition.” Rock and Soil Mechanics, Vol. 24, No. 5, pp. 795–799, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2003.05.024. (in Chinese)
Zhang, Z., Jiang, Q., Zhou, C., and Liu, X. (2014). “Strength and failure characteristics of Jurassic Red-Bed sandstone under cyclic wetting–drying conditions.” Geophysical Journal International, Vol. 198, No. 2, pp. 1034–1044, DOI: 10.1093/gji/ggu181.
Zhang, Z. H., Sun, Q. C., Li, D. Z., Du, M. P., and Yao, H. Y. (2015). “Experimental study on permeability characteristics of red sandstone under cyclic seepage pressures.” Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, Vol. 37, No. 5, pp. 937–943, DOI: 10.11779/CJGE201505021. (in Chinese)
Zhao, Y., Cui, P., Hu, L. B., and Hueckel, T. (2011). “Multi-scale chemomechanical analysis of the slip surface of landslides in the Three Gorges, China.” Science China Technological Sciences, Vol. 54, No. 7, pp. 1757–1765, DOI: 10.1007/s11431-011-4370-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, H., Zhang, Z. & Li, D. Experimental Study on the Permeability Characteristics of Sandstone in Different Chemical Solutions. KSCE J Civ Eng 22, 3271–3277 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-1611-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-1611-4