Abstract
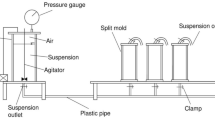
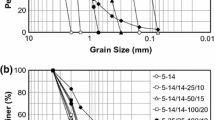
The aim of this experimental study was to investigate the penetrability of ultrafine Portland cement suspensions with or without additives into sand specimens and the strength and permeability of grouted sand samples. It was shown that ultrafine Portland cement grouts with dispersive agent could be used to treat not only medium to fine sand but also 100% fine sand where chemical grouts can only penetrate The basic rheological properties of ultrafine Portland cement suspensions with or without additives were studied. The penetration performance of suspensions into various graded medium to fine sand specimens prepared at different relative densities was examined. The unconfined compressive strength and the permeability characteristics of sand specimens permeated with ultrafine Portland cement suspensions with or without additives were searched at different time intervals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitcin, P. C., Ballivy, G., and Parizeau, R. (1984). “The use of condensed silica fume in grouts.” Innovative Cement Grouting, ACI Special Publication, Vol. 83, pp. 1–18.
ASTM C 191-04b (2002). Standard test method for time of setting of hydraulic cement by vicat needle, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
ASTM C 939-02 (2002). Standard test method for flow of grout for preplaced-aggregate concrete, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
ASTM C 940-98a (2002). Standard test method for expansion and bleeding of freshly mixed grouts for preplaced aggregate concrete in the laboratory, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
ASTM D 2487-11 (2011). Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
ASTM D 4219-02 (2002). Standard test method for unconfined compressive strength index chemical-grouted, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
ASTM D 4253-00 (2002). Standard test method for maximum index density and unit weight of soils using a vibratory table, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
ASTM D 4254-00 (2002). Standard test method for minimum index density and unit weight of soils and calculation of relative density, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
ASTM D 5856-95 (2002). Standard test method for measurement of hydraulic conductivity of porous material using a rigid-wall, compaction-mold permeameter, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
ASTM D 854-02 (2002). Standard test method for specific gravity of soil solids by water pycnometer, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
Bremen, R. (1997). “The use of additives in cement grouts.” The Int. J. Hydropower Dams 4, pp. 71–76.
Burwell, E. B. (1958). “Cement and clay grouting of foundations: Practice of the corps of engineers.” Journal of Soil Mech. and Found Division, Vol. 84, No. 1, pp. 1–22.
BS EN 12715 (2000). Execution of special geotechnical work: Grouting, British Adopted European Standard, London, UK.
Clarke, W. J. (1984). “Performance characteristics of microfine cement.” Preprint 84-023, ASCE, pp. 1–14.
DePaoli, B., Bosco, B., Granata, R., and Bruce, D. A. (1992). “Fundamental observations on cement based grouts (2): Microfine cements and the Cemill1 process.” Grouting, Soil Improvement and Geosynthetics, New Orleans, pp. 486–499.
Domone, P. L. and Tank, S. B. (1986). “Use of condensed silica fume in Portland cement grouts.” Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Fly Ash, Silica Fume, Slag and Natural Pozzolans in Concrete, Madrid, Vol. 2, pp. 1231–1260.
Eklund, D. and Stille, H. (2008). “Penetrability due to filtration tendency of cement based grouts.” Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, Vol. 23, No. 4, pp. 389–398, DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2007.06.011.
Eriksson, M., Friedrich, M., and Vorschulze, C. (2004). “Variations in the rheology and penetrability of cement-based grouts-an experimental study.” Cement and Concrete Research, Vol. 34, No. 7, pp. 1111–1119, DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.11.023.
Hakansson, U., Hassler, L., and Stille, H. (1992). “Rheological properties of microfine cement grouts with additives.” Grouting, Soil Improvement and Geosynthetics, Proc. ASCE Conf., New Orleans, pp. 551–563.
Henn, R. W. and Soule, N. C. (2010). Ultrafine cement in pressure grouting, ASCE Publications, Virginia, USA.
Lombardi, G. (1985). “The role of cohesion in cement grouting of rock.” 15th International Congress on Large Dams, Lausanne, Vol. 3, No. 58, pp. 235–260.
Markou, I., Christodoulou, D., and Atmatzidis, D. (2012). “Effect of sand gradation on the groutability of cement suspensions.” Grouting and Deep Mixing, pp. 2003–2012, DOI: 10.1061/9780784412350.0175.
Mollamahmutoglu, M. (2003). “Treatment of medium to coarse-grained sands by Fine Grained Portland Cement (FGPC) as an alternative grouting material to silicate-ester grouts.” Cement Concrete Aggregate, Vol. 25, No. 1, pp. 1235–1242, DOI: 10.1520/CCA10514J.
Mollamahmutoglu, M., Yilmaz, Y., and Kutlu, I. (2007). “Grouting performance of ultrafine cement and microsilica mix into sands.” J. ASTM International, Vol. 4, No. 4, pp. 1–7.
Mollamahmutoğlu, M., Avc, E., and Ozarslan, M. (2012). “Engineering properties of various graded medium to fine sand grouted with Ultrafin 12 cement.” Proc. The Third International Conference on New Developments in Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Nicosia (Lefkoşe), Vol. 1, No. 83, pp. 657–664.
Perret, S., Palardy, D., and Ballivy, G. (2000). “Rheological behavior and setting time of microfine cement-based grouts.” ACI Materials J., Vol. 97, No. 4, pp. 472–478, DOI: 10.14359/7413.
Schwarz, L. G. (1997). Roles of rheology and chemical filtration on injectability on microfine cement grouts, PhD Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanstone, Illinois, USA.
Schwarz, L. G. and Chirumalla, M. (2007). “Effect of injection pressure on permeability and strength of microfine cement grouted sand.” Grouting for Ground Improvement: Innovative Concepts and Applications, ASCE, Colorado, Vol. 1, pp. 168.
Schwarz, L. G. and Krizek, R. J. (1994). “Effect of preparation technique on permeability and strength of cement-grouted sand.” Geotechnical Testing J., Vol. 17, No. 4, pp. 434–443.
Taylor, H. F. W. (1990). Cement chemistry, Section 4.1.4, Acedemic Press, London.
Warner, J. (2003). “Soil solidification with ultrafine cement grout. grouting and ground treatment.” Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference, Geotechnical Special Publication, Reston, ASCE, New Orleans, pp. 1360–1371.
Zebovitz, S., Krizek, R. J., and Atmatzidis, D., K. (1989). “Injection of fine sands with very fine cement grout.” J. Geotech. Eng., Vol. 115, No. 12, pp. 1717–173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mollamahmutoğlu, M., Avci, E. Ultrafine Portland cement grouting performance with or without additives. KSCE J Civ Eng 19, 2041–2050 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-014-1445-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-014-1445-7