Abstract
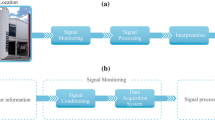
In this paper, recent research and application activities on smart sensing, monitoring, and damage detection for civil infrastructures are briefly introduced. Emphasis is given to the activities in Korea. First, the state of the art in smart sensors technology is reviewed including optical fiber sensors, piezoelectric sensors, and wireless sensors. Then, a brief overview is given to the recent advances in the structural monitoring/damage detection techniques such as ambient vibration-based bridge health evaluation, piezoelectric sensors-based local damage detection, wireless sensor networks and energy harvesting, and wireless power transmission by laser/optoelectronic devices. Finally, recent collaborative R&D activities on smart structure technologies in Korea are discussed, which have been carried out on test-road bridges, cable-stayed bridges, and railroad bridges, sharing the up-to-date information and promoting the smart sensors and monitoring technologies for applications to civil infrastructures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, Y. K. and Sohn, H. (2009). “Experimental validations of a baselinefree crack detection technique using Dual-PZTs.” Proc., SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
An, Y. K. and Sohn, H. (2010). “Instantaneous crack detection under varying temperature and static loading conditions.” Struct. Control Health Monit., Vol. 17, No. 7, pp. 730–741.
Aoki, S., Fujino, Y., and Abe, M. (2003). “Intelligent bridge maintenance system using MEMS and network technology.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Brown, W. C. (1996). “The history of wireless power transmission.” Solar Energy, Vol. 56, No. 1, pp. 3–21.
Cawley, P. and Alleyne, D. (1996). “The use of Lamb waves for the long range inspection of large structures.” Ultrason, Vol. 34, No. 2, pp. 287–290.
Cho, S., Jo, H., Jang, S., Park, J., Jung, H., Yun, C-B., Spencer, B. F., and Seo, J. (2010). “Structural health monitoring of a cable-stayed bridge using smart sensor technology: Data analysis.” Smart Syst. Struct., Vol. 6, No. 5–6, pp. 461–480.
Cho, S., Yun, C-B., Lynch, J. P., Zimmerman, A. T., Spencer, B. F., and Nagayama, T. (2008). “Smart wireless sensor technology for structural health monitoring of civil structures.” Int. J. Steel Struct., Vol. 8, pp. 267–275.
Choo, J.F., Ha, D-H., and Koh, H-M. (2009). “A neural network-based damage detection algorithm using dynamic responses measured in civil structures.” The Fifth Int. Joint Conf. on INC, pp. 682–685.
Chung, H. C., Enomoto, T., Shinozuka, M., Chou, P., Park, C., Yokoi, I., and Morishita, S. (2004). “Real-time visualization of structural response with wireless MEMS sensors.” Proc. 13th World Conf. Earthquake Engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
Diaz Valdes, S. H. and Soutis, C. (2000). “Health monitoring of composites using lamb waves generated by piezoelectric devices.” Plast., Rubber Compos., Vol. 29, No. 9, pp. 475–481.
Draeger, C., Cassereau, D., and Fink, M. (1997). “Theory of the timereversal process in solids.” J. Acoust. Soc. America, Vol. 102, No. 3, pp. 1289–1295.
Farrar, C. R. (2001). “Historical overview of structural health monitoring. Lecture notes on structural health monitoring using statistical pattern recognition.” Los Alamos Dynamics, Los Alamos, USA.
Farrar, C. R., Allen, D. W., Ball, S., Masquelier, M. P., and Park, G. (2005). “Coupling sensing hardware with data interrogation software for structural health monitoring.” Proc. 6th Int. Symp. Dyn. Prob. Mech., Ouro Preto, Brazil.
Feng, M. Q. and Kim, D. H. (2006). “Novel fiber optic accelerometer system using geometric moiré fringe.” Sensor. Actuat. A-Phys., Vol. 128, No. 1, pp. 37–42.
Feng, M. Q., Kim, J. M., and Xue, H. (1998). “Identification of a dynamic system using ambient vibration measurements.” J. Appl. Mech., Vol. 65, No. 4, pp. 1010–1021.
Gao, Q., Shi, B., Zhang, W., Ke, M-Y., Liu., H-X., and Zhan, D. (2005). “Application of distributed fiber optic sensor to bridge and pavement health monitoring.” J. Disaster Prevention Mitigation Eng., Vol. 25, No. 1, pp. 14–19.
Gao, Y. and Spencer, Jr. B. F. (2008). Structural health monitoring strategies for smart sensor networks, Newmark Structural Engineering Laboratory Report Series 011.
Ghosh, T., Kundu, T., and Karpur, P. (1998). “Efficient use of Lamb modes for detecting defects in large plates.” Ultrason, Vol. 36, No. 7, pp. 791–801.
Giurgiutiu, V. and Rogers, C. A. (1997). “Electro-Mechanical (E/M) impedance method for structural health monitoring and nondestructive evaluation.” Proc. Int. Workshop on Struct. Health Monit., Stanford, CA, USA.
Glynne-Fones, P. and White, N. M. (2001). “Self-powered systems: A review of energy sources.” Sens. Rev., Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 91–97.
Grisso, B. L. and Inman, D. J. (2005). “Developing an autonomous onorbit impedance-based SHM for thermal protection systems.” Int. Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, pp. 435–442.
Hall, S. R. (1999). “The effective management and use of structural health data.” Proc. 2nd Int. Workshop on Struct. Health Monit, Technomic, Lancaster, PA, USA.
Heo, G. and Jeon, J. (2009). “A smart monitoring system based on ubiquitous computing technique for infra-structural system: Centering on identification of dynamic characteristics of self-anchored suspension bridge.” KSCE J. Civil Eng., Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 333–337.
Jang, S., Jo, H., Cho, S., Mechitov, K., Rice, J. A., Sim, S., Jung, H., Yun, C-B., Spencer, B. F., and Agha, G. (2010). “Structural health monitoring of a cable-stayed bridge using smart sensor technology: Deployment and evaluation.” Smart Syst. Struct., Vol. 6, No. 5–6, pp. 439–459.
Jang, J-H., Yeo, I., Shin, S., and Chang, S-P. (2002). “Experimental investigation of system-identification-based damage assessment on structures.” J. Struct. Eng., ASCE, Vol. 128, No. 5, pp. 673–682.
Johnson, G. A., Vohra, S. T., Danver, B. A., Pran, K., Havsgard, G. B., and Wang, G. (1999). “Vibration monitoring of a ship water jet with fiber Bragg gratings.” Proc. 13th Int. Conf. on Optical Fiber Sensors (OFS-13), Kyongju, Korea.
Kang, J. S., Park, S.-K., Shin, S., and Lee, H. S. (2005). “Structural system identification in time domain using measured acceleration.” J. Sound Vib., Vol. 288, No. 1–2, pp. 215–234.
Kehlenbach, M. and Das, S. (2002). “Identifying damage in plates by analyzing lamb wave propagation characteristics.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 364–375.
Keilers, C. H. and Chang, F-K. (1995). “Identifying delamination in composite beam using built-in piezoelectrics.” J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct., Vol. 6, No. 5, pp. 647–672.
Kessler, S., Spearing, S. M., and Soutis, C. (2002). “Damage detection in composite materials using Lamb wave methods.” Smart Mater. Struct., Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 269–278.
Kim, Y. S., An, S. S., Ahn, S. R., and Yang, D. S. (2009). “The strategic planning of safety management network for infrastructure.” Proc Proc. 8th Int. Conf. on Structural Safety and Reliability, Osaka, Japan.
Kim, K. S., Baek, Y., and Yoo, K. (2010). “Pavement roughness monitoring method using fiber optic vibration sensors.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 364–375.
Kim, K. S., Cho, S. K., and Bae, B. (2003a). “High-speed weigh-inmotion measurement with Bragg grating sensors.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 364–375.
Kim, K. S., Chung, C., and Kim, H. J. (2003b). “Fiber optic structural monitoring of concrete beam retrofitted by composite patches.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 364–375.
Kim, J., Grisso, B. L., Ha, D. S., and Inman, D. J. (2007a). “An alldigital low-power structural health monitoring system.” Proc. IEEE Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security.
Kim, J., Grisso, B. L., Ha, D. S., and Inman, D. J. (2007b). “A Systemon-board approach for impedance-based structural health monitoring.” Proc. SPIE, 6529, 65290O.1-65290O.9.
Kim, S-W. and Kim, N-S. (2009). “Multi-point dynamic displacement measurements of structures using digital image correlation technique.” J. Earthquake Eng. Soc. Korea, Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 11–19.
Kim, D. K., Kim, J-I., and Feng, M. Q. (2001). “Instrumentation of bridges for structural health monitoring.” KSCE J. of Civil Eng., Vol. 5, No. 3, pp. 231–242.
Kim, S., Pakzad, S., Culler, D., Demmel, J., Fenves, G., Glaser, S., and Turon, M. (2007). “Health monitoring of civil infrastructures using wireless sensor networks.” Proc. the 6th Int. Conf. on Inf. Process. Sensor Networks, pp. 254–263.
Kim, J. T., Park, J. H., Yoon, H. S., and Yi, J. H. (2007). “Vibrationbased damage detection in beams using genetic algorithm.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 263–280.
Kim, B. and Roh, Y. (2008). “Piezoelectric sensor system for structural health monitoring.” Advances in Science and Technology, Vol. 56, pp. 194–199.
Kim, D. Y., Seon J. H., Roh, Y., Park, S. H., and Yun, C. B. (2005). “Damage detection of civil infrastructures with piezoelectric oscillator sensors.” Proc. KSCE Conference, pp. 2907–2910.
Kim, S. B. and Sohn, H. (2006). “Baseline-free crack detection in steel structures using lamb waves and PZT polarity.” Earthquake Eng. Soc. Korea., Vol. 10, No. 6, pp. 79–91.
Kim, K. S., Song, Y. C., Pang, G. S., and Yoon, D. J. (2005). “Study on the application of fiber Bragg grating sensors for the containment structures of nuclear power plants.” Proc. 2nd Int. Workshop on Adv. Smart Mater. Smart Struct. Technol., Gyeongju, Korea.
Kim, J-T. and Stubbs, N. (1995). “Damage detection in jacket-type structures from few mode shapes.” J. Ocean Eng. Technol., Vol. 8, No. 1, pp. 144–153.
Kim, J-T., Yun, C-B., and Yi J-H. (2003). “Temperature effects on frequency-based damage detection in plate-girder bridges.” KSCE J. Civil Eng., KSCE, Vol. 7, No. 6, pp. 725–733.
KISTEC (2007). Key national infrastructure safety management network setup plan, Project Report.
Knecht A. and Manetti L. (2001) “Using GPS in structural health monitoring.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Koo, K-Y., Lee, J-J., Yun, C-B., and Kim, J-T. (2008). “Damage detection in beam-like structures using deflections obtained by modal flexibility matrices.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 4, No. 5, pp. 605–628.
Kwon, I-B., Choi, M-Y., Yu, J-W., and Baik, S-J. (2001). “Development of fiber optic BOTDA sensor.” Korean J. Opt. Photonics, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 294–299.
Kwon, I-B., Jin, G., Seo, D-C., Kim, C-Y., Lee, N-K., and Yun, C-B. (2009). “Feasibility study for monitoring of off-shore pipelines using BOTDA system.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 364–375.
Kwon, I-B., Kim, C-Y., Cho, S-B., and Lee, J-J. (2003). “Temperature compensation of a strain sensing signal from a fiber optic brillouin optical time domain analysis sensor.” J. Opt. Soc. Korea, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 106–112.
Kwon, S-J., Shin, S., Lee, H. S., and Park, Y. H. (2003). “Design of accelerometer layout for structural monitoring and damage detection.” KSCE J. Civil Eng., Vol. 7, No. 6, pp. 717–724.
Lee, J-J., Cho, S-J., Shinozuka, M., Yun, C-B., and Lee, C-G. (2006a). “Evaluation of bridge load carrying capacity based on dynamic displacement measurement using real-time image processing techniques.” Int. J. Steel Struct., Vol. 6, No. 5, pp. 377–385.
Lee, J-J., Fukuda, Y., Shinozuka, M., Cho, S., and Yun, C-B. (2007b). “Development and application of a vision-based displacement measurement system for structural health monitoring of civil structures.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 374–384.
Lee, J. W., Kim, J. D., Yun, C-B., Yi, J. H., and Shim, J. M. (2002). “Health monitoring method for bridges under ordinary traffic loadings.” J. Sound Vib., Vol. 257, No. 2, pp. 247–264.
Lee, J-J., Lee, J.W., Yi, J.H., Yun, C-B., and Jung, H. Y. (2005). “Neural networks-based damage detection for bridges considering errors in baseline finite element models.” J. Sound Vib., Vol. 280, No. 3–5, pp. 555–578.
Lee, J-J. and Shinozuka, M. (2006b), “Real-time displacement measurement of a flexible bridge using digital image processing techniques.” Exp. Mech., Vol. 46, No. 1, pp. 105–114.
Lee, J-J. and Yun, C-B. (2007a). “Damage localization for bridges using probabilistic neural networks.” KSCE J. Civil Eng., Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 111–120.
Levis, P., Madden, S., Polastre, J., Szewczyk, R., Whitehouse, K., Woo, A., Gay, D., Hill, J., Welsh, M., Brewer, E., and Culler, D. (2005). TinyOS: An operating system for sensor networks, Ambient Intelli gence, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Lynch, J. P., Law, K. H., Kiremidjian, A. S., Kenny, T. W., Carryer, E., and Patridge, A. (2001). “The design of a wireless sensing unit for structural health monitoring.” Proc. 3rd Int. Workshop on Struct. Health Monit., Stanford, CA, USA.
Lynch, J. P., Law, K. H., Kiremidjian, A. S., Carryer, E., Kenny, T. W., Partridge, A., and Sundararajan, A. (2002). “Validation of a wireless modular monitoring system for structures.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Lynch, J. P. and Loh, K. J. (2006a). “A summery review of wireless sensors and sensor networks for structural health monitoring.” The Shock and Vib. Digest, Vol. 38, No. 2, pp. 91–128.
Lynch, J. P., Wang, Y., Loh, K. J., Yi, J. H., and Yun, C. B. (2006b). “Performance monitoring of the geumdang bridge using a dense network of high-resolution wireless sensors.” Smart Mater. Struct., Vol. 15, No. 6, pp. 1561–1575.
Mascarenas, D. L., Park, G., Farinholt, K., Todd, M. D., and Farrar, C. R. (2009). “A low-power wireless sensing device for remote inspection of bolted joints.” J. Aero. Eng., Vol. 223, No. 5, pp. 565–575.
Mascarenas, D. L., Todd, M. D., Park, G., and Farrar, C. R. (2007). “Development of an impedance-based wireless sensor node for structural health monitoring.” Smart Mater. Struct., Vol. 16, No. 6, pp. 2137–2145.
Mateu, L. and Moll, F. (2005). “Review of energy harvesting techniques and applications for microelectronics.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Mathuna, C. O., O’Donnell, T., Martinez-Catala, R. V., Rohan, J., and O’Flynn, B. (2008). “Energy scavenging for long-term deployable wireless sensor networks.” Talanta, Vol. 75, No. 3, pp. 613–623.
Min, J., Park, S., Yun, C-B., and Song, B. (2010). “Development of a low-cost multifunctional wireless impedance sensor node.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 6, No. 5–6, pp. 689–709.
Monkhouse, R. S. C., Wilcox, P. D., and Cawley, P. (1997). “Flexible inter-digital PVDF transducers for the generation of lamb waves in structures.” Ultrason., Vol. 35, No. 7, pp. 489–498.
Myung, H., Lee, S. M., and Lee, B. J. (2010), “Paired structured light for structural health monitoring robot system.” Struct. Health Monit., doi: 10.1177/1475921710365413.
Nagayama, T. and Spencer, Jr. B. F. (2007). Structural health monitoring using smart sensors, Newmark Structural Engineering Laboratory Report N. 1, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, Illinois.
Nagayama, T, Moinzadeh, P., Mechitov, K., Ushita, M., Makihata, N., Ieiri, M., Agha, G., Spencer Jr. B. F., Fujino, Y., and Seo, J. (2010). “Reliable multi-hop communication for structural health monitoring.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 6, No. 5–6, pp. 481–504.
Nagayama, T., Spencer, B. F., Agha, G. A., and Mechitov, K. A. (2006). “Model-based data aggregation for structural monitoring employing smart sensors.” Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. Networked Sensing Systems, Chicago, USA.
Nassif, H. H., Gindy, M., and Davis, J. (2005), “Comparison of laser Doppler vibrometer with contact sensors for monitoring bridge deflection and vibration.” NDT&E Int., Vol. 38, No. 3, pp. 213–218
Osmont, D., Devillers, D., and Taillade, F. (2001). “Health monitoring of sandwich plates based on the analysis of the interaction of lamb waves with damages.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Overly, T. G., Park, G., Farinholt, K. M., and Farrar, C. R. (2008). “Development of an extremely compact impedance-based wireless sensing device.” Smart Mater. Struct., Vol. 17, No. 6:065011.
Overly, T. G., Park, G., Farrar, C. R., and Allemang, R. J. (2007). “Compact hardware development for structural health monitoring and sensor diagnostics using admittance measurements.” Proc. IMAC-XXV: A Conf. and Expo. on Struct. Dyn., Orlando, FL, USA.
Overschee, P. V. and De Moor, B. (1993). “Subspace algorithms for the stochastic identification problem.” Automatics, Vol. 29, No. 3, pp. 649–660.
Pakzad, S. N. (2010). “Development and deployment of large scale wireless sensor network on a long-span bridge.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 6, No. 5–6, pp. 525–543.
Pandey, A. K. and Biswas, M. (1994). “Damage detection in structures using changes in flexibility.” J. Sound. Vib., Vol. 169, No. 1, pp. 3–17.
Paradiso, J. A. and Starner, T. (2005). “Energy scavenging for mobile and wireless electronics.” IEEE PErv. Comput., Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 18–27.
Park, S., Ahmad, S., Yun, C-B., and Roh, Y. (2006a). “Multiple crack detection of concrete structures using impedance-based structural health monitoring techniques.” Exp. Mech., Vol. 46, No. 5, pp. 609–618.
Park, G., Farrar, C. R., Rutherford, A. C., and Robertson, A. N. (2006). ’Piezoelectric active sensor self-diagnostics using electrical admittance measurements.” Vib. Acoust., Vol. 128, No. 4, pp. 469–76.
Park, J., Jung, H-J., Jo, H., Jang, S., and Spencer, B. F. (2010). “Feasibility study of wind generator for smart wireless sensor node in cable-stayed bridge.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Park, J. H., Kim, J-T., Hong, D-S., Mascarenas, D., and Lynch, J. P. (2010). “Autonomous smart sensor nodes for global and local damage detection of prestressed concrete bridges based on accelerations and impedance measurement.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 6, No. 5–6, pp. 711–730.
Park, H-J., Koo, K. Y., and Yun, C-B. (2007). “Modal flexibility-based damage detection technique of steel beam by dynamic strain measurements using FBG sensors.” Int. J. Steel Struct., Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 11–18.
Park, S., Lee, J-J., Inman, D. J., and Yun, C-B. (2008), “Electromechanical impedance-based wireless structural health monitoring using PCA and k-means clustering algorithm.” J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct., Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 509–520.
Park, H. W., Park, M. W., Ahn, B. K., and Lee, H. S. (2007). “1-norm based regularization scheme for system identification of structures with discontinuous system parameters.” Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng., Vol. 69, No. 3, pp. 504–523.
Park, G., Rosing, T., Todd, M. D., Farrar, C. R., and Hodgkiss, W. (2008). “Energy harvesting for structural health monitoring sensor networks.” J. Infrastruct. Syst., Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 64–79.
Park, S., Shin, H-H., and Yun, C-B. (2009). “Wireless impedance sensor nodes for functions of structural damage identification and sensordiagnosis.” Smart Mater. Struct., Vol. 18, No. 5, pp. 1–11.
Park, G., Sohn, H., Farrar, C. R., and Inman, D. J. (2003). “Overview of piezoelectric impedance-based health monitoring and path forward.” Shock and Vib. Digest, Vol. 35, No. 6, pp. 451–463.
Park, H-J., Sohn, H. Yun, C-B., Chung, J., and Kwon, I-B. (2010). “A wireless guided wave excitation technique based on laser and optoelectronics.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 6, Nos. 5–6, pp. 749–765.
Park, S., Yun, C-B., and Roh, Y-R. (2006b). “Active sensing-based realtime nondestructive evaluations for steel bridge members.” KSCE J. Civil Eng., KSCE, Vol. 10, No. 1, pp. 33–39.
Qiwai, M. A., Thomas, J. P., Kellogg, J. C., and Baucom, J. (2004). “Energy harvesting concepts for small electric unmanned systems.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Raghavan A. and Cesnik C. E. S. (2004). “Modeling of piezoelectric based lamb-wave generation and sensing for structural health monitoring.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Raghavan, A. and Cesnik, C. E. S. (2007). “Review of guided-wave structural health monitoring.” Shock and Vib. Digest, Vol. 39, No. 2, pp. 91–114.
Rice, J. A., Mechitov, K., Sim, S., Nagayama, T., Jang, S., Kim, R., Spencer Jr. B. F., Agha, G., and Fujino, Y. (2010). “Flexible smart sensor framework for autonomous structural health monitoring.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 6, No. 5–6, pp. 423–438.
Rice, J. A. and Spencer, B. F. (2008). “Structural health monitoring sensor development for the Imote2 platform.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Roundy, S. J. (2003). Energy scavenging for wireless sensor nodes with a focus on vibration to electricity conversion, Ph.D. dissertation, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA, USA.
Ryu, C. Y. and Hong, C. S. (2002). “Development of fiber bragg grating sensor system using wavelength-swept fiber laser.” Smart Mater. Structures, Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 468–473.
Shin, S. and Oh, S. H. (2007). “Damage assessment of shear buildings by synchronous estimation of stiffness and damping using measured acceleration.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 245–261.
Sim, S. H., Carbonell-Marquez, J. F., Spencer, Jr., B. F., and Jo, H. (2010). “Decentralized random decrement technique for efficient data aggregation and system identification in wireless smart sensor networks.” Probabilist. Eng. Mech., Vol. 26, No. 1, pp. 81–91.
Sodano, H. A., Inman, D. J., and Park, G. (2004). “A review of power harvesting from vibration using piezoelectric materials.” Shock Vib. Digest, Vol. 36, No. 3, pp. 197–205.
Sohn, H. (2003). “Active sensing based structural health monitoring for flaw detection in composite structures.” KSCE J. Civil Eng., Vol. 7, No. 6, pp. 691–700.
Sohn, H. and Kim, S. B. (2009) “Development of dual PZT Transducers for instantaneous crack detection in thin plate structures.” IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control, Vol. 57, No. 1, pp. 229–240.
Sohn, H., Park, H. W., Law, K. H., Farrar, C. R. (2007). “Combination of a time reversal process and a consecutive outlier analysis for baseline-free damage diagnosis.” J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct., Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 335–346.
Straser, E. G. and Kiremidjian, A. S. (1998). “A modular, wireless damage monitoring system for structures.” Technical Report N. 128, John A Blume Earthquake Engineering Center, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, USA.
Talyor, S. G., Farinholt, K. M., Flynn, E. B., Figueiredo, E., Mascarenas, D. L., Moro, E. A., Park, G., Todd, M. D., and Farrar, C. R. (2009b). “A mobile-agent-based wireless sensing network for structural monitoring applications.” Meas. Sci. Technol., Vol. 20:045201.
Taylor, S. G., Farinholt, K. M., Park, G., and Farrar, C. R. (2009a). “Wireless impedance device for electromechanical impedance sensing and low-frequency vibration data acquisition.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Toksoy, T. and Aktan, A. E. (1994). “Bridge-condition assessment by modal flexibility.” Exp. Mech., Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 271–278.
Tomaszewska, A. (2010). “Influence of statistical errors on damage detection based on structural flexibility and mode shape curvature.” Comput. Struct., Vol. 88, pp. 154–164.
Tseng, K. K., Soh, C. K., Gupta, A., and Bhalla, S. (2000). “Health monitoring of civil infrastructures using smart piezoceramic transducers.” Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Comput. Method. for Smart Struct. Mater., Madrid, Spain.
Vohra, S. T., Todd, M. D., Johnson, G. A., Chang, C. C., and Danver, B. A. (1999). “Fiber Bragg grating sensor system for civil structure monitoring: applications and field tests.” Proc. 13th Int. Conf. on Optical Fiber Sensors (OFS-13), Kyongju, Korea.
Wahbeh, A. M., Caffrey, J. P., and Masri, S. F. (2003). “A vision-based approach for the direct measurement of displacements in vibrating systems.” Smart Mater. Struct, Vol. 12,, No. 5 pp. 785–794.
Wang, Y., Lynch, J. P., and Law, K. H. (2005). “Validation of an integrated network system for real-time wireless monitoring of civil structures.” Proc. 5th Int. Ws. Struct. Health Monit., CA, USA.
Yan, A. M. and Golinval, J. C. (2005). “Structural damage localization by combining flexibility and stiffness methods.” Eng. Struct., Vol. 27, No. 12, pp. 1752–1761.
Yeatman, E. M. (2003). “Energy harvesting-small scale energy production from ambient source.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Yi, J-H. and Yun, C-B. (2004). “Comparative study on modal identification methods using output-only information.” Struct. Engrg. Mech., Vol. 17, No. 3–4, pp. 445–466.
Yi, J-H., Cho, S., Koo, K-Y., Yun, C-B., Kim, J-T., Lee, C-G., and Lee, W-T. (2007). “Structural performance evaluation of a steel-plate girder bridge using ambient acceleration measurements.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 281–298.
Yun, C-B. and Bahng, E-Y. (2000). “Substructural identification using neural networks.” Comput. Struct., Vol. 77, No. 1, pp. 41–52.
Yun, C-B., Lee, J-J., and Koo, K-Y. (2009a) “Smart structure technologies for civil infrastructures in Korea: recent research and applications.” Struct. Infrastruct. Eng, Online-Published.
Yun, C-B., Lee, H-J., and Lee, C-G. (1997). “Sequential prediction-error method for structural identification.” J. Engrg. Mech., ASCE, Vol. 123, No. 2, pp. 115–122.
Yun, C-B., Sohn, H., Lee, J-J., Park, S., Wang, M. L., Zhang, Y. F., and Lynch, J. P. (2009b). “US-Korea collaborative research for bridge monitoring test beds.” Proc. 5th Int. Workshop on Adv. Smart Mater. Smart Struct. Technol., Boston, USA.
Zagrai, A. N. and Giurgiutiu, V. (2001). “Electro-mechanical impedance method for crack detection in thin wall structures.” Proc. 3rd Int. Workshop on Struct. Health Monit., Stanford Univ., CA, USA.
Zhang, Z. and Aktan, A. E. (1995). “The Damage Indices for the constructed facilities.” Proc. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA.
Zhao, J. and DeWolf, J. T. (1999). “Sensitivity study for vibrational parameters used in damage detection.” J. Struct. Eng., Vol. 125, No. 4, pp. 410–416.
Zhao, F. and Guibas, L. (2004). “Wireless sensor networks: An information processing within wireless monitoring systems.” J. Infrastruct. Syst., Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 102–113.
Zhou, D., Ha D. S., and Inman, D. J. (2010). “Ultra low-power active wireless sensor for structural health monitoring.” Smart Struct. Syst., Vol. 6, No. 5–6, pp. 672–687.
Zhou, Z., He, J., Yan, K., and Ou, J. (2008). “Fiber-reinforced polymerpackaged optical fiber sensors based on Brillouin optical timedomain analysis.” Opt. Eng., Vol. 47, No. 1, 014401.
Zimmerman, A. T. and Lynch, J. P. (2009) “A parallel simulated annealing architecture for model updating in wireless sensor networks.” IEEE Sens. J., Vol. 9, No. 11, pp. 1503–1510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, CB., Min, J. Smart sensing, monitoring, and damage detection for civil infrastructures. KSCE J Civ Eng 15, 1–14 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-011-0001-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-011-0001-y