Abstract
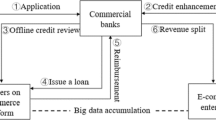
After building a dynamic evolutionary game model, the essay studies the stability of the equilibrium in the game between the commercial banks and the closed-loop supply chain (CLSC) enterprises. By design of systematic mechanism based on system dynamics theory, capital chains of independent small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) on CLSC are organically linked together. Moreover, a comparative simulation is studied for the previous independent and post-design dependent systems. The study shows that with business expanding and market risk growing, the independent finance chains of SMEs on CLSC often take on a certain vulnerability, while the SMEs closed-loop supply chain finance system itself is with a strong rigidity and concerto.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
YAN J H, XU X Q. Analysis the SME modes of supply chain finance [J]. Shanghai Finance, 2007(2): 14–16 (in Chinese).
CHEN L H, PENG F C. Supply chain finance: The new finance methods of SME [J]. Hubei Social Science, 2008(11): 101–103 (in Chinese).
YU J M. Resolving the problems of SME finance by supply chain finance [J]. Economics Cross, 2008(3): 99–102 (in Chinese).
PENG L J. Research about SEM’s financing under supply chain finance modes [D]. Guangzhou: Management School, Jinan University, 2001 (in Chinese).
HU Y H, HUANG S Q. Background and innovation of supply chain finance [J]. Finance Research, 2009(8): 194–206 (in Chinese).
ZHAO Y J, YANG X S, LIU X B. Supply chain finance and SME credit loan ability promotion [J]. The Theory and Practice of Finance, 2009(10): 46–51 (in Chinese).
STEPHENS K. Commentary: Quality principles, philosophies and methodologies applicable to the mortgage-finance supply chain [J]. Quality Management Journal, 2009, 16: 26–27.
ZIPKIN P. Quality snags in the mortgage-finance supply chain [J]. Quality Management Journal, 2009, 16: 7–18.
WUTTKE D A, BLOME C, HENKE M. Focusing the financial flow of supply chains: An empirical investigation of financial supply chain management [J]. International Journal Prod Economics, 2013, 145: 773–789.
ZHANG H. The credit valuation modes research of SME based on supply chain finance [J]. Journal of Southeast University (Philosoply and Social Science), 2008, 10(Sup 2): 54–58 (in Chinese).
WANG S G, XU L. The analysis of supply chain finance modes and risks [J]. Commercial Times, 2009(22): 75–76 (in Chinese).
XIONG X, MA J, ZHAO W J, et al. The appraise of credit risk under supply chain finance [J]. The Management Reviews of Nankai, 2009, 12(4): 92–98 (in Chinese).
SHI G. The contract coordinate research based on supply chain finance [D]. Chengdu: Management School, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2008 (in Chinese).
WAN H D. Supply chain finance models analysis [J]. Economy Problem, 2008(11): 109–112 (in Chinese).
WANG Q. On the credit risk evaluation system of supply chain finance based on decision tree [J]. New Finance, 2010(4): 38–41 (in Chinese).
ZHOU X N. Financial management of supply chain [J]. System of Engineer, 2010, 28(8): 85–88.
HE Y Q, GUO T T. The SME games activities analysis under supply chain finance [J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Engineering and Technology), 2010, 32(2): 183–187 (in Chinese).
XU Y, HU B, QIAN R. Analysis on stability of strategic alliances based on stochastic evolutionary game including simulations [J]. System Engineering: Theory & Practice, 2011, 31(5): 920–926 (in Chinese).
QIAO X. The cost and profits analysis under supply chain finance models [J]. Commercial Economy, 2011(11): 42–45 (in Chinese).
LI W L. The game simulation of supply chain finance credit risks based on multi-agent [D]. Guangzhou: Management School, South China University of Technology, 2012 (in Chinese).
CHEN T K, LIAO H H, KUO H J. Internal liquidity risk, financial bullwhip effects and corporate bond yield spreads, supply chain perspectives [J]. Journal of Bank Finance, 2013, 37: 2434–2456.
YANG Y Z. On commercial banks supply chain finance risks [J]. The Forum of Finance, 2007 (10): 42–45 (in Chinese).
TIAN L, LIU WX. On commercial banks’ supply chain finance operation [J]. Finance & Economy, 2011(6): 60–63 (in Chinese).
ZHOU C M. On the supply chain finance risk management of commercial banks [J]. Journal of Shanxi Finance and Economics University, 2009, 31(2): 115–116 (in Chinese).
ZHANG X, LI H P. On the credit models and risk control of deal chain finance business of bank [J]. New Finance, 2011(4): 44–46 (in Chinese).
BRASS R G. Supply chain finance [J]. Supply Manage, 2009, 14: 23–25.
LEE C H, RHEE B D. Trade credit for supply chain coordination [J]. Europe Journal of Operation Research, 2011, 214(1): 136–146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the Natural Science Research Fund of Hubei Province (No. 2014BDH121)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C. Small and medium-sized enterprises closed-loop supply chain finance risk based on evolutionary game theory and system dynamics. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 21, 355–364 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-016-1733-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-016-1733-0