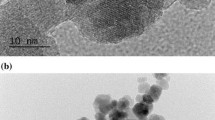
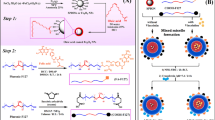
Abstract
Introduction
With an emphasis on the radioresistant nature of glioblastoma cells, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the radio-thermo-sensitizing effects of PCL-PEG-coated Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) as a carrier of 5-iodo-2-deoxyuridine (IUdR) in monolayer culture of U87MG human glioma cell line.
Methods
Following monolayer culture of U87MG cells, nanoparticle uptake was assessed using Prussian blue staining and ICP-OES method. The U87MG cells were treated with an appropriate concentration of free IUdR and PCL-PEG-coated SPIONs (MNPs) loaded with IUdR (IUdR/MNPs) for 24 h, subjected to hyperthermia (water bath and alternating magnetic field (AMF)) at 43 °C, and exposed to X-ray (2 Gy, 6 MV). The combined effects of hyperthermia with or without magnetic nanoparticles on radiosensitivity of the U87MG cells were evaluated using colony formation assay (CFA) and Flowcytometry.
Results
Prussian blue staining and ICP-OES showed that the nanoparticles were able to enter the cells. The results also indicated that IUdR/MNPs combined with X-ray radiation and hyperthermia significantly decreased the colony formation ability of monolayer cells (1.11, 1.41 fold) and increased the percentage of apoptotic (2.47, 4.1 fold) and necrotic cells (12.28, 29.34 fold), when compared to IUdR combined with X-ray and hyperthermia or IUdR/MNPs + X-ray. MTT results revealed that the presence of IUdR/MNPs significantly increased the toxicity of AMF hyperthermia compared to the water bath method.
Conclusions
Our study showed that SPIONs/PCL-PEG, as a carrier of IUdR, can enhance the cytotoxic effects of radiotherapy and hyperthermia and act as a radio-thermo-sensitizing agent.
Graphic Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzalipour, R., S. Khoei, S. Khoee, S. Shirvalilou, N. Jamali Raoufi, M. Motevalian, and M. R. Karimi. Dual-targeting temozolomide loaded in folate-conjugated magnetic triblock copolymer nanoparticles to improve the therapeutic efficiency of rat brain gliomas. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 5(11):6000–6011, 2019.
Afzalipour, R., S. Khoei, S. Khoee, S. Shirvalilou, N. J. Raoufi, M. Motevalian, and M. Y. Karimi. Thermosensitive magnetic nanoparticles exposed to alternating magnetic field and heat-mediated chemotherapy for an effective dual therapy in rat glioma model. Nanomedicine 31:2021.
Asadi, L., S. Shirvalilou, S. Khoee, and S. Khoei. Cytotoxic effect of 5-fluorouracil-loaded polymer-coated magnetite nanographene oxide combined with radiofrequency. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 18(8):1148–1155, 2018.
Asayesh, T., V. Changizi, and N. Eyvazzadeh. Assessment of cytotoxic damage induced by irradiation combined with hyperthermia and Gemcitabine on cultured glioblastoma spheroid cells. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 120:44–48, 2016.
Bao, S., Q. Wu, R. E. McLendon, Y. Hao, Q. Shi, A. B. Hjelmeland, M. W. Dewhirst, D. D. Bigner, and J. N. Rich. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444(7120):756–760, 2006.
Bayart, E., F. Pouzoulet, L. Calmels, J. Dadoun, F. Allot, J. Plagnard, J. L. Ravanat, A. Bridier, M. Denoziere, J. Bourhis, and E. Deutsch. Enhancement of IUdR radiosensitization by low-energy photons results from increased and persistent DNA damage. PLoS ONE 12(1):2017.
Brandes, A. A., A. Tosoni, E. Franceschi, M. Reni, G. Gatta, and C. Vecht. Glioblastoma in adults. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 67(2):139–152, 2008.
Bree, C. V., N. A. Franken, P. J. Bakker, L. J. Klomp-Tukker, G. W. Barendsen, and J. B. A. Kipp. Hyperthermia and incorporation of halogenated pyrimidines: radiosensitization in cultured rodent and humor tumor cells. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 39:489–496, 1997.
Cassim, S., A. Giustini, A. Petryk, R. Strawbridge, and P. Hoopes. In: Iron oxide nanoparticle hyperthermia and radiation cancer treatment, SPIE BiOS: Biomedical Optics, International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp. 71810O–71810O-8, 2009.
Davis, M. E. Glioblastoma: overview of disease and treatment. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 20(5):S2–S8, 2016.
Dilnawaz, F., A. Singh, C. Mohanty, and S. K. Sahoo. Dual drug loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Biomaterials 31(13):3694–3706, 2010.
Du, J., W.-L. Lu, X. Ying, Y. Liu, P. Du, W. Tian, Y. Men, J. Guo, Y. Zhang, and R.-J. Li. Dual-targeting topotecan liposomes modified with tamoxifen and wheat germ agglutinin significantly improve drug transport across the blood− brain barrier and survival of brain tumor-bearing animals. Mol. Pharm. 6(3):905–917, 2009.
Dubey, N., R. Varshney, J. Shukla, A. Ganeshpurkar, P. P. Hazari, G. P. Bandopadhaya, A. K. Mishra, and P. Trivedi. Synthesis and evaluation of biodegradable PCL/PEG nanoparticles for neuroendocrine tumor targeted delivery of somatostatin analog. Drug Deliv. 19(3):132–142, 2012.
Esmaelbeygi, E., S. Khoei, S. Khoee, and S. Eynali. Role of iron oxide core of polymeric nanoparticles in the thermosensitivity of colon cancer cell line HT-29. Int. J. Hyperthermia 31(5):489–497, 2015.
Feng, Q.-W., Z.-G. Cui, Y.-J. Jin, L. Sun, M.-L. Li, S. A. Zakki, D.-J. Zhou, and H. Inadera. Protective effect of dihydromyricetin on hyperthermia-induced apoptosis in human myelomonocytic lymphoma cells. Apoptosis 24(3):290–300, 2019.
Fu, Y., and W. J. Kao. Drug release kinetics and transport mechanisms of non-degradable and degradable polymeric delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 7(4):429–444, 2010.
Hauser, A. K., M. I. Mitov, E. F. Daley, R. C. McGarry, K. W. Anderson, and J. Z. Hilt. Targeted iron oxide nanoparticles for the enhancement of radiation therapy. Biomaterials 105:127–135, 2016.
Hegi, M. E., A.-C. Diserens, T. Gorlia, M.-F. Hamou, N. De Tribolet, M. Weller, J. M. Kros, J. A. Hainfellner, W. Mason, and L. Mariani. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 352(10):997–1003, 2005.
Iliakis, G., and S. Kurtzman. Keynote address: application of non-hypoxic cell sensitizers in radiobiology and radiotherapy: rationale and future prospects. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 16(5):1235–1241, 1989.
Jordan, A., P. Wust, R. Scholz, B. Tesche, H. Fähling, T. Mitrovics, T. Vogl, J. Cervos-Navarro, and R. Felix. Cellular uptake of magnetic fluid particles and their effects on human adenocarcinoma cells exposed to AC magnetic fields in vitro. Int. J. Hyperthermia 12(6):705–722, 1996.
Kargar, S., S. Khoei, S. Khoee, S. Shirvalilou, and S. R. Mahdavi. Evaluation of the combined effect of NIR laser and ionizing radiation on cellular damages induced by IUdR-loaded PLGA-coated Nano-graphene oxide. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 21:91–97, 2018.
Kato, T. A., A. Tsuda, M. Uesaka, A. Fujimori, T. Kamada, H. Tsujii, and R. Okayasu. In vitro characterization of cells derived from chordoma cell line U-CH1 following treatment with X-rays, heavy ions and chemotherapeutic drugs. Radiat. Oncol. 6(1):1–9, 2011.
Khoei, S., S. Delfan, A. Neshasteh-Riz, and S. R. Mahdavi. Evaluation of the combined effect of 2ME2 and 60Co on the inducement of DNA damage by IUdR in a spheroid model of the U87MG glioblastoma cancer cell line using alkaline comet assay. Cell J. 13(2):83, 2011.
Kim, W., H. Youn, S. Lee, E. Kim, D. Kim, J. S. Lee, J.-M. Lee, and B. Youn. RNF138-mediated ubiquitination of rpS3 is required for resistance of glioblastoma cells to radiation-induced apoptosis. Exp. Mol. Med. 50(1):2018.
Kutikov, A. B., and J. Song. Biodegradable PEG-based amphiphilic block copolymers for tissue engineering applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 1(7):463–480, 2015.
Laurent, S., S. Dutz, U. O. Häfeli, and M. Mahmoudi. Magnetic fluid hyperthermia: focus on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 166(1):8–23, 2011.
Man, J., J. D. Shoemake, T. Ma, A. E. Rizzo, A. R. Godley, Q. Wu, A. M. Mohammadi, S. Bao, J. N. Rich, and S. Y. Jennifer. Hyperthermia sensitizes glioma stem-like cells to radiation by inhibiting AKT signaling. Cancer Res. 75(8):1760–1769, 2015.
Mohammadi, S., S. Khoei, and S. R. Mahdavi. The combination effect of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) coated iron oxide nanoparticles as 5-fluorouracil carrier and X-ray on the level of DNA damages in the DU 145 human prostate carcinoma cell line. J. Bionanosci. 6(1):23–27, 2012.
Nazli, C., T. I. Ergenc, Y. Yar, H. Y. Acar, and S. Kizilel. RGDS-functionalized polyethylene glycol hydrogel-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles enhance specific intracellular uptake by HeLa cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 7:1903–1920, 2012.
Neshasteh-Riz, A., W. Angerson, J. Reeves, G. Smith, R. Rampling, and R. Mairs. Incorporation of iododeoxyuridine in multicellular glioma spheroids: implications for DNA-targeted radiotherapy using Auger electron emitters. Br. J. Cancer 75(4):493, 1997.
Oghabian, M. A., M. Jeddi-Tehrani, A. Zolfaghari, F. Shamsipour, S. Khoei, and S. Amanpour. Detectability of Her2 positive tumors using monoclonal antibody conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles in MRI. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11(6):5340–5344, 2011.
Rajaee, Z., S. Khoei, S. R. Mahdavi, M. Ebrahimi, S. Shirvalilou, and A. Mahdavian. Evaluation of the effect of hyperthermia and electron radiation on prostate cancer stem cells. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 57(2):133–142, 2018.
Rajaee, Z., S. Khoei, A. Mahdavian, S. Shirvalilou, S. R. Mahdavi, and M. Ebrahimi. Radio-thermo-sensitivity induced by gold magnetic nanoparticles in the monolayer culture of human prostate carcinoma cell line DU145. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 20(3):315–324, 2020.
Rezaie, P., S. Khoei, S. Khoee, S. Shirvalilou, and S. R. Mahdavi. Evaluation of combined effect of hyperthermia and ionizing radiation on cytotoxic damages induced by IUdR-loaded PCL-PEG-coated magnetic nanoparticles in spheroid culture of U87MG glioblastoma cell line. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 94(11):1027–1037, 2018.
Sanz, B., M. P. Calatayud, T. E. Torres, M. L. Fanarraga, M. R. Ibarra, and G. F. Goya. Magnetic hyperthermia enhances cell toxicity with respect to exogenous heating. Biomaterials 114:62–70, 2017.
Shand, N., F. Weber, L. Mariani, M. Bernstein, A. Gianella-Borradori, Z. A. Long, A. Sorensen, and N. Barbier. A phase 1-2 clinical trial of gene therapy for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme by tumor transduction with the herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene followed by ganciclovir. Hum. Gene Ther. 10(14):2325–2335, 1999.
Shirvalilou, S., S. Khoei, A. J. Esfahani, M. Kamali, M. Shirvaliloo, R. Sheervalilou, and P. Mirzaghavami. Magnetic hyperthermia as an adjuvant cancer therapy in combination with radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for recurrent/progressive glioblastoma: a systematic review. J. Neuro-Oncol. 1–10, 2021.
Shirvalilou, S., S. Khoei, S. Khoee, N. J. Raoufi, M. R. Karimi, and A. Shakeri-Zadeh. Development of a magnetic nano-graphene oxide Carrier for improved glioma-targeted drug delivery and imaging: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. Chemico-Biol. Interact. 295:97–108, 2018.
Stupp, R., W. P. Mason, M. J. Van Den Bent, M. Weller, B. Fisher, M. J. Taphoorn, K. Belanger, A. A. Brandes, C. Marosi, and U. Bogdahn. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 352(10):987–996, 2005.
Sun, L., Z.-G. Cui, S. A. Zakki, Q.-W. Feng, M.-L. Li, and H. Inadera. Mechanistic study of nonivamide enhancement of hyperthermia-induced apoptosis in U937 cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 120:147–159, 2018.
Taylor, U., S. Klein, S. Petersen, W. Kues, S. Barcikowski, and D. Rath. Nonendosomal cellular uptake of ligand-free, positively charged gold nanoparticles. Cytometry Part A 77(5):439–446, 2010.
Ulery, B. D., L. S. Nair, and C. T. Laurencin. Biomedical applications of biodegradable polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B 49(12):832–864, 2011.
Van Tellingen, O., B. Yetkin-Arik, M. De Gooijer, P. Wesseling, T. Wurdinger, and H. de Vries. Overcoming the blood–brain tumor barrier for effective glioblastoma treatment. Drug Resist. Updates 19:1–12, 2015.
Xu, H., and Y. Pan. Experimental evaluation on the heating efficiency of magnetoferritin nanoparticles in an alternating magnetic field. Nanomaterials 9(10):1457, 2019.
Yi, G.-Q., B. Gu, and L.-K. Chen. The safety and efficacy of magnetic nano-iron hyperthermia therapy on rat brain glioma. Tumor Biol. 35(3):2445–2449, 2014.
Yuan, X., C. Fahlman, K. Tabassi, and J. A. Williams. Synthetic, implantable, biodegradable polymers for controlled release of radiosensitizers. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 14(3):177–186, 1999.
Zheng, S., X. Gao, X. Liu, T. Yu, T. Zheng, Y. Wang, and C. You. Biodegradable micelles enhance the antiglioma activity of curcumin in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 11:2721, 2016.
Acknowledgments
We thank Pasteur Institute of Iran for providing U87MG cells. The Radiotherapy Centre of Asia Hospital is acknowledged for providing training and equipment for Radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
No human studies were carried out by the author for this article. No animal studies were carried out by the authors for this article.
Funding
This work was supported by Grant No. 25052 from the School of Medicine of Iran University of Medical Sciences (IUMS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Associate Editor Pinar Zorlutuna oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoei, S., Hosseini, V., Hosseini, M. et al. Enhancement of Radio-Thermo-Sensitivity of 5-Iodo-2-Deoxyuridine-Loaded Polymeric-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles Triggers Apoptosis in U87MG Human Glioblastoma Cancer Cell Line. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 14, 365–377 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-021-00675-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-021-00675-y