Abstract
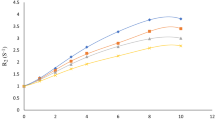
We investigated the effect of magnesium chloride (MgCl2) on the nuclear magnetic resonance dose–response of polyacrylamide-type (PAGAT, NIPAM, and VIPET) gel dosimeters containing acrylamide, N-isopropylacrylamide, and N-vinylpyrrolidone as a monomer, respectively. The dose-transverse relaxation rates (1/T2 = R2) obtained from magnetic resonance imaging data revealed that a substantial increase in the dose–R2 response occurred as the concentration of MgCl2 in the gel dosimeters increased. The sensitivity of the PAGAT gel with 1.0 M MgCl2 was found to be approximately one order higher than that of the same gel without MgCl2. In addition, the water equivalences of the gels with MgCl2 were evaluated over a wide range of photon energies. The results indicated that MgCl2 acts as a powerful sensitizer to radiation-induced free-radical polymerization in polyacrylamide-type gel dosimeters, but does not interfere with the desirable properties of basic polyacrylamide-type gel dosimeters (i.e., the dose rate and dose integration).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibbott GS. Clinical applications of gel dosimeters. J Phys Conf Ser. 2006;56:108–31.
Maryanski MJ, Gore JC, Kennan RP, Schulz RJ. NMR relaxation enhancement in gels polymerized and cross-linked by ionizing radiation: a new approach to 3D dosimetry by MRI. Magn Reson Imaging. 1993;11:253–8.
Maryanski MJ, Zastavker YZ, Gore JC. Radiation dose distributions in three dimensions from tomographic optical density scanning of polymer gels: II. Optical properties of the BANG polymer gel. Phys Med Biol. 1996;41:2705–17.
Hilts M, Audet C, Duzenli C, Jirasek A. Polymer gel dosimetry using X-ray computed tomography: a feasibility study. Phys Med Biol. 2000;44:2559–71.
Baldock C, De Deene Y, Doran S, Ibbott G, Jirasek A, Lepage M, McAuley KB, Oldham M, Schreiner LJ. Polymer gel dosimetry. Phys Med Biol. 2010;55:R1–63.
De Deene Y, Vergote K, Claeys C, De Wagter C. The fundamental radiation properties of normoxic polymer gel dosimeters: a comparison between a methacrylic acid based gel and acrylamide based gels. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51:653–73.
Karlsson A, Gustavsson H, Månsson S, McAuley KB, Bäck SÅJ. Dose integration characteristics in normoxic polymer gel dosimetry investigated using sequential beam irradiation. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52:4697–706.
Koeva VI, Olding T, Jirasek A, Schreiner LJ, McAuley KB. Preliminary investigation of the NMR, optical and X-ray CT dose-response of polymer gel dosimeters incorporating cosolvents to improve dose sensitivity. Phys Med Biol. 2009;54:2779–90.
Jirasek A, Hilts M, McAuley KB. Polymer gel dosimeters with enhanced sensitivity for use in X-ray CT polymer gel dosimetry. Phys Med Biol. 2010;55:5269–281.
Kozicki M, Jaszczak M, Maras P, Dudek M, Cłapa M. On the development of a VIPARnd radiotherapy 3D polymer gel dosimeter. Phys Med Biol. 2017;62:986–1008.
Chain JNM, Jirasek A, Schreiner LJ, McAuley KB. Cosolvent-free polymer gel dosimeters with improved dose sensitivity and resolution for X-ray CT dose response. Phys Med Biol. 2011;56:2091–102.
Hayashi S, Fujiwara F, Usui S, Tominaga T. Effect of inorganic salt on the dose sensitivity of polymer gel dosimeter. Radiat Phys Chem. 2012;81:884–8.
Kolokolkina NV, Penenzhik MA, Virnik AD, Martynenko AI, Yanovskii YG, Topchiev DA, Kabanov VA. Effect of inorganic salts on reaction rate in high-conversion polymerization of N-trimethylammoniumethyl methacrylate methyl sulphate in aqueous solutions. Polym Sci USSR. 1986;28:166–70.
Hayashi S, Kawamura H, Usui S, Tominaga T. Comparison of the influence of inorganic salts on the NMR dose sensitivity of polyacrylamide-based gel dosimeter. J Phys Conf Ser. 2013;444:012094.
Venning AJ, Hill B, Brindha S, Healy BJ, Baldock C. Investigation of the PAGAT polymer gel dosimeter using magnetic resonance imaging. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50:3875–88.
Senden RJ, De Jean P, McAuley KB, Schreiner LJ. Polymer gel dosimeters with reduced toxicity: a preliminary investigation of the NMR and optical dose–response using different monomers. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51:3301–14.
Papadakis AE, Maris TG, Zacharopoulou F, Pappas E, Zacharakis G, Damilakis J. An evaluation of the dosimetric performance characteristics of N-vinylpyrrolidone-based polymer gels. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52:5069–83.
Pavoni JF, Baffa O. An evaluation of dosimetric characteristics of MAGIC gel modified by adding formaldehyde-MAGIC-f. Radiat Meas. 2012;47:1074–82.
Berger MJ, Hubbell JH, Seltzer SM, Chang J, Coursey JS, Sukumar R, Zucker DS, Olsen K. XCOM: photon cross sections database, web ver. 1.5. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg; 2010. http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/xcom/index.cfm. Accessed 3 Jan 2018.
Taylor ML, Smith RL, Dossing F, Franich RD. Robust calculation of effective atomic numbers: the Auto-Z eff software. Med Phys. 2012;39:1769–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies performed with human or animal participants.
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, Si., Kawamura, H., Usui, S. et al. Influence of magnesium chloride on the dose–response of polyacrylamide-type gel dosimeters. Radiol Phys Technol 11, 375–381 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-018-0473-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-018-0473-2