Abstract
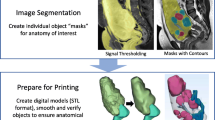
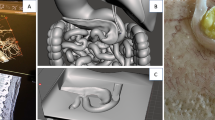
We propose an approach to supporting pre-surgical planning for the uterus by integrating medical image analysis and physical model generation based on 3D printing. With our method, we first segment the patient-specific anatomy and lesions of the uterus on MR images; then, we create a 3D physical model, an exact replica of the patient’s uterus in terms of size and softness, with transparency for easy observation of the internal structures of the uterus. In our experiments, we created pre-surgical models of hysterectomy for five patients who had been diagnosed to have uterine endometrial cancer. An experienced radiologist, the surgeons, and all of the patients cooperated in our experiment for carrying out subjective evaluations of the usefulness of our model. The accuracy of the physical models was evaluated quantitatively by comparison between the MR images of the patients and the CT images of the models. The results showed that the mean values of the errors in gap ranged from 1.19 to 2.22 mm, which was satisfactory for the surgeons. The feedback from both surgeons and patients demonstrated the usefulness and convenience of the models for efficient patient explanation understanding and pre-surgical planning by surgeons.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sue W, Sarah S-B. Radiological appearances of uterine fibroids. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2009;19(3):222–31.
Fallahi A, Pooyan M, Ghanaati H, Oghabian MA, Khotanlou H, Shakiba M, et al. Uterine segmentation and volume measurement in uterine fibroid patients MRI using fuzzy C-Mean algorithm and morphological operations. Iran J Radiol. 2011;8(3):150–6.
Aluwee SAZBS, Kato H, Zhou X, Hara T, Fujita H, Kanematsu M, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of uterine fibroids: a preliminary investigation into the usefulness of 3D-rendered images for surgical planning. SpringerPlus. 2015;4(1):384.
Preece D, Williams SB, Lam R, Weller R. “Let’s Get Physical”: advantages of a physical model over 3D computer models and textbooks in learning imaging anatomy. Anat Sci Educ. 2013;6(4):216–24.
Nolden M, Zelzer S, Seitel A, Wald D, Müller M, Franz AM, et al. The medical imaging interaction toolkit: challenges and advances: 10 years of open-source development. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2013;8(4):607–20.
Lorensen WE, Cline HE. Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. Comput Graphics. 1987;21(4):163–9.
Ploch CC, Mansi CSSA, Jayamohan J, Kuhl E. Using 3D printing to create personalized brain models for neurosurgical training and preoperative planning. World Neurosurg. 2016;90:668–74.
Stein D, Fritzsche KH, Nolden M, Meinzer HP, Wolf I. The extensible open-source rigid and affine image registration module of the Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit (MITK). Comput Methods Progr Biomed. 2010;100(1):79–86.
Olszewski R, Szymor P, Kozakiewicz M. Accuracy of three-dimensional, paper-based models generated using a low-cost, three-dimensional printer. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg. 2014;42(8):1847–52.
Naftulin JS, Kimchi EY, Cash SS. Streamlined, inexpensive 3D printing of the brain and skull. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(8):e0136198.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank members of the Fujita Laboratory and K. Miyaki from Exseal Corporation, Japan, for supplying the casting materials. This research was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (Grant No. 26108005), in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Grant No. C26330134), Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan, and a research grant of Graduate School of Medicine at Gifu University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Statement of human rights and informed consent
This study was approved by the human research committee of the institutional review board and complied with the guidelines of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1999. Written informed consent was obtained, from the five patients with endometrial cancer.
About this article
Cite this article
Sayed Aluwee, S.A.Z.B., Zhou, X., Kato, H. et al. Evaluation of pre-surgical models for uterine surgery by use of three-dimensional printing and mold casting. Radiol Phys Technol 10, 279–285 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-017-0397-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-017-0397-2