Abstract
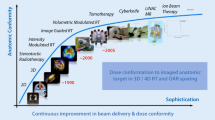
Image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) is in the midst of a strong development and implementation cycle, stimulated by pioneering work performed in Japan. We present a review of the rationale, technology, and methodology of image guidance, as well as an overview of current work in IGRT at the Massachusetts General Hospital. The technology is rapidly evolving, and synergisms between the various acquisition approaches are converging to provide unparalleled information on target and normal tissue location and motion. With these new approaches to patient localization, we expect improved clinical results to be forthcoming.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawson LA, Jaffray DA. Advances in image-guided radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(8):938–46.
Dawson LA, et al. Accuracy of daily image guidance for hypofractionated liver radiotherapy with active breathing control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62(4):1247–52.
Balter JM, et al. Daily targeting of intrahepatic tumors for radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;52(1):266–71.
Hong TS, et al. The impact of daily setup variations on head-and-neck intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61(3):779–88.
De Crevoisier R, et al. Increased risk of biochemical and local failure in patients with distended rectum on the planning CT for prostate cancer radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62(4):965–73.
Ghilezan M, et al. Online image-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: How much improvement can we expect? A theoretical assessment of clinical benefits and potential dose escalation by improving precision and accuracy of radiation delivery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;60(5):1602–10.
Martinez AA, et al. Improvement in dose escalation using the process of adaptive radiotherapy combined with three-dimensional conformal or intensity-modulated beams for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;50(5):1226–34.
Millender LE, et al. Daily electronic portal imaging for morbidly obese men undergoing radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59(1):6–10.
Barker JL Jr, et al. Quantification of volumetric and geometric changes occurring during fractionated radiotherapy for head-and-neck cancer using an integrated CT/linear accelerator system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59(4):960–70.
Sonke JJ, Lebesque J, Van Herk M. Variability of four-dimensional computed tomography patient models. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70(2):590–8.
Engelsman M, et al. How much margin reduction is possible through gating or breath hold? Phys Med Biol. 2005;50(3):477–90.
Dawson LA, Sharpe MB. Image-guided radiotherapy: rationale, benefits, and limitations. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:848–58.
White E, Kane G. Radiation medicine practice in the image-guided radiation therapy era: new roles and new opportunities. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(4):298–305.
Verellen D, De Ridder M, Storme G. A (short) history of image-guided radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2008;86(1):4–13.
Gragoudas ES, et al. Proton irradiation of malignant melanoma of the ciliary body. Br J Ophthalmol. 1979;63(2):135–9.
Verhey LJ, et al. Precise positioning of patients for radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982;8(2):289–94.
Biggs PJ, Goitein M, Russell MD. A diagnostic X ray field verification device for a 10 MV linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985;11(3):635–43.
Shirato H, et al. Physical aspects of a real-time tumor-tracking system for gated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48(4):1187–95.
Britton K, et al. Evaluation of inter-and intrafraction organ motion during IMRT for localized prostate cancer measured by a newly developed on-board image-guided system. Radiat Med. 2005;23(1):14–24.
Uematsu M, et al. A dual computed tomography linear accelerator unit for stereotactic radiation therapy: a new approach without cranially fixated stereotactic frames. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;35(3):587–92.
Balter JM, Kessler ML. Imaging and alignment for image-guided radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(8):931–7.
Guha C, et al. Tumor biology-guided radiotherapy treatment planning: gross tumor volume versus functional tumor volume. Semin Nucl Med. 2008;38(2):105–13.
Heron DE, et al. PET-CT in radiation oncology—the impact on diagnosis, treatment planning, and assessment of treatment response. Am J Clin Oncol-Cancer Clin Trials. 2008;31(4):352–62.
Li G, et al. Advances in 4D medical imaging and 4D radiation therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2008;7(1):67–81.
Zanzonico P. PET-based biological imaging for radiation therapy treatment planning. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2006;16(1):61–101.
Zapotoczna A, et al. Current role and future perspectives of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in radiation oncology for prostate cancer. Neoplasia. 2007;9(6):455–63.
Achterberg N, Muller RG. Multibeam tomotherapy: a new treatment unit devised for multileaf collimation, intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Med Phys. 2007;34(10):3926–42.
Beavis AW. Is tomotherapy the future of IMRT? Br J Radiol. 2004;77(916):285–95.
Jaffray D, et al. Review of image-guided radiation therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2007;7(1):89–103.
Webb S. The physical basis of IMRT and inverse planning. Br J Radiol. 2003;76(910):678–89.
Xing L, et al. Overview of image-guided radiation therapy. Med Dosim. 2006;31(2):91–112.
Chang JY, et al. Image-guided radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3(2):177–86.
Devisetty K, Chen LF, Chmura SJ. Evolving use of radiotherapy and radiosurgery in the treatment of pituitary adenomas. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2006;6(9):S93–8.
Drummond KJ, Zhu JJG, Black PM. Meningiomas: updating basic science, management, and outcome. Neurologist. 2004;10(3):113–30.
Fennessy FM, et al. MR imaging—guided interventions in the genitourinary tract: an evolving concept. Radiol Clin North Am. 2008;46(1):149–66.
Kurtz JM, Kinkel K. Breast conservation in the 21st century. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36(15):1919–24.
Langer CJ, et al. Cooperative group portfolio in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Are we making progress? Clin Lung Cancer. 2008;9(2):85–91.
Lefkopoulos D, et al. Present and future of the Image Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT) and its applications in lung cancer treatment. Cancer Radiother. 2007;11(1–2):23–31.
Lohr F, et al. Image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Aktuelle Urologie. 2007;38(5):386–91.
Park C, Zhang G, Choy H. 4-Dimensional conformal radiation therapy: image-guided radiation therapy and its application in lung cancer treatment. Clin Lung Cancer. 2006;8(3):187–94.
Timmerman RD, Forster KM, Cho LC. Extracranial stereotactic radiation delivery. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2005;15(3):202–7.
Vogelbaum MA, Suh JH. Resectable brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(8):1289–94.
Yamada Y, Lovelock DM, Bilsky MH. A review of image-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for spinal tumors. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(2):226–35.
Yamada Y, et al. Multifractionated image-guided and stereotactic intensity-modulated radiotherapy of paraspinal tumors: a preliminary report. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62(1):53–61.
Yamada Y, Lovelock M, Bilsky MH. Image-guided intensity-modulated radiation therapy of spine tumors. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2006;6(3):207–11.
Bortfeld T, Chen G. Introduction: intrafractional organ motion and its management. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004;14(1):1.
Jaffray D. Image-guided radiation therapy: from concept to practice. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(4):243–306.
Kessler M. Image registration and data fusion in radiation therapy. Br J Radiol. 2006;79:S99–108.
Swerdloff S. Data handling in radiation therapy in the age of image-guided radiation therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(5):287–92.
Berbeco RI, et al. Integrated radiotherapy imaging system (IRIS): design considerations of tumour tracking with linac gantry-mounted diagnostic X-ray systems with flat-panel detectors. Phys Med Biol. 2004;49(2):243–55.
Pouliot J, et al. Low-dose megavoltage cone-beam CT for radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61(2):552–60.
Pouliot J. Megavoltage imaging, megavoltage cone beam CT and dose-guided radiation therapy. Front Radiat Ther Oncol. 2007;40:132–42.
Mackie TR, et al. Image guidance for precise conformal radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;56(1):89–105.
Berbeco RI, et al. Clinical feasibility of using an epid in cine mode for image-guided verification of stereotactic body radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69(1):258–66.
Mackie TR. History of tomotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51(13):R427–53.
Raaymakers B, et al. Integrating a MRI scanner with a 6 MV radiotehrapy accelerator. Phys Med Biol. 2007;49:4109–18.
Dempsey JF. http://www.viewray.com, cited 2008.
Balter JM, Cao Y. Advanced technologies in image-guided radiation therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(4):293–7.
Lee SW, et al. Clinical assessment and characterization of a dual-tube kilovoltage X-ray localization system in the radiotherapy treatment room. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2008;9(1):1–15.
Jin JY, et al. Evaluation of residual patient position variation for spinal radiosurgery using the Novalis image guided system. Med Phys. 2008;35(3):1087–93.
Teh BS, et al. Versatility of the novalis system to deliver image-guided stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for various anatomical sites. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2007;6(4):347–54.
Ernst-Stecken A, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy to the rat hippocampus—determination of dose response and tolerance. Strahlentherapie Und Onkologie. 2007;183(8):440–6.
Soete G, et al. X-ray-assisted positioning of patients treated by conformal arc radiotherapy for prostate cancer: comparison of setup accuracy using implanted markers versus bony structures. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67(3):823–7.
Verellen D, et al. Breathing-synchronized irradiation using stereoscopic KV-imaging to limit influence of interplay between leaf motion and organ motion in 3D-CRT and IMRT: dosimetric verification and first clinical experience. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(4):S108–19.
Wurm RE, et al. Image guided respiratory gated hypofractionated Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (H-SBRT) for liver and lung tumors: initial experience. Acta Oncologica. 2006;45(7):881–9.
Yan H, Yin FF, Kim JH. A phantom study on the positioning accuracy of the Novalis Body system. Med Phys. 2003;30(12):3052–60.
Watchman CJ, et al. Patient positioning using implanted gold markers with the novalis body system in the thoracic spine. Neurosurgery. 2008;62(5 Suppl):A62–8 (discussion A68).
Fuller CD, et al. Method comparison of ultrasound and kilovoltage X-ray fiducial marker imaging for prostate radiotherapy targeting. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51(19):4981–93.
Ryu SI, et al. Image-guided hypo-fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery to spinal lesions. Neurosurgery. 2001;49(4):838–46.
Seppenwoolde Y, et al. Accuracy of tumor motion compensation algorithm from a robotic respiratory tracking system: a simulation study. Med Phys. 2007;34(7):2774–84.
Shiu AS, et al. Near simultaneous computed tomography image-guided stereotactic spinal radiotherapy: an emerging paradigm for achieving true stereotaxy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;57(3):605–13.
Amies C, et al. A multi-platform approach to image guided radiation therapy (IGRT). Med Dosim. 2006;31(1):12–9.
Charlie CM, Paskalev K. In-room CT techniques for image-guided radiation therapy. Med Dosim. 2006;31(1):30–9.
Wong JR, et al. Image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer by CT–linear accelerator combination: prostate movements and dosimetric considerations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61(2):561–9.
Ma CM, Paskalev K. In-room CT techniques for image-guided radiation therapy. Med Dosim. 2006;31(1):30–9.
Thieke C, et al. Kilovoltage CT using a linac–CT scanner combination. Br J Radiol. 2006;79(Spec No 1):S79–86.
Lattanzi J, et al. Ultrasound-based stereotactic guidance in prostate cancer—quantification of organ motion and set-up errors in external beam radiation therapy. Comput Aided Surg. 2000;5(4):289–95.
Boda-Heggemann J, et al. Accuracy of ultrasound-based (BAT) prostate-repositioning: a three-dimensional on-line fiducial-based assessment with cone-beam computed tomography. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70(4):1247–55.
Roeske JC, et al. Evaluation of changes in the size and location of the prostate, seminal vesicles, bladder, and rectum during a course of external beam radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;33(5):1321–9.
Beard CJ, et al. Analysis of prostate and seminal vesicle motion: implications for treatment planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;34(2):451–8.
Melian E, et al. Variation in prostate position quantitation and implications for three-dimensional conformal treatment planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;38(1):73–81.
Langen KM, et al. Evaluation of ultrasound-based prostate localization for image-guided radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;57(3):635–44.
Cury F, et al. Ultrasound-based image guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer—comparison of cross modality and intramodlaity methods for daily localization during external beam radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(5):1562–7.
Bert C, et al. Clinical experience with a 3D surface patient setup system for alignment of partial-breast irradiation patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;64(4):1265–74.
Bert C, et al. A phantom evaluation of a stereo-vision surface imaging system for radiotherapy patient setup. Med Phys. 2005;32(9):2753–62.
Willoughby TR, et al. Target localization and real-time tracking using the Calypso 4D localization system in patients with localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65(2):528–34.
Litzenberg DW, et al. Positional stability of electromagnetic transponders used for prostate localization and continuous, real-time tracking. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68(4):1199–206.
Langen KM, et al. Observations on real-time prostate gland motion using electromagnetic tracking. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71(4):1084–90.
Kupelian P, et al. Multi-institutional clinical experience with the Calypso System in localization and continuous, real-time monitoring of the prostate gland during external radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67(4):1088–98.
Bissonnette JP. Quality assurance of image-guidance technologies. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(4):278–86.
Herman MG, et al. Clinical use of electronic portal imaging: report of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 58. Med Phys. 2001;28(5):712–37.
Kutcher GJ, et al. Comprehensive QA for radiation oncology: report of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 40. Med Phys. 1994;21(4):581–618.
Mutic S, et al. Quality assurance for computed-tomography simulators and the computed-tomography-simulation process: report of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 66. Med Phys. 2003;30(10):2762–92.
Yoo S, et al. A quality assurance program for the on-board imagers. Med Phys. 2006;33(11):4431–47.
van Herk M. Different styles of image-guided radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(4):258–67.
de Boer H, BJM H. eNAL: an extension of the NAL setup correction protocol for effective use of weekly follow-up measurements. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67(5):1586–95.
West JB, et al. Fiducial point placement and the accuracy of point-based, rigid body registration. Neurosurgery. 2001;48(4):810–6 (discussion 816–7).
Fitzpatrick JM, West JB, Maurer CR Jr. Predicting error in rigid-body point-based registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1998;17(5):694–702.
Gierga DP, et al. Comparison of target registration errors for multiple image-guided techniques in accelerated partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70(4):1239–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G.T.Y., Sharp, G.C. & Mori, S. A review of image-guided radiotherapy. Radiol Phys Technol 2, 1–12 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-008-0045-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-008-0045-y