Abstract
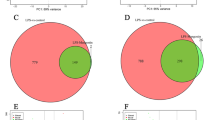
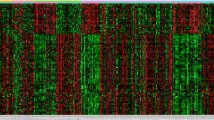
Stress-induced gastric ulcer is one of the common complications affecting patients after trauma, mainly leading to gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, and severe cases may be life-threatening. However, the molecular mechanism of stress-induced gastric ulcer remains unclear. In the present study, RNA-sequencing was performed on gastric tissues of normal rats (C), stress-induced gastric ulcer rats (T0), and rats recovered from gastric ulcer for 3 days (T3), and bioinformatics analysis was performed to determine changes in gene expression and biological pathways. The protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were constructed by STRING and visualized by the Cytoscape software. The associated transcriptional factor (TFs)–gene regulatory network of the hub DEGs was also constructed. Pairwise comparisons obtained 103 (T0_C), 127 (T3_T0), and 13 (T3_C) DEGs, respectively. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis indicated DEGs in T0_C and T3_T0 were significantly enriched in response to oxygen-containing compound, response to organic substance, and response to external stimulus. Pathway analysis suggested that DEGs were enriched in TNF signaling pathway, PPAR signaling pathway, apoptosis, and IL-17 signaling pathway. Seven hub genes (Fos, Jun, Nfkbia, Dusp1, Pim3, Junb, and Fosb) were obtained from the PPI networks of T0_C and T3_T0. Key TFs with close interactions, such as Fos, Jun, Nfkbia, Junb, Egr1, and Fosb, were screened This study used RNA-sequencing and bioinformatics analysis to screen out genes associated with gastric ulcer, which can help reveal the molecular mechanism of gastric ulcer development and restoration, and provide reference for the treatment of human gastric ulcers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelwahab SI (2013) Protective mechanism of gallic acid and its novel derivative against ethanol-induced gastric ulcerogenesis: involvement of immunomodulation markers, Hsp70 and Bcl-2-associated X protein. Int Immunopharmacol 16:296–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2013.04.005
Adachi M, Horiuchi G, Ikematsu N, Tanaka T, Terao J, Satouchi K, Tokumura A (2011) Intragastrically administered lysophosphatidic acids protect against gastric ulcer in rats under water-immersion restraint stress. Dig Dis Sci 56:2252–2261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1595-0
Al Moutaery M, Al Rayes H, Al Swailam R, Elfaki I, Khan HA, Arshaduddin M, Tariq M (2012) Protective effect of a cysteine prodrug and antioxidant, L-2-oxothiazolidine-4-carboxylate, against ethanol-induced gastric lesions in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:233–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2010.08.012
Almasaudi SB, El-Shitany NA, Abbas AT, Abdel-dayem UA, Ali SS, Al Jaouni SK, Harakeh S (2016) Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiulcer potential of manuka honey against gastric ulcer in rats. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:3643824. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3643824
Arab HH, Salama SA, Omar HA, el SA A, Maghrabi IA (2015) Diosmin protects against ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats: novel anti-ulcer actions. PLoS One 10:e0122417. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122417
Aziz RS, Siddiqua A, Shahzad M, Shabbir A, Naseem N (2019) Oxyresveratrol ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric ulcer via downregulation of IL-6, TNF-alpha, NF-kB, and COX-2 levels, and upregulation of TFF-2 levels. Biomed Pharmacother 110:554–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.002
Beregovyi SM, Chervinska TM, Dranitsina AS, Szabo S, Tolstanova GM (2015) Redox-sensitive transcription factors Egr-1 and Sp-1 in the pathogenesis of experimental gastric ulcer. Ukrainian Biochemical Journal 87:70–77
Castro GA, Carvalho JE, Tinti SV, Possenti A, Sgarbieri VC (2010) Anti-ulcerogenic effect of a whey protein isolate and collagen hydrolysates against ethanol ulcerative lesions on oral administration to rats. J Med Food 13:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2008.0277
Chai J, Baatar D, Tarnawski A (2004) Serum response factor promotes re-epithelialization and muscular structure restoration during gastric ulcer healing. Gastroenterology 126:1809–1818. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2004.03.021
Choi HS et al (2013) The effect of polaprezinc on gastric mucosal protection in rats with ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage: comparison study with rebamipide. Life Sci 93:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2013.05.019
El-Maraghy SA, Rizk SM, Shahin NN (2015) Gastroprotective effect of crocin in ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats. Chem Biol Interact 229:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2015.01.015
Elshazly SM, Abd El Motteleb DM, Ibrahim I (2018) Hesperidin protects against stress induced gastric ulcer through regulation of peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma in diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact 291:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.06.027
Gong SN, Zhu JP, Ma YJ, Zhao DQ (2019) Proteomics of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus of rats with stress-induced gastric ulcer. World J Gastroenterol 25:2911–2923. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i23.2911
Granholm A et al (2019) Predictors of gastrointestinal bleeding in adult ICU patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med 45:1347–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-019-05751-6
Kawanaka H, Tomikawa M, Jones MK, Pai R, Szabo IL, Sugimachi K, Sarfeh IJ, Tarnawski AS (2001) Portal hypertensive gastric mucosa has reduced activation of MAP kinase (ERK2) in response to alcohol injury: a key to impaired healing? FASEB J 15:574–576. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.00-0450fje
Lee KH, Kim JR (2012) Regulation of HGF-mediated cell proliferation and invasion through NF-kappaB, JunB, and MMP-9 cascades in stomach cancer cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 29:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-011-9449-x
Leng H et al. (2019) Regulation of stress-induced gastric ulcers via central oxytocin and a potential mechanism through the VTA-NAc dopamine pathway. Neurogastroenterol Motil : the official journal of the European Gastrointestinal Motility Society:e13655 https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13655
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Luiz-Ferreira A et al (2012) Healing, antioxidant and cytoprotective properties of Indigofera truxillensis in different models of gastric ulcer in rats. Int J Mol Sci 13:14973–14991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114973
Nguyen T, Chai J, Li A, Akahoshi T, Tanigawa T, Tarnawski AS (2007) Novel roles of local insulin-like growth factor-1 activation in gastric ulcer healing: promotes actin polymerization, cell proliferation, re-epithelialization, and induces cyclooxygenase-2 in a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent manner. Am J Pathol 170:1219–1228
Pillinger MH et al (2007) Helicobacter pylori stimulates gastric epithelial cell MMP-1 secretion via CagA-dependent and -independent ERK activation. J Biol Chem 282:18722–18731. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M703022200
Quan J, Zhou L, Qu J (2015) Knockdown of Pim-3 suppresses the tumorigenicity of glioblastoma by regulating cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 61:42–50
Sato H, Matsui T, Arakawa Y (2002) The protective effect of catechin on gastric mucosal lesions in rats, and its hormonal mechanisms. J Gastroenterol 37:106–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350200004
Sinha K, Sadhukhan P, Saha S, Pal PB, Sil PC (2015) Morin protects gastric mucosa from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, indomethacin induced inflammatory damage and apoptosis by modulating NF-kappaB pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850:769–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.01.008
Tamaddonfard E, Erfanparast A, Farshid AA, Imani M, Mirzakhani N, Salighedar R, Tamaddonfard S (2019) Safranal, a constituent of saffron, exerts gastro-protective effects against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer. Life Sci 224:88–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.054
Tarnawski AS (2005a) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of gastrointestinal ulcer healing. Dig Dis Sci 50:24–33
Tarnawski AS (2005b) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of gastrointestinal ulcer healing. Dig Dis Sci 50(Suppl 1):S24–S33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2803-6
Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A (2012) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial regeneration and neovascularization during healing of gastric and esophageal ulcers. Curr Med Chem 19:16–27
Teng F et al (2018) DUSP1 induces apatinib resistance by activating the MAPK pathway in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep 40:1203–1222. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6520
Trapnell C et al (2010) Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol 28:511–515. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1621
Wang G, Liu G, Ye Y, Fu Y, Zhang X (2019) Bufothionine exerts anti-cancer activities in gastric cancer through Pim3. Life Sci 232:116615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116615
Wu JZ et al (2018) Protective role of beta-patchoulene from Pogostemon cablin against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats: involvement of anti-inflammation and angiogenesis. Phytomedicine 39:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2017.12.024
Yang CA et al (2013) A frequent Toll-like receptor 1 gene polymorphism affects NK- and T-cell IFN-gamma production and is associated with Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric disease. Helicobacter 18:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/hel.12001
Ye YN et al (2001) A mechanistic study of proliferation induced by Angelica sinensis in a normal gastric epithelial cell line. Biochem Pharmacol 61:1439–1448. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(01)00625-6
Zhou G, Soufan O, Ewald J, Hancock REW, Basu N, Xia J (2019) NetworkAnalyst 3.0: a visual analytics platform for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W234–W241. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz240
Zhu W et al (2018) The molecular mechanism and clinical significance of LDHA in HER2-mediated progression of gastric cancer. Am J Transl Res 10:2055–2067
Funding
The study was supported by the Natural science research projects of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (18KJB310001), Programs of Senior Talent Foundation of Jiangsu University (14JDG045 and 12JDG084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pan Huang and Weihong Tang designed and ran the experiment; Rong Shen, Xiaoli Ju, Genbao Shao, and Xiao Xu performed the bioinformatics analysis; Anqi Jiang, Xiaobin Qian, and Miao Chen conducted transcription factor analysis; Zhengrong Zhou and Caifang Ren wrote and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Pan Huang and Weihong Tang contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, P., Tang, W., Shen, R. et al. Analysis of candidate biomarkers and related transcription factors involved in the development and restoration of stress-induced gastric ulcer by transcriptomics. Cell Stress and Chaperones 25, 265–275 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01070-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01070-8