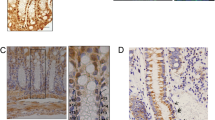
Abstract
To explore possible relationships between mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) polymorphism and the expression levels of stress-responder nuclear genes we assembled five cybrid cell lines by repopulating 143B.TK− cells, depleted of their own mtDNA (Rho0 cells), with foreign mitochondria with different mtDNA sequences (lines H, J, T, U, X). We evaluated, at both basal and under heat stress conditions, gene expression (mRNA) and intra-mitochondrial protein levels of HSP60 and HSP75, two key components in cellular stress response. At basal conditions, the levels of HSP60 and HSP75 mRNA were lower in one cybrid (H) than in the others (p = 0.005 and p = 0.001, respectively). Under stress conditions, the H line over-expressed both genes, so that the inter-cybrid difference was abolished. Moreover, the HSP60 intra-mitochondrial protein levels differed among the cybrid lines (p = 0.001), with levels higher in H than in the other cybrid lines. On the whole, our results provide further experimental evidence that mtDNA variability influences the cell response to stressful conditions by modulating components involved in this response. Sentence summary of the article: the results reported in the present study provide important experimental evidence that in human cells mtDNA variability is able to influence the cellular response to heat stress by modulating both the transcription of genes involved in this response and their intra-mitochondrial protein levels.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- RFLP:
-
restriction fragment length polymorphism
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse-transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
References
Amin J, Ananthan J, Voellmy R (1988) Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol 8:3761–3769
Arya R, Mallik M, Lakhotia SC (2007) Heat shock genes—integrating cell survival and death. J Biosci 32:595–610. doi:10.1007/s12038-007-0059-3
Bai RK, Leal SM, Covarrubias D, Liu A, Wong LJ (2007) Mitochondrial genetic background modifies breast cancer risk. Cancer Res 67:4687–4694. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3554
Baudouin SV, Saunders D, Tiangyou W et al (2005) Mitochondrial DNA and survival after sepsis: a prospective study. Lancet 366:2118–2121. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67890-7
Bellizzi D, Cavalcante P, Taverna D, Rose G, Passarino G, Salvioli S, Franceschi C, De Benedictis G (2006) Gene expression of cytokines and cytokine receptors is modulated by the common variability of the mitochondrial DNA in cybrid cell lines. Genes Cells 11:883–891. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2443.2006.00986.x
Biswas G, Guha M, Avadhani NG (2005) Mitochondria-to-nucleus stress signaling in mammalian cells: nature of nuclear genes targets, transcription regulation, and induced resistance to apoptosis. Gene 354:132–139. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2005.03.028
Carette J, Lehnert S, Chow TY (2002) Implication of PBP74/mortalin/GRP75 in the radio-adaptive response. Int J Radiat Biol 78:183–190. doi:10.1080/09553000110097208
Carrieri G, Bonafè M, De Luca M et al (2001) Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups and APOE4 allele are non-independent variables in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Genet 108:194–198. doi:10.1007/s004390100463
Chandra D, Choy G, Tang DG (2007) Cytosolic accumulation of HSP60 during apoptosis with or without apparent mitochondrial release: evidence that its pro-apoptotic or pro-survival functions involve differential interactions with caspase-3. J Biol Chem 282:31289–31301. doi:10.1074/jbc.M702777200
Cheng MY, Hartl FU, Martin J et al (1989) Mitochondrial heat-shock protein hsp60 is essential for assembly of proteins imported into yeast mitochondria. Nature 337:620–625. doi:10.1038/337620a0
Crispim D, Canani LH, Gross JL, Tschiedel B, Souto KE, Roisenberg I (2006) The European-specific mitochondrial cluster J/T could confer an increased risk of insulin-resistance and type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the m.4216T > C and m.4917A > G variants. Ann Hum Genet 70:488–495. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2005.00249.x
Danielson SR, Carelli V, Tan G, Martinuzzi A, Schapira AH, Savontaus ML, Cortopassi GA (2005) Isolation of transcriptomal changes attributable to LHON mutations and the cybridization process. Brain 128:1026–1037. doi:10.1093/brain/awh447
De Benedictis G, Carrieri G, Garasto S, Rose G, Varcasia O, Bonafè M, Franceschi C, Jazwinski SM (2000) Does a retrograde response in human aging and longevity exist? Exp Gerontol 35:795–801. doi:10.1016/S0531-5565(00)00169-8
Felts SJ, Owen BA, Nguyen P, Trepel J, Donner DB, Toft DO (2000) The hsp90-related protein TRAP1 is a mitochondrial protein with distinct functional properties. J Biol Chem 275:3305–3312. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.5.3305
Frydman J (2001) Folding of newly translated proteins in vivo: the role of molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Biochem 70:603–647. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.603
Habich C, Burkart V (2007) Heat shock protein 60: regulatory role on innate immune cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:742–751. doi:10.1007/s00018-007-6413-7
Hadari YR, Haring HU, Zick Y (1997) p75, a member of the heat shock protein family, undergoes tyrosine phosphorylation in response to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 272:657–662. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.1.657
Hua G, Zhang Q, Fan Z (2007) Heat shock protein 75 (TRAP1) antagonizes reactive oxygen species generation and protects cells from granzyme M-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 282:20553–20560. doi:10.1074/jbc.M703196200
Itoh H, Komatsuda A, Ohtani H et al (2002) Mammalian HSP60 is quickly sorted into the mitochondria under conditions of dehydration. Eur J Biochem 269:5931–5938. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03317.x
Jahangir Tafrechi RS, Svensson PJ, Janssen GM, Szuhai K, Maassen JA, Raap AK (2005) Distinct nuclear gene expression profiles in cells with mtDNA depletion and homoplasmic A3243G mutation. Mutat Res 578:43–52. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.02.002
Johnson KR, Zheng QY, Bykhovskaya Y, Spirina O, Fischel-Ghodsian N (2001) A nuclear-mitochondrial DNA interaction affecting hearing impairment in mice. Nat Genet 27:191–194. doi:10.1038/84831
Kazuno AA, Munakata K, Tanaka M, Kato N, Kato T (2008) Relationships between mitochondrial DNA subhaplogroups and intracellular calcium dynamics. Mitochondrion 8:164–169. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2007.12.002
Maruszak A, Canter JA, Styczyńska M, Zekanowski C, Barcikowska M (2008) Mitochondrial haplogroup H and Alzheimer’s disease-Is there a connection? Neurobiol. Aging Feb 26 [Epub ahead of print]
Mishmar D, Ruiz-Pesini E, Golik P et al (2003) Natural selection shaped regional mtDNA variation in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:171–176. doi:10.1073/pnas.0136972100
Mokranjac D, Neupert W (2005) Protein import into mitochondria. Biochem Soc Trans 33:1019–1023. doi:10.1042/BST20051019
Murray JI, Whitfield ML, Trinklein ND, Myers RM, Brown PO, Botstein D (2004) Diverse and specific gene expression responses to stresses in cultured human cells. Mol Biol Cell 15:2361–2374. doi:10.1091/mbc.E03-11-0799
Pockley AG, Muthana M, Calderwood SK (2008) The dual immunoregulatory reoles of stress proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 33:71–79
Pravenec M, Hyakukoku M, Houstek J et al (2007) Direct linkage of mitochondrial genome variation to risk factors for type 2 diabetes in conplastic strains. Genome Res 17:1319–1326. doi:10.1101/gr.6548207
Pridgeon JW, Olzmann JA, Chin LS, Li L (2007) PINK1 protects against oxidative stress by phosphorylating mitochondrial chaperone TRAP1. PLoS Biol 5:e172. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050172
Roubertoux PL, Sluyter F, Carlier M et al (2003) Mitochondrial DNA modifies cognition in interaction with the nuclear genome and age in mice. Nat Genet 35:65–69. doi:10.1038/ng1230
Ryan MT, Herd SM, Sberna G, Samuel MM, Hoogenraad NJ, Høj PB (1997) The genes encoding mammalian chaperonin 60 and chaperonin 10 are linked head-to-head and share a bidirectional promoter. Gene 196:9–17. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00111-X
Ryan MT, Hoogenraad NJ (2007) Mitochondrial-nuclear communications. Annu Rev Biochem 76:701–722. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.052305.091720
Saibil HR (2008) Chaperone machines in action. Curr Opin Struct Biol 18:35–42. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2007.11.006
Tokalov SV, Pieck S, Gutzeit HO (2003) Comparison of the reactions to stress produced by X-rays or electromagnetic fields (50 Hz) and heat; induction of heat shock genes and cell cycle effects in human cells. J Appl Biomed 1:85–92
Torroni A, Huoponen K, Francalacci P et al (1996) Classification of European mtDNAs from an analysis of three European populations. Genetics 144:1835–1850
Trinklein ND, Chen WC, Kingston RE, Myers RM (2004) Transcriptional regulation and binding of heat shock factor 1 and heat shock factor 2 to 32 human heat shock genes during thermal stress and differentiation. Cell Stress Chaperones 9:21–28
Vives-Bauza C, Ponzalo R, Manfredi G, Garcia-Arumi E, Andrei AL (2006) Enhanced ROS production and antioxidant defenses in cybrids harbouring mutations in mtDNA. Neurosci Lett 391:136–141. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.08.049
Voloboueva LA, Duan M, Onyang Y (2008) Overexpression of mitochondrial HSP70/HSP75 protects astrocytes against ischemic injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1009–1016. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600600
Wallace DC (2005) A mitochondrial paradigm of metabolic and degenerative disease, aging, and cancer: a dawn for evolutionary medicine. Annu Rev Genet 39:359–407. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.39.110304.095751
Zhao Q, Wang J, Levichkin IV, Stasinopoulos S, Ryan MT, Hoogenraad NJ (2002) A mitochondrial specific stress response in mammalian cells. EMBO J 21:4411–4419. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf445
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by Fondo Sociale Europeo—FSE (PhD course in Molecular Biopathology, University of Calabria, Italy) and by University Grants for Scientific Research (ex 60%).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
D. Bellizzi and D. Taverna equally contributed to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material
RFLP analysis of common variability in parental and cybrid cell lines. +/− indicate the presence/absence of the restriction site with reference to the MITOMAP sequence (www.mitomap.org). (DOC 575 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellizzi, D., Taverna, D., D’Aquila, P. et al. Mitochondrial DNA variability modulates mRNA and intra-mitochondrial protein levels of HSP60 and HSP75: experimental evidence from cybrid lines. Cell Stress and Chaperones 14, 265–271 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-008-0081-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-008-0081-x