Abstract
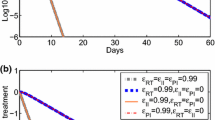
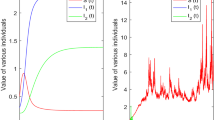
In this paper, we investigate a stochastic multi-stage model to evaluate the influence of treatment intensification with the integrase inhibitor raltegravir on viral load and 2-LTR dynamics in HIV patients under suppressive therapy. Firstly, it is proven that the model has a unique global positive solution. Secondly, by constructing a Lyapunov function, we establish sufficient conditions for the existence of a unique ergodic stationary distribution if \(R_{0}^{S}>1\). Thirdly, we obtain sufficient criterions \(R_{0}^{s}<1\) for disease extinction. Finally, the analytical results are demonstrated via two simulation examples. Our contribution also concentrates on proposing a method constructing Lyapunov function, which can be successfully used for the research about stationary distribution of epidemic model with nonlinear stochastic perturbation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perelson, A., Neumann, A., Markowitz, M., Leonard, J., Ho, D.: HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span, and viral generation time. Science 271, 1582–1586 (1996)
Culshaw, R.V., Ruan, S., Webb, G.: A mathematical model of cell-to-cell spread of HIV-1 that includes a time delay. J. Math. Biol. 46, 425–444 (2003)
Nowak, M., Bangham, C.: Population dynamics of immune response to persistent viruses. Science 272, 74–79 (1996)
Chun, T.W., Davey, R.T., Ostrowski, M., et al.: Relationship between pre-existing viral reservoirs and the re-emergence of plasma viremia after discontinuation of highly active anti-retroviral therapy. Nat. Med. 6, 757–761 (2000)
Davey, R.T., Bhat, N., Yoder, C., et al.: HIV-1 and T cell dynamics after interruption of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in patients with a history of sustained viral suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 15109–15114 (1999)
Gandhi, R.T., Coombs, R.W., Chan, E.S., et al.: No effect of raltegravir intensification on viral replication markers in the blood of HIV-1-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. J. AIDS 59, 229–235 (2012)
Besson, G.J., McMahon, D., Maldarelli, F., et al.: Short-course raltegravir intensification does not increase 2 long terminal repeat episomal HIV-1 DNA in patients on effective antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 54, 451–453 (2012)
Wang, X., Minkb, G., Linb, D., Song, X., Rong, L.: Influence of raltegravir intensification on viral load and 2-LTR dynamics in HIV patients on suppressive antiretroviral therapy. J. Theor. Biol. 416, 16–27 (2017)
Lahrouz, A., Omari, L.: Extinction and stationary distribution of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with non-linear incidence. Stat. Probab. Lett. 83, 960–968 (2013)
Hieu, N.T., Du, N.H., Auger, P., Dang, N.H.: Dynamical behavior of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 10, 56–73 (2015)
Cai, Y., Kang, Y., Banerjee, M., Wang, W.: A stochastic epidemic model incorporating media coverage. Commun. Math. Sci. 14, 893–910 (2015)
Mao, X., Renshaw, E., Marion, G.: Environmental brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics. Stoch. Proc. Appl. 97, 95–110 (2002)
Dalal, N., Greenhalgh, D., Mao, X.: A stochastic model for internal HIV dynamics. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 341, 1084–1101 (2008)
Wang, Y., Jiang, D., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: Stationary distribution of an HIV model with general nonlinear incidence rate and stochastic perturbations. J. Frankl. Inst. 356, 6610–6637 (2019)
Wang, Y., Jiang, D., Hayat, T., Ahmad, B.: A stochastic HIV infection model with T-cell proliferation and CTL immune response. Appl. Math. Comput. 31515, 477–493 (2017)
Liu, Q., Jiang, D.: Stationary distribution of a stochastic staged progression HIV model with imperfect vaccination. Physica A 5271, Article 121271(2019)
Ji, C.: The threshold for a stochastic HIV-1 infection model with Beddington-DeAngelis incidence rate. Appl. Math. Modelling 64, 168–184 (2018)
Qi, K., Jiang, D.: The impact of virus carriers screening and seeking treatment actively on dynamical behavior of a stochastic HIV/AIDS infection model. Appl. Math. Modelling 85, 378–404 (2020)
Feng, T., Qiu, Z., Meng, X., Rong, L.: Analysis of a stochastic HIV-1 infection model with degenerate diffusion. Appl. Math. Comput. 3481, 437–455 (2019)
Liu, Q., Jiang, D.: Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic SIR model with nonlinear perturbation. Appl. Math. Lett. 73, 8–15 (2017)
Liu, Q., Jiang, D., Hayat, T., Ahmad, B.: Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic predator-prey model with additional food and nonlinear perturbation. Appl. Math. Comput. 320, 226–239 (2018)
Lv, X., Meng, X., Wang, X.: Extinction and stationary distribution of an impulsive stochastic chemostat model with nonlinear perturbation. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 110, 273–279 (2018)
Li, X., Song, G., Xia, Y., Yuan, C.: Dynamical behaviors of the tumor-immune system in a stochastic environment. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 79, 2193–2217 (2019)
Song, M., Zuo, W., Jiang, D., Hayat, T.: Stationary distribution and ergodicity of a stochastic cholera model with multiple pathways of transmission. J. Frankl. Inst. 357, 10773–10798 (2020)
Lu, C.: Dynamics of a stochastic Markovian switching predator-prey model with infinite memory and general Lévy jumps. Math. Comput. Simulat. 181, 316–332 (2021)
Zou, X., Li, Q., Lv, J.: Stochastic bifurcations, a necessary and sufficient condition for a stochastic Beddington-DeAngelis predator-prey model. Appl. Math. Lett. (in Press)
Lu, C., Ding, X.: Periodic solutions and stationary distribution for a stochastic predator-prey system with impulsive perturbations. Appl. Math. Comput. 350, 313–322 (2019)
Lu, C., Ding, X.: Dynamical behavior of stochastic delay Lotka-Volterra competitive model with general Lévy jumps. Physica A 531, Article 121730(2019)
Zuo, W., Jiang, D.: Stationary distribution and periodic solution for stochastic predator-prey systems with nonlinear predator harvesting. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 36, 65–80 (2016)
Khasminskii, R.: Stochastic stability of differential equations. Sijthoff and noordhoff, alphen aan den rijn, the netherlands (1980)
Liu, M., Deng, M.: Analysis of a stochastic hybrid population model with Allee effect. Appl. Math. Comput. 364, 124582 (2020)
Zhang, X., Peng, H.: Stationary distribution of a stochastic cholera epidemic model with vaccination under regime switching. Appl. Math. Lett. 102, Article 106095 (2020)
Liu, Q., Jiang, D., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A., Ahmad, B.: Stationary distribution of a stochastic cholera model between communities linked by migration. Appl. Math. Comput. 37315, Article 125021(2020)
Wei, F., Xue, R.: Stability and extinction of SEIR epidemic models with generalized nonlinear incidence. Math. Comput. Simulat. 170, 1–15 (2020)
Zhao, D., Yuan, S.: Noise-induced bifurcations in the stochastic chemostat model with general nutrient uptake functions. Appl. Math. Lett. 103, Article 106180(2020)
Liu, M., Bai, C.: Optimal harvesting of a stochastic mutualism model with regime-switching. Appl. Math. Comput. 37315, Article 125040(2020)
Li, X., Wang,R., Yin,G.: Moment bounds and ergodicity of switching diffusion systems involving two-time-scale Markov chains. Syst. Control Lett. 132, Article 104514 (2019)
Liu,Q., Jiang,D.: The dynamics of a stochastic vaccinated tuberculosis model with treatment. Physica A 527, Article 121274 (2019)
Higham, D.J.: An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev. 43, 525–546 (2001)
Mohri, H., Bonhoeffer, S., Monard, S., et al.: Rapid turnover of T lymphocytes in SIV-infected rhesus macaques. Science 279, 1223–1227 (1998)
Sedaghat, A.R., Dinoso, J.B., Shen, L., et al.: Decay dynamics of HIV-1 depend on the inhibited stages of the viral life cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 4832–4837 (2008)
Wang, X., Song, X., Tang, S., et al.: Dynamics of an HIV model with multiple infection stages and treatment with different drug classes. Bull. Math. Biol. 78, 322–349 (2016)
Rong, L., Perelson, A.S.: Modeling latently infected cell activation: viral and latent reservoir persistence, and viral blips in HIV-infected patients on potent therapy. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5, e1000533 (2009)
Ramratnam, B., Bonhoeffer, S., Binley, J., et al.: Rapid production and clearance of HIV-1 and hepatitis C virus assessed by large volume plasma apheresis. Lancet 354, 1782–1785 (1999)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the editor and reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally and significantly in writing this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work is supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (Nos. ZR2018MA023, ZR2020QA008, ZR2019BA022), the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants no. 11901329, a Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program of China (Nos. J16LI09).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Sun, G. & Zhang, Y. Stationary distribution and extinction of a multi-stage HIV model with nonlinear stochastic perturbation. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 68, 885–907 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01530-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01530-z