Abstract
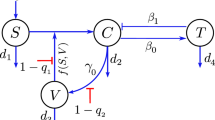
To explore the effect of direct cell-to-cell transmission on viral infection dynamics under the exposure of the non-cytolytic cure mechanism, a mathematical model integrating both the virus-to-cell and cell-to-cell transmissions with a non-cytolytic cure rate of infected cells in the presence of humoral immunity has been considered. Parameter variation experimentation suggests that a high cell-to-cell infection rate induces the chronic infection state in the host, whereas a high non-cytolytic cure rate positively contributes to the reduction of the viral load. We observe that a moderate cure rate under the exposure of a weak cell-to-cell transmission can effectively reduce the level of infection. Further, we examine the effect of cell-free transmission on the infection dynamics under the influence of cell-to-cell transmission. To substantiate our hypothesis, we present a case study of five HIV-1 infected patients to depict the primary HIV-1 infection dynamics in a real life scenario through model prediction.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaout, R.A., Wodarz, D., et al.: HIV-1 dynamics revisited: biphasic decay by cytotoxic T lymphocyte killing? Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 267(1450), 1347–1354 (2000)
Bonhoeffer, S., May, R.M., Shaw, G.M., Nowak, M.A.: Virus dynamics and drug therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94(13), 6971–6976 (1997)
Chen, S.S., Cheng, C.Y., Takeuchi, Y.: Stability analysis in delayed within-host viral dynamics with both viral and cellular infections. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 442(2), 642–672 (2016)
Cifuentes-Muñoz, N., Dutch, R.E., Cattaneo, R.: Direct cell-to-cell transmission of respiratory viruses: the fast lanes. PLoS Pathog. 14(6), e1007015 (2018)
Ciupe, S.M., Ribeiro, R.M., Nelson, P.W., Perelson, A.S.: Modeling the mechanisms of acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Theor. Biol. 247(1), 23–35 (2007)
Dahari, H., Lo, A., Ribeiro, R.M., Perelson, A.S.: Modeling hepatitis C virus dynamics: liver regeneration and critical drug efficacy. J. Theor. Biol. 247(2), 371–381 (2007)
Dahari, H., Major, M., Zhang, X., Mihalik, K., Rice, C.M., Perelson, A.S., Feinstone, S.M., Neumann, A.U.: Mathematical modeling of primary hepatitis C infection: noncytolytic clearance and early blockage of virion production. Gastroenterology 128(4), 1056–1066 (2005)
Dhar, M., Samaddar, S., Bhattacharya, P.: Modeling the effect of non-cytolytic immune response on viral infection dynamics in the presence of humoral immunity. Nonlinear Dyn. 98(1), 637–655 (2019)
Dhar, M., Samaddar, S., Bhattacharya, P.: Effect of non-cytolytic cure and saturation response: an in silico study to instigate the viral spread inhibition. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(6), 407 (2020)
Dhar, M., Samaddar, S., Bhattacharya, P., Upadhyay, R.K.: Viral dynamic model with cellular immune response: a case study of HIV-1 infected humanized mice. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 524, 1–14 (2019)
Dubey, B., Dubey, P., Dubey, U.S.: Modeling the intracellular pathogen-immune interaction with cure rate. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 38, 72–90 (2016)
Duggal, S., Chugh, T.D., Duggal, A.K.: HIV and malnutrition: effects on immune system. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 784740 (2012)
Guidotti, L.G., Chisari, F.V.: Noncytolytic control of viral infections by the innate and adaptive immuneresponse. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 19(1), 65–91 (2001)
Guidotti, L.G., Rochford, R., Chung, J., Shapiro, M., Purcell, R., Chisari, F.V.: Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 284(5415), 825–829 (1999)
Hattaf, K., Yousfi, N.: A generalized virus dynamics model with cell-to-cell transmission and cure rate. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016(1), 174 (2016)
Hattaf, K., Yousfi, N., Tridane, A.: Mathematical analysis of a virus dynamics model with general incidence rate and cure rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 13(4), 1866–1872 (2012)
Hethcote, H.W.: The mathematics of infectious diseases. SIAM Rev. 42(4), 599–653 (2000)
Hofbauer, J.: To persist or not to persist-differential equations in ecology
Jung, M.C., Pape, G.R.: Immunology of hepatitis B infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2(1), 43–50 (2002)
Lai, X., Zou, X.: Modeling cell-to-cell spread of HIV-1 with logistic target cell growth. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 426(1), 563–584 (2015)
Li, F., Wang, J.: Analysis of an HIV infection model with logistic target-cell growth and cell-to-cell transmission. Chaos Solitons Fractals 81, 136–145 (2015)
Liu, X., Wang, H., Hu, Z., Ma, W.: Global stability of an HIV pathogenesis model with cure rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 12(6), 2947–2961 (2011)
Lucas, W.J.: Plant viral movement proteins: agents for cell-to-cell trafficking of viral genomes. Virology 344(1), 169–184 (2006)
Marino, S., Hogue, I.B., Ray, C.J., Kirschner, D.E.: A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology. J. Theor. Biol. 254(1), 178–196 (2008)
Marsh, M., Helenius, A.: Virus entry: open sesame. Cell 124(4), 729–740 (2006)
Merwaiss, F., Czibener, C., Alvarez, D.E.: Cell-to-cell transmission is the main mechanism supporting bovine viral diarrhea virus spread in cell culture. J. Virol. 93(3), e01776-18 (2019)
Mothes, W., Sherer, N.M., Jin, J., Zhong, P.: Virus cell-to-cell transmission. J. Virol. 84(17), 8360–8368 (2010)
Murase, A., Sasaki, T., Kajiwara, T.: Stability analysis of pathogen-immune interaction dynamics. J. Math. Biol. 51(3), 247–267 (2005)
Nowak, M.A., Bangham, C.R.: Population dynamics of immune responses to persistent viruses. Science 272(5258), 74–79 (1996)
Obaid, M.A., Elaiw, A.: Stability of virus infection models with antibodies and chronically infected cells. In: Abstract and Applied Analysis, vol. 2014. Hindawi (2014)
Organization, W.H., et al.: Global health sector strategy on HIV 2016–2021. Towards ending aids. Tech. rep., World Health Organization (2016)
Pan, S., Chakrabarty, S.P.: Threshold dynamics of HCV model with cell-to-cell transmission and a non-cytolytic cure in the presence of humoral immunity. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 61, 180–197 (2018)
Reyes-Silveyra, J., Mikler, A.R.: Modeling immune response and its effect on infectious disease outbreak dynamics. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 13(1), 10 (2016)
Sattentau, Q.: Avoiding the void: cell-to-cell spread of human viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6(11), 815 (2008)
Shen, P., Fillatreau, S.: Suppressive functions of b cells in infectious diseases. Int. Immunol. 27(10), 513–519 (2015)
Shi, X., Zhou, X., Song, X.: Dynamical behavior of a delay virus dynamics model with CTL immune response. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(3), 1795–1809 (2010)
Stafford, M.A., Corey, L., Cao, Y., Daar, E.S., Ho, D.D., Perelson, A.S.: Modeling plasma virus concentration during primary HIV infection. J. Theor. Biol. 203(3), 285–301 (2000)
Tian, Y., Liu, X.: Global dynamics of a virus dynamical model with general incidence rate and cure rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 16, 17–26 (2014)
Uzman, A.: Molecular biology of the cell: Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., and Walter, P. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 31(4), 212–214 (2003)
Van den Driessche, P., Watmough, J.: Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180(1–2), 29–48 (2002)
Wang, K., Jin, Y., Fan, A.: The effect of immune responses in viral infections: a mathematical model view. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 19, 3379–3396 (2014)
Wodarz, D.: Mathematical models of immune effector responses to viral infections: virus control versus the development of pathology. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 184(1), 301–319 (2005)
Wodarz, D., Christensen, J.P., Thomsen, A.R.: The importance of lytic and nonlytic immune responses in viral infections. Trends Immunol. 23(4), 194–200 (2002)
Xiao, F., Fofana, I., Heydmann, L., Barth, H., Soulier, E., Habersetzer, F., Doffoël, M., Bukh, J., Patel, A.H., Zeisel, M.B., et al.: Hepatitis C virus cell–cell transmission and resistance to direct-acting antiviral agents. PLoS Pathog. 10(5), e1004128 (2014)
Yousfi, N., Hattaf, K., Rachik, M.: Analysis of a HCV model with ctl and antibody responses. Appl. Math. Sci. 3(57), 2835–2845 (2009)
Zhong, P., Agosto, L.M., Munro, J.B., Mothes, W.: Cell-to-cell transmission of viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 3(1), 44–50 (2013)
Zhou, X., Song, X., Shi, X.: A differential equation model of HIV infection of cd4+ t-cells with cure rate. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 342(2), 1342–1355 (2008)
Zumla, A., Malon, P., Henderson, J., Grange, J.M.: Impact of HIV infection on tuberculosis. Postgrad. Med. J. 76(895), 259–268 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhar, M., Samaddar, S. & Bhattacharya, P. Modeling the cell-to-cell transmission dynamics of viral infection under the exposure of non-cytolytic cure. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 65, 885–911 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-020-01420-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-020-01420-w