Abstract
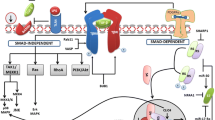
ADAMTS13, a plasma reprolysin-like metalloprotease, proteolyzes von Willebrand factor (VWF). ADAMTS13 is primarily synthesized by hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), and mainly regulates thrombogenesis by cleaving VWF. Recent studies demonstrate that ADAMTS13 also plays a role in the down-regulation of inflammation, regulation angiogenesis, and degradation of extracellular matrix. The purpose of this review is to introduce the state of progress with respect to some of the theorized roles of ADAMTS13.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furlan M, Robles R, Galbusera M, Remuzzi G, Kyrle PA, Brenner B, Krause M, Scharrer I, Aumann V, Mittler U, et al. von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(22):1578–84.
Tsai HM, Lian EC. Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(22):1585–94.
Uemura M, Tatsumi K, Matsumoto M, Fujimoto M, Matsuyama T, Ishikawa M, Iwamoto TA, Mori T, Wanaka A, Fukui H, et al. Localization of ADAMTS13 to the stellate cells of human liver. Blood. 2005;106(3):922–4.
Wang A, Duan Q, Wu J, Liu X, Sun Z. The expression of ADAMTS13 in human microvascular endothelial cells. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2015;11:11.
Shang D, Zheng XW, Niiya M, Zheng XL. Apical sorting of ADAMTS13 in vascular endothelial cells and Madin-Darby canine kidney cells depends on the CUB domains and their association with lipid rafts. Blood. 2006;108(7):2207–15.
Manea M, Tati R, Karlsson J, Bekassy ZD, Karpman D. Biologically active ADAMTS13 is expressed in renal tubular epithelial cells. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010;25(1):87–96.
Tati R, Kristoffersson AC, Stahl AL, Morgelin M, Motto D, Satchell S, Mathieson P, Manea-Hedstrom M, Karpman D. Phenotypic expression of ADAMTS13 in glomerular endothelial cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):24.
Manea M, Kristoffersson A, Schneppenheim R, Saleem MA, Mathieson PW, Morgelin M, Bjork P, Holmberg L, Karpman D. Podocytes express ADAMTS13 in normal renal cortex and in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 2007;138(5):651–62.
Suzuki M, Murata M, Matsubara Y, Uchida T, Ishihara H, Shibano T, Ashida S, Soejima K, Okada Y, Ikeda Y. Detection of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS-13) in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;313(1):212–6.
Liu L, Choi H, Bernardo A, Bergeron AL, Nolasco L, Ruan C, Moake JL, Dong JF. Platelet-derived VWF-cleaving metalloprotease ADAMTS-13. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(11):2536–44.
Moake JL. Thrombotic microangiopathies. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(8):589–600.
Fujimura Y, Matsumoto M, Yagi H, Yoshioka A, Matsui T, Titani K. Von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease and Upshaw–Schulman syndrome. Int J Hematol. 2002;75(1):25–34.
Epperla N, Hemauer K, Friedman KD, George JN, Foy P. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura related to a novel mutation in ADAMTS13 gene and management during pregnancy. Am J Hematol. 2016;28(10):24311.
Krabbe JG, Kemna EW, Strunk AL, Jobse PA, Kramer PA, Dikkeschei LD, van den Heuvel LP, Fijnheer R, Verdonck LF. Adult-onset congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura caused by a novel compound heterozygous mutation of the ADAMTS13 gene. Int J Hematol. 2015;102(4):477–81.
Kim HY, Lee KO, Yoo KH, Kim SH, Oh D, Kim HJ. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (Upshaw–Schulman syndrome) caused by novel ADAMTS13 mutations. Br J Haematol. 2015. doi:10.1111/bjh.13564.
Ferrari B, Cairo A, Pontiggia S, Mancini I, Masini L, Peyvandi F. Congenital and acquired ADAMTS13 deficiency: two mechanisms, one patient. J Clin Apher. 2015;30(4):252–6.
Benevides TC, Orsi FA, Colella MP, Percout Pde O, Moura MS, Dias MA, Lins BD, Paula EV, Vassallo J, Annichino-Bizzachi J. Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura due to antibody-mediated ADAMTS13 deficiency precipitated by a localized Castleman’s disease: a case report. Platelets. 2015;26(3):263–6.
Reuken PA, Kussmann A, Kiehntopf M, Budde U, Stallmach A, Claus RA, Bruns T. Imbalance of von Willebrand factor and its cleaving protease ADAMTS13 during systemic inflammation superimposed on advanced cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2015;35(1):37–45.
Ikeda H, Tateishi R, Enooku K, Yoshida H, Nakagawa H, Masuzaki R, Kondo Y, Goto T, Shiina S, Kume Y, et al. Prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma development by plasma ADAMTS13 in chronic hepatitis B and C. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2011;20(10):2204–11.
Huang Y, Zhang SD, McCrudden C, Chan KW, Lin Y, Kwok HF. The prognostic significance of PD-L1 in bladder cancer. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(6):3075–84.
Hugenholtz GC, Adelmeijer J, Meijers JC, Porte RJ, Stravitz RT, Lisman T. An unbalance between von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 in acute liver failure: implications for hemostasis and clinical outcome. Hepatology. 2013;58(2):752–61.
Lee M, Rodansky ES, Smith JK, Rodgers GM. ADAMTS13 promotes angiogenesis and modulates VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 2012;84(2):109–15.
Levy GG, Nichols WC, Lian EC, Foroud T, McClintick JN, McGee BM, Yang AY, Siemieniak DR, Stark KR, Gruppo R, et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature. 2001;413(6855):488–94.
Zheng X, Chung D, Takayama TK, Majerus EM, Sadler JE, Fujikawa K. Structure of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13), a metalloprotease involved in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(44):41059–63.
Plaimauer B, Zimmermann K, Volkel D, Antoine G, Kerschbaumer R, Jenab P, Furlan M, Gerritsen H, Lammle B, Schwarz HP, et al. Cloning, expression, and functional characterization of the von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13). Blood. 2002;100(10):3626–32.
Okano E, Ko S, Kanehiro H, Matsumoto M, Fujimura Y, Nakajima Y. ADAMTS13 activity decreases after hepatectomy, reflecting a postoperative liver dysfunction. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57(98):316–20.
Kume Y, Ikeda H, Inoue M, Tejima K, Tomiya T, Nishikawa T, Watanabe N, Ichikawa T, Kaneko M, Okubo S, et al. Hepatic stellate cell damage may lead to decreased plasma ADAMTS13 activity in rats. FEBS Lett. 2007;581(8):1631–4.
Sporn LA, Marder VJ, Wagner DD. Inducible secretion of large, biologically potent von Willebrand factor multimers. Cell. 1986;46(2):185–90.
Dong JF, Moake JL, Nolasco L, Bernardo A, Arceneaux W, Shrimpton CN, Schade AJ, McIntire LV, Fujikawa K, Lopez JA. ADAMTS-13 rapidly cleaves newly secreted ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers on the endothelial surface under flowing conditions. Blood. 2002;100(12):4033–9.
Chauhan AK, Goerge T, Schneider SW, Wagner DD. Formation of platelet strings and microthrombi in the presence of ADAMTS-13 inhibitor does not require P-selectin or beta3 integrin. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(3):583–9.
Chauhan AK, Motto DG, Lamb CB, Bergmeier W, Dockal M, Plaimauer B, Scheiflinger F, Ginsburg D, Wagner DD. Systemic antithrombotic effects of ADAMTS13. J Exp Med. 2006;203(3):767–76.
McEver RP. Selectins: initiators of leucocyte adhesion and signalling at the vascular wall. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;107(3):331–9.
Fan Z, Ley K. Leukocyte arrest: biomechanics and molecular mechanisms of beta2 integrin activation. Biorheology. 2015;52(5–6):353–77.
Thomas MR, Storey RF. The role of platelets in inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 2015;114(3):449–58.
Rabinovich A, Cohen JM, Kahn SR. Predictive value of markers of inflammation in the postthrombotic syndrome: a systematic review: inflammatory biomarkers and PTS. Thromb Res. 2015;136(2):289–97.
Sudoyo AW, Rachman A, Harimurti K. Angiogenesis, inflammation, platelets count, and metastatic status as a predictor for thrombosis risk in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Acta Med Indones. 2015;47(1):11–5.
Ghasemzadeh M, Hosseini E. Platelet-leukocyte crosstalk: linking proinflammatory responses to procoagulant state. Thromb Res. 2013;131(3):191–7.
Chauhan AK, Kisucka J, Brill A, Walsh MT, Scheiflinger F, Wagner DD. ADAMTS13: a new link between thrombosis and inflammation. J Exp Med. 2008;205(9):2065–74.
Motto DG, Chauhan AK, Zhu G, Homeister J, Lamb CB, Desch KC, Zhang W, Tsai HM, Wagner DD, Ginsburg D. Shigatoxin triggers thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in genetically susceptible ADAMTS13-deficient mice. J Clin Investig. 2005;115(10):2752–61.
Habe K, Wada H, Ito-Habe N, Hatada T, Matsumoto T, Ohishi K, Maruyama K, Imai H, Mizutani H, Nobori T. Plasma ADAMTS13, von Willebrand factor (VWF) and VWF propeptide profiles in patients with DIC and related diseases. Thromb Res. 2012;129(5):598–602.
Fukushima H, Nishio K, Asai H, Watanabe T, Seki T, Matsui H, Sugimoto M, Matsumoto M, Fujimura Y, Okuchi K. Ratio of von Willebrand factor propeptide to ADAMTS13 is associated with severity of sepsis. Shock. 2013;39(5):409–14.
Ota M, Mochizuki S, Shimoda M, Abe H, Miyamae Y, Ishii K, Kimura H, Okada Y. ADAM23 is down-regulated in side population and suppresses lung metastasis of lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2016;22(10):12895.
Martin AC, Cardoso AC, Selistre-de-Araujo HS, Cominetti MR. Recombinant disintegrin domain of human ADAM9 inhibits migration and invasion of DU145 prostate tumor cells. Cell Adhes Migr. 2015;9(4):293–9.
Wagstaff L, Kelwick R, Decock J, Edwards DR. The roles of ADAMTS metalloproteinases in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Front Biosci. 2011;16:1861–72.
Rodriguez-Manzaneque JC, Fernandez-Rodriguez R, Rodriguez-Baena FJ, Iruela-Arispe ML. ADAMTS proteases in vascular biology. Matrix Biol. 2015;46:38–45.
Stanton H, Melrose J, Little CB, Fosang AJ. Proteoglycan degradation by the ADAMTS family of proteinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;12(29):2.
Cauwe B, Van den Steen PE, Opdenakker G. The biochemical, biological, and pathological kaleidoscope of cell surface substrates processed by matrix metalloproteinases. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;42(3):113–85.
Luque A, Carpizo DR, Iruela-Arispe ML. ADAMTS1/METH1 inhibits endothelial cell proliferation by direct binding and sequestration of VEGF165. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(26):23656–65.
Rodriguez-Manzaneque JC, Lane TF, Ortega MA, Hynes RO, Lawler J, Iruela-Arispe ML. Thrombospondin-1 suppresses spontaneous tumor growth and inhibits activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and mobilization of vascular endothelial growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(22):12485–90.
Lee M, Keener J, Xiao J, Long Zheng X, Rodgers GM. ADAMTS13 and its variants promote angiogenesis via upregulation of VEGF and VEGFR2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72(2):349–56.
Ruggeri ZM. The role of von Willebrand factor in thrombus formation. Thromb Res. 2007;120(1):9.
Jung J, Lee HJ, Lee JM, Na KH, Hwang SG, Kim GJ. Placenta extract promote liver regeneration in CCl4-injured liver rat model. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011;11(8):976–84.
Ali SO, Darwish HA, Ismail NA. Modulatory effects of curcumin, silybin-phytosome and alpha-R-lipoic acid against thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis in rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2014;216:26–33.
Duarte S, Shen XD, Fondevila C, Busuttil RW, Coito AJ. Fibronectin-alpha4beta1 interactions in hepatic cold ischemia and reperfusion injury: regulation of MMP-9 and MT1-MMP via the p38 MAPK pathway. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(10):2689–99.
Zhang K, Gao Y, Zhong M, Xu Y, Li J, Chen Y, Duan X, Zhu H. Hepatoprotective effects of Dicliptera chinensis polysaccharides on dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis rats and its underlying mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;179:38–44.
Peng Y, Chen Q, Yang T, Tao Y, Lu X, Liu C. Cultured mycelium Cordyceps sinensis protects liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in acute liver injured mice. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(3):1815–27.
Kim TH, Mars WM, Stolz DB, Petersen BE, Michalopoulos GK. Extracellular matrix remodeling at the early stages of liver regeneration in the rat. Hepatology. 1997;26(4):896–904.
Kim TH, Mars WM, Stolz DB, Michalopoulos GK. Expression and activation of pro-MMP-2 and pro-MMP-9 during rat liver regeneration. Hepatology. 2000;31(1):75–82.
Bockmeyer CL, Kern DS, Forstmeier V, Lovric S, Modde F, Agustian PA, Steffens S, Birschmann I, Traeder J, Dammrich ME, et al. Arteriolar vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in benign nephrosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(9):3493–501.
Gardner SE, Humphry M, Bennett MR, Clarke MC. Senescent vascular smooth muscle cells drive inflammation through an interleukin-1alpha-dependent senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35(9):1963–74.
Wu Y, Liu G, Chen W, Yang M, Zhu C. 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide 1-beta-d-ribofuranoside reduces intimal hyperplasia of tissue engineering blood vessel by inhibiting phenotype switch of vascular smooth muscle cell. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016;7(10):33585.
Belo VA, Guimaraes DA, Castro MM. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 as a potential mediator of vascular smooth muscle cell migration and chronic vascular remodeling in hypertension. J Vasc Res. 2015;52(4):221–31.
Bockmeyer CL, Forstmeier V, Modde F, Lovric S, Claus RA, Schiffer M, Agustian PA, Grothusen C, Grote K, Birschmann I, et al. ADAMTS13–marker of contractile phenotype of arterial smooth muscle cells lost in benign nephrosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(6):1871–81.
Acknowledgments
The work presented in the review article was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30672243, 81200354), the Population and Family Planning Committee of Hubei Province (No. JS-20130017), Huazhong University of Science and Technology (No. 2013YGYL016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author states that he has no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Li, X., Xiao, J. et al. ADAMTS13: more than a regulator of thrombosis. Int J Hematol 104, 534–539 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-2091-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-2091-2