Abstract
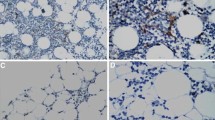
Aplastic anemia (AA) is a serious hematological disorder characterized by pancytopenia and defective bone marrow (BM) microenvironment. Previous investigations have demonstrated that there is a defect of angiogenesis in the BM of patients with AA. However, whether abnormalities of the BM microenvironment, particularly the overall specialization of niches, which have been classified into osteoblastic, vascular, and perivascular niches, are involved in the pathogenesis of AA is unknown. In the present study, 46 patients with AA and 15 controls were selected. The cellular elements of the BM microenvironment, including endosteal, vascular, and perivascular cells, were analyzed by immunohistochemical staining in situ. Patients with AA showed markedly fewer endosteal cells [0.33 vs 3.67 per high-power field (hpf); P < 0.05], vascular cells (8.00 vs 12.67 per hpf; P < 0.05), and perivascular cells (7.17 vs 10.67 per hpf; P < 0.05) compared with controls. These data indicate that AA is associated with impaired hematopoietic stem cell niches.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philpott NJ, Scopes J, Marsh JC, Gordon-Smith EC, Gibson FM. Increased apoptosis in aplastic anemia bone marrow progenitor cells: possible pathophysiologic significance. Exp Hematol. 1995;23:1642–8.
Zeng W, Chen G, Kajigaya S, Nunez O, Charrow A, Billings EM, et al. Gene expression profiling in CD34 cells to identify differences between aplastic anemia patients and healthy volunteers. Blood. 2004;103:325–32.
Zeng W, Kajigaya S, Chen G, Risitano AM, Nunez O, Young NS. Transcript profile of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from the bone marrow of acquired aplastic anemia patients. Exp Hematol. 2004;32:806–14.
Maciejewski JP, Selleri C, Sato T, Anderson S, Young NS. A severe and consistent deficit in marrow and circulating primitive hematopoietic cells (long-term culture-initiating cells) in acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 1996;88:1983–91.
Podesta M, Piaggio G, Frassoni F, Pitto A, Zikos P, Sessarego M, et al. The assessment of the hematopoietic reservoir after immunosuppressive therapy or bone marrow transplantation in severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 1998;91:1959–65.
Scopes J, Daly S, Atkinson R, Ball SE, Gordon-Smith EC, Gibson FM. Aplastic anemia: evidence for dysfunctional bone marrow progenitor cells and the corrective effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in vitro. Blood. 1996;87:3179–85.
Young NS, Barrett AJ. The treatment of severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 1995;85:3367–77.
Kamio T, Ito E, Ohara A, Kosaka Y, Tsuchida M, Yagasaki H, et al. Relapse of aplastic anemia in children after immunosuppressive therapy: a report from the Japan Childhood Aplastic Anemia Study Group. Haematologica. 2011;96:814–9.
Jalaeikhoo H, Khajeh-Mehrizi A. Immunosuppressive therapy in patients with aplastic anemia: a single-center retrospective study. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0126925.
Yoshizato T, Dumitriu B, Hosokawa K, Makishima H, Yoshida K, Townsley D, et al. Somatic mutations and clonal hematopoiesis in aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:35–47.
Calado RT, Graf SA, Wilkerson KL, Kajigaya S, Ancliff PJ, Dror Y, et al. Mutations in the SBDS gene in acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2007;110:1141–6.
Holmberg LA, Seidel K, Leisenring W, Torok-Storb B. Aplastic anemia: analysis of stromal cell function in long-term marrow cultures. Blood. 1994;84:3685–90.
Juneja HS, Gardner FH. Functionally abnormal marrow stromal cells in aplastic anemia. Exp Hematol. 1985;13:194–9.
Park M, Park CJ, Jang S, Kim DY, Lee JH, Lee JH, et al. Reduced expression of osteonectin and increased natural killer cells may contribute to the pathophysiology of aplastic anemia. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2015;23:139–45.
Zhang L, Wang HJ, Li HQ, Yang DL, Yan ZS, Wu YH. et al [Bone marrow microvessel density and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with aplastic anemia]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2007;28:528–31.
Fureder W, Krauth MT, Sperr WR, Sonneck K, Simonitsch-Klupp I, Mullauer L, et al. Evaluation of angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in the bone marrow of patients with aplastic anemia. Am J Pathol. 2006;168:123–30.
Gupta P, Khurana N, Singh T, Gupta D, Dhingra KK. Bone marrow angiogenesis in aplastic anemia-a study of CD 34 and VEGF expression in bone marrow biopsies. Hematology. 2009;14:16–21.
Calvi LM, Adams GB, Weibrecht KW, Weber JM, Olson DP, Knight MC, et al. Osteoblastic cells regulate the haematopoietic stem cell niche. Nature. 2003;425:841–6.
Kiel MJ, Yilmaz OH, Iwashita T, Yilmaz OH, Terhorst C, Morrison SJ. SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell. 2005;121:1109–21.
Yoon KA, Cho HS, Shin HI, Cho JY. Differential regulation of CXCL5 by FGF2 in osteoblastic and endothelial niche cells supports hematopoietic stem cell migration. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21:3391–402.
Kopp HG, Avecilla ST, Hooper AT, Rafii S. The bone marrow vascular niche: home of HSC differentiation and mobilization. Physiology (Bethesda). 2005;20:349–56.
He N, Zhang L, Cui J, Li Z. Bone marrow vascular niche: home for hematopoietic stem cells. Bone Marrow Res. 2014;2014:128436.
Avraham H, Banu N, Scadden DT, Abraham J, Groopman JE. Modulation of megakaryocytopoiesis by human basic fibroblast growth factor. Blood. 1994;83:2126–32.
Ding L, Saunders TL, Enikolopov G, Morrison SJ. Endothelial and perivascular cells maintain haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2012;481:457–62.
Camitta BM. Criteria for severe aplastic anaemia. Lancet. 1988;1:303–4.
Camitta BM. What is the definition of cure for aplastic anemia? Acta Haematol. 2000;103:16–8.
Marsh JC, Ball SE, Cavenagh J, Darbyshire P, Dokal I, Gordon-Smith EC, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2009;147:43–70.
Tuzuner N, Bennett JM. Reference standards for bone marrow cellularity. Leuk Res. 1994;18:645–7.
Ji JL, Xu MY, Huang F, Liu H. Bone marrow angiogenesis in aplastic anemia. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2006;14:79–82.
Kong Y, Chang YJ, Wang YZ, Chen YH, Han W, Wang Y, et al. Association of an impaired bone marrow microenvironment with secondary poor graft function after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19:1465–73.
Perez-Atayde AR, Sallan SE, Tedrow U, Connors S, Allred E, Folkman J. Spectrum of tumor angiogenesis in the bone marrow of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Pathol. 1997;150:815–21.
Schofield R. The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells. 1978;4:7–25.
Gong JK. Endosteal marrow: a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells. Science. 1978;199:1443–5.
Colmone A, Sipkins DA. Beyond angiogenesis: the role of endothelium in the bone marrow vascular niche. Transl Res. 2008;151:1–9.
Kowanetz M, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathways: therapeutic perspective. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5018–22.
Corselli M, Chin CJ, Parekh C, Sahaghian A, Wang W, Ge S, et al. Perivascular support of human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Blood. 2013;121:2891–901.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the excellent laboratory assistance of the pathologist Wei Xu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest that could inappropriately influence the content of this article.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Mo, W., Zhang, Y. et al. Impairment of hematopoietic stem cell niches in patients with aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol 102, 645–653 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1881-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1881-2