Abstract
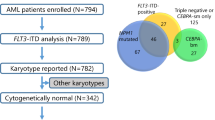
Cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia (cn-AML) is a group of heterogeneous diseases. Gene mutations are increasingly used to assess the prognosis of cn-AML patients and guide risk-adapted treatment. In the present study, we analyzed the molecular genetics characteristics of 373 adult cn-AML patients and explored the relationship between TET2 gene mutations or different genetic mutation patterns and prognosis. We found that 16.1 % of patients had TET2 mutations, 31.6 % had FLT3 internal tandem duplications (ITDs), 6.2 % had FLT3 tyrosine kinase domain mutations, 2.4 % had c-KIT mutations, 37.8 % had NPM1 mutations, 11.3 % had WT1 mutations, 5.9 % had RUNX1 mutations, 11.5 % had ASXL1 mutations, 3.8 % had MLL-PTDs, 7.8 % had IDH1 mutations, 7.8 % had NRAS mutations, 12.3 % had IDH2 mutations, 1.6 % had EZH2 mutations, and 14.7 % had DNMT3A mutations, while none had CBL mutations. Gene mutations were detected in 76.94 % (287/373) of all patients. In the NPM1m+ patients, those with TET2 mutations were associated with a shorter median overall survival (OS) as compared to TET2 wild-type (wt) patients (9.9 vs. 27.0 months, respectively; P = 0.023); Interestingly, the TET2 mutation was identified as an unfavorable prognostic factor and was closely associated with a shorter median OS as compared to TET2-wt (9.5 vs. 32.2 months, respectively; P = 0.013) in the NPM1m+/FLT3-ITDm− patient group. Thus, identification of TET2 combined with classic NPM1 and FLT3-ITD mutations allowed us to stratify cn-AML into distinct subtypes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Estey E, Döhner H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2006;368:1894–907.
Fröhling S, Scholl C, Gilliland DG, Levine RL. Genetics of myeloid malignancies: pathogenetic and clinical implications. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6285–95.
Mrózek K, Marcucci G, Paschka P, Whitman SP, Bloomfield CD. Clinical relevance of mutations and gene-expression changes in adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics: are we ready for a prognostically prioritized molecular classification? Blood. 2007;109:431–48.
Kelly LM, Gilliland DG. Genetics of myeloid leukemias. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2002;3:179–98.
Jan M, Snyder TM, Corces-Zimmerman MR, Vyas P, Weissman IL, Quake SR, et al. Clonal evolution of preleukemic hematopoietic stem cells precedes human acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:149ra118.
Foran JM. New prognostic markers in acute myeloid leukemia: perspective from the clinic. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2010;2010:47–55.
Miyazaki Y, Kuriyama K, Miyawaki S, Ohtake S, Sakamaki H, Matsuo T, et al. Cytogenetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) with trilineage dysplasia: Japan Adult Leukaemia Study Group-AML 92 study. Br J Haematol. 2003;120:56–62.
Schlenk RF, Döhner K, Krauter J, Fröhling S, Corbacioglu A, Bullinger L, et al. Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1909–18.
Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E, Alcalay M, Rosati R, Pasqualucci L, et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:254–66.
Dicker F, Haferlach C, Sundermann J, Wendland N, Weiss T, Kern W, et al. Mutation analysis for RUNX1, MLL-PTD, FLT3-ITD, NPM1 and NRAS in 269 patients with MDS or secondary AML. Leukemia. 2010;24:1528–32.
Döhner K, Schlenk RF, Habdank M, Scholl C, Rücker FG, Corbacioglu A, et al. Mutant nucleophosmin (NPM1) predicts favorable prognosis in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: interaction with other gene mutations. Blood. 2005;106:3740–6.
Singh H, Werner L, Deangelo D, Ballen K, Amrein P, Wadleigh M, et al. Clinical outcome of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia and FLT3 mutations. Am J Hematol. 2010;85:956–7.
Stirewalt DL, Radich JP. The role of FLT3 in haematopoietic malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:650–65.
Fuchs O, Provaznikova D, Kocova M, Kostecka A, Cvekova P, Neuwirtova R, et al. CEBPA polymorphisms and mutations in patients with acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, multiple myeloma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008;40:401–5.
Szankasi P, Ho AK, Bahler DW, Efimova O, Kelley TW. Combined testing for CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) mutations and promoter methylation in acute myeloid leukemia demonstrates shared phenotypic features. Leuk Res. 2011;35:200–7.
Boissel N, Leroy H, Brethon B, Philippe N, de Botton S, Auvrignon A, et al. Incidence and prognostic impact of c-Kit, FLT3, and Ras gene mutations in core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia (CBF-AML). Leukemia. 2006;20:965–70.
Döhner K, Tobis K, Ulrich R, Fröhling S, Benner A, Schlenk RF, et al. Prognostic significance of partial tandem duplications of the MLL gene in adult patients 16 to 60 years old with acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics: a study of the Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group Ulm. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3254–61.
Shide K, Kameda T, Shimoda H, Yamaji T, Abe H, Kamiunten A, et al. TET2 is essential for survival and hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis. Leukemia. 2012;26:2216–23.
Koh KP, Yabuuchi A, Rao S, Huang Y, Cunniff K, Nardone J, et al. TET1 and TET2 regulate 5-hydroxymethylcytosine production and cell lineage specification in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8:200–13.
Figueroa ME, Abdel-Wahab O, Lu C, Ward PS, Patel J, Shih A, et al. Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 mutations result in a hypermethylation phenotype, disrupt TET2 function, and impair hematopoietic differentiation. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:553–67.
Nibourel O, Kosmider O, Cheok M, Boissel N, Renneville A, Philippe N, et al. Incidence and prognostic value of TET2 alterations in de novo acute myeloid leukemia achieving complete remission. Blood. 2010;116:1132–5.
Tefferi A, Lim KH, Abdel-Wahab O, Lasho TL, Patel J, Patnaik MM, et al. Detection of mutant TET2 in myeloid malignancies other than myeloproliferative neoplasms: CMML, MDS, MDS/MPN and AML. Leukemia. 2009;23:1343–5.
Metzeler KH, Maharry K, Radmacher MD, Mrózek K, Margeson D, Becker H, et al. TET2 mutations improve the new European LeukemiaNet risk classification of acute myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1373–81.
Patel JP, Gönen M, Figueroa ME, Fernandez H, Sun Z, Racevskis J, et al. Prognostic relevance of integrated genetic profiling in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2012;12:1079–89.
Ley TJ, Ding L, Walter MJ, McLellan MD, Lamprecht T, Larson DE, et al. DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2424–33.
Chou WC, Chou SC, Liu CY, Chen CY, Hou HA, Kuo YY, et al. TET2 mutation is an unfavorable prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia patients with intermediate-risk cytogenetics. Blood. 2011;118:3803–10.
Ito S, D’Alessio AC, Taranova OV, Hong K, Sowers LC, Zhang Y. Role of Tet proteins in 5mC to 5hmC conversion, ES-cell self-renewal and inner cell mass specification. Nature. 2010;466:1129–33.
Tahiliani M, Koh KP, Shen Y, Pastor WA, Bandukwala H, Brudno Y, et al. Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science. 2009;324:930–5.
Ko M, Huang Y, Jankowska AM, Pape UJ, Tahiliani M, Bandukwala HS, et al. Impaired hydroxylation of 5-methylcytosine in myeloid cancers with mutant TET2. Nature. 2010;468:839–43.
Figueroa ME, Lugthart S, Li Y, Erpelinck-Verschueren C, Deng X, Christos PJ, et al. DNA methylation signatures identify biologically distinct subtypes in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:13–27.
Delhommeau F, Dupont S, Della Valle V, James C, Trannoy S, Massé A, et al. Mutation in TET2 in myeloid cancers. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2289–301.
Kosmider O, Gelsi-Boyer V, Cheok M, Grabar S, Della-Valle V, Picard F, et al. TET2 mutation is an independent favorable prognostic factor in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs). Blood. 2009;114:3285–91.
Kunimoto H, Fukuchi Y, Sakurai M, Sadahira K, Ikeda Y, Okamoto S, et al. Tet2 disruption leads to enhanced self-renewal and altered differentiation of fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells. Sci Rep. 2012;2:273.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from National Key Scientific Projects of China (2011CB933501); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81270617,81302046); Jiangsu Province Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars; Foundation of Jiangsu Province Health Department (H200915); and Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20133201120021).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
X. Tian and Y. Xu contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, X., Xu, Y., Yin, J. et al. TET2 gene mutation is unfavorable prognostic factor in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia patients with NPM1+ and FLT3-ITD− mutations. Int J Hematol 100, 96–104 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-014-1595-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-014-1595-x