Abstract
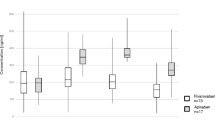
We sought to investigate specific hemostasis activation markers during electrophysiologic study (EPS) with consequent radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFA). Sixty patients were studied prospectively during routine EPS with RFA for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Blood samples were drawn before the insertion of venous sheaths (T0), at the end of EPS (T1), and 30 min after completion of RFA (T2). To study coagulation and fibrinolytic and platelet activity, we measured concentrations of thrombin–antithrombin III (TAT), D-dimers (DD), plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1), tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA), and circulating platelet aggregates. The results are expressed as median and show 95% confidence levels. Levels of DD increased from 0.24 mg/L at T0 to 0.37 mg/L at T1 (P < 0.001) and to 0.59 mg/L at T2 (P < 0.001). TAT levels increased from 5.29 μg/L at T0 to 35.80 μg/L at T1 (P < 0.001) and decreased to 26.30 μg/L at T2 (P < 0.001). PAI-1 concentration decreased from 30.10 μg/L at T0 to 26.4 μg/L at T1 (P < 0.001). t-PA at T2 increased to 5.10 μg/L from 4.75 μg/L at T1 (P = 0.001). No other differences between corresponding medians were statistically significant (P > 0.05). We found that concentrations of DD at T2 versus T1 depended on the number of radiofrequency energy applications (r S = 0.387; P = 0.002). Marked platelet activation was observed from the start of the procedure, without changes during the procedure.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hindricks G. The Multicentre European Radiofrequency Survey (MERFS): complications of radiofrequency catheter ablation of arrhythmias. Eur Heart J. 1993;14:1644–53.
Thakur RK, Klein GJ, Yee R, Guiraudon GM. Complications of radiofrequency catheter ablation: a review. Can J Cardiol. 1994;10:835–9.
Calkins H, Yong P, Miller JM, Olshansky B, Carlson M, Saul JP, et al. Catheter ablation of accessory pathways, atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia, and the atrioventricular junction: final results of a prospective, multicenter clinical trial. The Atakr Multicenter Investigators Group. Circulation. 1999;99:262–70.
Zhou L, Keane D, Reed G, Ruskin J. Thromboembolic complications of cardiac radiofrequency catheter ablation: a review of the reported incidence, pathogenesis and current research directions. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1999;10:611–20.
Blanc JJ, Almendral J, Brignole M, Fatemi M, Gjesdal K, Gonzáles-Torrecilla E, et al. Consensus document on antithrombotic therapy in the setting of electrophysiological procedures. Europace. 2008;10:513–27.
Wu KK, Hoak JC. A new method for the quantitative detection of platelet aggregates in patients with arterial insufficiency. Lancet. 1974;2:924–6.
Hintye J. NCSS, PASS and GESS. Kaysville: NCSS; 2007. http://www.ncss.com.
Huang SK. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias: appraisal of an evolving therapeutic modality. Am Heart J. 1989;118:1317–23.
Haines DE, Verow AF. Observations on electrode–tissue interface temperature and effect on electrical impedance during radiofrequency ablation of ventricular myocardium. Circulation. 1990;82:1034–8.
Huang SK, Graham AR, Wharton K. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of the left and right ventricles: anatomic and electrophysiologic observations. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1988;11:449–59.
Katritsis DG, Hossein-Nia M, Anastasakis A, Poloniecki J, Holt DW, Camm AJ, et al. Myocardial injury induced by radiofrequency and low energy ablation: a quantitative study of CK isoforms, CK-MB, and troponin-T concentrations. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1998;21:1410–6.
Chang DC, Reese TS. Changes in membrane structure induced by electroporation as revealed by rapid-freezing electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1990;58:1–12.
van Oeveren W, Crijns HJ, Korteling BJ, Wegereef EW, Haan J, Tigchelaar I, Hoekstra A. Blood damage, platelet and clotting activation during application of radiofrequency or cryoablation catheters: a comparative in vitro study. J Med Eng Technol. 1999;23:20–5.
Nath S, Redick JA, Whayne JG, Haines DE. Ultrastructural observations in the myocardium beyond the region of acute coagulation necrosis following radiofrequency catheter ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1994;5:838–45.
Khairy P, Chauvet P, Lehmann J, Lambert J, Macle L, Tanguay JF, et al. Lower incidence of thrombus formation with cryoenergy versus radiofrequency catheter ablation. Circulation. 2003;107:2045–50.
Matsudaira K, Nakagawa H, Wittkampf FHM, Yamanashi WS, Imai S, Pitha JV, et al. High incidence of thrombus formation without impedance rise during radiofrequency ablation using electrode temperature control. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003;26:1227–37.
Ma J, Cheng G, Xu G, Weng S, Lu X. Effect of radiofrequency catheter ablation on endothelial function and oxidative stress. Acta Cardiol. 2006;61:339–42.
Jesel L, Morel O, Pynn S, Radulescu B, Grunebaum L, Freyssinet JM, et al. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial flutter induces the release of platelet and leukocyte-derived procoagulant microparticles and a prothrombotic state. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2009;32:193–200.
Sasano T, Hirao K, Yano K, Kawabata M, Okishige K, Isobe M. Delayed thrombogenesis following radiofrequency catheter ablation. Circ J. 2002;66:671–6.
Shuman MA, Levine SP. Thrombin generation and secretion of platelet factor 4 during blood clotting. J Clin Invest. 1978;61:1102–6.
Manolis AS, Melita-Manolis H, Vassilikos V, Maounis T, Chiladakis J, Christopoulou-Cokkinou V, Cokkinos DV. Thrombogenicity of radiofrequency lesions: results with serial D-dimer determinations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;28:1257–61.
Dorbala S, Cohen AJ, Hutchinson LA, Menchavez-Tan E, Steinberg JS. Does radiofrequency ablation induce a prethrombotic state? Analysis of coagulation system activation and comparison to electrophysiologic study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1998;9:1152–60.
Anfinsen OG, Gjesdal K, Brosstad F, Orning OM, Aass H, Kongsgaard E, Amlie JP. The activation of platelet function, coagulation, and fibrinolysis during radiofrequency catheter ablation in heparinized patients. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1999;10:503–12.
Anfinsen OG, Gjesdal K, Aass H, Brosstad F, Orning OM, Amlie JP. When should heparin preferably be administered during radiofrequency catheter ablation? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2001;24:5–12.
Michelucci A, Antonucci E, Conti AA, Liotta AA, Fedi S, Padeletti L, et al. Electrophysiologic procedures and activation of the hemostatic system. Am Heart J. 1999;138:128–32.
Lee DSY, Dorian P, Downar E, Burns M, Yeo EL, Gold WL, et al. Thrombogenicity of radiofrequency ablation procedures: what factors influence thrombin generation? Europace. 2001;3:195–200.
Kozlovaite V, Grybauskas P, Cimbolaityte J, Mongirdiene A, Sileikis V, Zabiela V, et al. Coagulation alterations in treating arrhythmias with radiofrequency ablation. Medicina (Kaunas). 2009;45:706–11.
Hochholzer W, Schlittenhardt D, Arentz T, Stockinger J, Weber R, Bűrkle G, et al. Platelet activation and myocardial necrosis in patients undergoing radiofrequency and cryoablation of isthmus-dependent atrial flutter. Europace. 2007;9:490–5.
Maly J, Pecka M, Pleskot M, Cernohorsky D, Pidrman V, Stasek J, et al. Changes of the platelet activity in invasive cardiological procedures. Vnitr Lek. 1996;5:314–9.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Internal Grant Agency Ministry of Health Czech Republic No. NA 6603-3.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Parizek, P., Haman, L., Pleskot, M. et al. Hemostatic changes before and during electrophysiologic study and radiofrequency catheter ablation. Int J Hematol 93, 452–457 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-011-0806-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-011-0806-y