Abstract
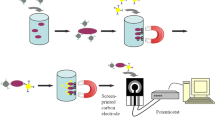
Sensitive, simple, and rapid pathogen separation and detection methods are essential for the early diagnosis and immediate medical treatment of bacterial infections. In this study, a novel strategy based on vancomycin (Van)-modified ovalbumin (OVA) mediated magnetic nanoprobes (MBs-OVA-Van) combined with multiplex polymerase chain reaction (mPCR) was developed for efficient isolation and detection of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Bacillus cereus (B. cereus). Van conjugated to ovalbumin coated magnetic microcarrier via strong covalent interaction. In addition, Van binds through hydrogen bonds with d-alanyl-d-alanine moieties on the surface of gram-positive bacteria cell wall. Under optimum conditions, the MBs-OVA-Van showed that the capture efficiency (CE) for S. aureus and B. cereus in PBS and juice samples were around 91%, 92% and 89%, 85%, respectively. In addition, with a mixture containing both target bacteria in PBS and juice samples, the CE for S. aureus and B. cereus were recorded at about 90%, 91% and 80%, 84%, respectively. The MBs-OVA-Van plus mPCR method applied in PBS and juice samples for both bacteria showed limits of detection at 102 CFU mL-1 in a < 3 h total assay time. The results indicated that the method holds promise for isolation and enrichment of gram-positive bacteria with S. aureus and B. cereus as models.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari N, Yazdian-Robati R, Shahdordizadeh M, Wang Z, Ghazvini K (2017) Aptasensors for quantitative detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Anal Biochem 533:18–25
Arcidiacono S, Pivarnik P, Mello CM, Senecal A (2008) Cy5 labeled antimicrobial peptides for enhanced detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. Biosens Bioelectron 23(11):1721–1727
Bhardwaj N, Bhardwaj SK, Nayak MK, Mehta J, Kim K-H, Deep A (2017) Fluorescent nanobiosensors for the targeted detection of foodborne bacteria. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 97:120–135
Brakstad OG, Aasbakk K, Maeland JA (1992) Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J Clin Microbiol 30(7):1654–1660
Campana R, van Hemert S, Baffone W (2017) Strain-specific probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria and their interference with human intestinal pathogens invasion. Gut Pathog 9(1):1–12
Chandra S, Mahto TK, Chowdhuri AR, Das B, Kumar Sahu S (2017) One step synthesis of functionalized carbon dots for the ultrasensitive detection of Escherichia coli and iron (III). Sensors Actuators B Chem 245:835–844
Chang Z-m, Wang Z, Shao D, Yue J, Lu M-m, Li L et al (2018) Fluorescent-magnetic Janus nanorods for selective capture and rapid identification of foodborne bacteria. Sensors Actuators B Chem 260:1004–1011
Chen C-T, Yu J-W, Ho Y-P (2019) Identification of bacteria in juice/lettuce using magnetic nanoparticles and selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry. J Food Drug Anal 27(2):575–584
Cook N (2003) The use of NASBA for the detection of microbial pathogens in food and environmental samples. J Microbiol Methods 53(2):165–174
Dietrich R, Jessberger N, Ehling-Schulz M, Märtlbauer E, Granum PE (2021) The Food Poisoning Toxins of Bacillus cereus. Toxins 13(2):98
Ehling-Schulz M, Koehler TM, Lereclus D (2019) The Bacillus cereus group: Bacillus species with pathogenic potential. Microbiol Spectr 7(3):875–902
Fayaz AM, Girilal M, Mahdy SA, Somsundar S, Venkatesan R, Kalaichelvan P (2011) Vancomycin bound biogenic gold nanoparticles: a different perspective for development of anti VRSA agents. Process Biochem 46(3):636–641
Feng J, Dai Z, Tian X, Jiang X (2018) Detection of Listeria monocytogenes based on combined aptamers magnetic capture and loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Food Control 85:443–452
Glasset B, Herbin S, Granier SA, Cavalié L, Lafeuille E, Guérin C et al (2018) Bacillus cereus, a serious cause of nosocomial infections: epidemiologic and genetic survey. PLoS One 13(5):e0194346
Hasan N, Guo Z, Wu H-F (2016) Large protein analysis of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry using amoxicillin functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(23):6269–6281
He Y, Chen S, Huang L, Wang Z, Wu Y, Fu F (2018) Combination of magnetic-beads-based multiple metal nanoparticles labeling with hybridization chain reaction amplification for simultaneous detection of multiple cancer cells with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 91(1):1171–1177
Hice SA, Clark KD, Anderson JL, Brehm-Stecher BF (2018) Capture, concentration, and detection of Salmonella in foods using magnetic ionic liquids and recombinase polymerase amplification. Anal Chem 91(1):1113–1120
Hu J, Zhang ZL, Wen CY, Tang M, Wu LL, Liu C, Zhu L, Pang DW (2016) Sensitive and quantitative detection of C-reaction protein based on immunofluorescent nanospheres coupled with lateral flow test strip. Anal Chem 88:6577–6584
Huang C-M, Lyu S-Y, Lin K-H, Chen C-L, Chen M-H, Shih H-W, Hsu NS, Lo IW, Wang YL, Li YS, Wu CJ, Li Y-S (2019) Teicoplanin reprogrammed with the N-acyl-glucosamine pharmacophore at the penultimate residue of aglycone acquires broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities effectively killing Gram-positive and -negative pathogens. ACS Infect Dis 5(3):430–442
Kim JH, Hahn YK, Chun H (2019) Multiplexed detection of pathogens using magnetic microparticles encoded by magnetic axes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 285:11–16
Kupradit C, Rodtong S, Ketudat-Cairns M (2013) Development of a DNA macroarray for simultaneous detection of multiple foodborne pathogenic bacteria in fresh chicken meat. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(12):2281–2291
Lee J-G, Sagui C, Roland C (2004) First principles investigation of vancomycin and teicoplanin binding to bacterial cell wall termini. J Am Chem Soc 126(27):8384–8385
Li J, Jiang H, Rao X, Liu Z, Zhu H, Xu Y (2018) Point-of-care testing of pathogenic bacteria at the single-colony level via gas pressure readout using aptamer-coated magnetic CuFe2O4 and vancomycin-capped platinum nanoparticles. Anal Chem 91(2):1494–1500
Lim J, Choi J, Guk K, Son SU, Lee DK, Yeom S-J, Kang T, Jung J, Lim E-K (2019) Peptidoglycan binding protein (PGBP)-modified magnetic nanobeads for efficient magnetic capturing of Staphylococcus aureus associated with sepsis in blood. Sci Rep 9(1):129
Liu Y, Singh P, Mustapha A (2018) Multiplex high resolution melt-curve real-time PCR assay for reliable detection of Salmonella. Food Control 91:225–230
Lowy FD (2009) Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 339(8):520–532
Majdinasab M, Hayat A, Marty JL (2018) Aptamer-based assays and aptasensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria in food samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 107:60–77
Martelet A, L’Hostis G, Nevers M-C, Volland H, Junot C, Becher F o, Muller BH (2015) Phage amplification and immunomagnetic separation combined with targeted mass spectrometry for sensitive detection of viable bacteria in complex food matrices. Anal Chem 87(11):5553–5560
Mei X, Zhai X, Lei C, Ye X, Kang Z, Wu X, Xiang R, Wang Y, Wang H (2019) Development and application of a visual loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick (LAMP-LFD) method for rapid detection of Salmonella strains in food samples. Food Control 104:9–19
Meng X, Li F, Li F, Xiong Y, Xu H (2017) Vancomycin modified PEGylated-magnetic nanoparticles combined with PCR for efficient enrichment and detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:546–555
Morad N, Misbah S (2018) vicK gene as potential identification marker for Staphylococcus aureus. J Biosci Med 6(11):98–110
Ozalp VC, Bayramoglu G, Kavruk M, Keskin BB, Oktem HA, Arica MY (2014) Pathogen detection by core–shell type aptamer-magnetic preconcentration coupled to real-time PCR. Anal Biochem 447:119–125
Pan J, Wang Y, Zhang C, Wang X, Wang H, Wang J et al (2018) Antigen-directed fabrication of a multifunctional nanovaccine with ultrahigh antigen loading efficiency for tumor photothermal-immunotherapy. Adv Mater 30(8):1704408
Qiao M, Liu X, Song J-W, Yang T, Chen M-L, Wang J-H (2018) Improving the adsorption capacity for ovalbumin by functional modification of aminated mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tryptophan. J Mater Chem B 6(46):7703–7709
Sanjay S, Akshay M, Nishant M, Samaresh D, Prashant M (2019) Vancomycin functionalized WO3 thin film-based impedance sensor for efficient capture and highly selective detection of Gram-positive bacteria. Biosens Bioelectron 136:23–30
Schwan WR (2019) Staphylococcus aureus toxins: armaments for a significant pathogen. Toxins 11(8):457
Schwartz O, Bercovici M (2014) Microfluidic assay for continuous bacteria detection using antimicrobial peptides and isotachophoresis. Anal Chem 86(20):10106–10113
Wang J, Li H, Li T, Ling L (2018) Determination of bacterial DNA based on catalytic oxidation of cysteine by G-quadruplex DNAzyme generated from asymmetric PCR: application to the colorimetric detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Microchim Acta 185(9):410
Wei J-L, Huang D-Y, Chen Y-C (2020a) Using gadolinium ions as affinity probes to selectively enrich and magnetically isolate bacteria from complex samples. Anal Chim Acta 1113:18–25
Wei S, Li J, He J, Zhao W, Wang F, Song X et al (2020b) Paper chip-based colorimetric assay for detection of Salmonella typhimurium by combining aptamer-modified Fe3O4@ Ag nanoprobes and urease activity inhibition. Microchim Acta 187(10):1–9
Wu Y, Wang M, Ouyang H, He Y, Zhao X, Fu Z (2018a) Teicoplanin-functionalized magnetic beads for detection of Staphylococcus aureus via inhibition of the luminol chemiluminescence by intracellular catalase. Microchim Acta 185(8):391
Wu Z-C, Isley NA, Boger DL (2018b) N-terminus alkylation of vancomycin: ligand binding affinity, antimicrobial activity, and site-specific nature of quaternary trimethylammonium salt modification. ACS Infect Dis 4(10):1468–1474
Xue L, Zheng L, Zhang H, Jin X, Lin J (2018) An ultrasensitive fluorescent biosensor using high gradient magnetic separation and quantum dots for fast detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors Actuators B Chem 265:318–325
Yang Z-Y, Shim W-B, Kim K-Y, Chung D-H (2010) Rapid detection of enterotoxigenic Clostridium perfringens in meat samples using immunomagnetic separation polymerase chain reaction (IMS−PCR). J Agric Food Chem 58(12):7135–7140
Yang S, Ouyang H, Su X, Gao H, Kong W, Wang M, Shu Q, Fu Z (2016) Dual-recognition detection of Staphylococcus aureus using vancomycin-functionalized magnetic beads as concentration carriers. Biosens Bioelectron 78:174–180
Zhang Z, Liu W, Xu H, Aguilar ZP, Shah NP, Wei H (2015) Propidium monoazide combined with real-time PCR for selective detection of viable Staphylococcus aureus in milk powder and meat products. J Dairy Sci 98(3):1625–1633
Zhang Y, Yan C, Yang H, Yu J, Wei H (2017) Rapid and selective detection of E. coli O157: H7 combining phagomagnetic separation with enzymatic colorimetry. Food Chem 234:332–338
Zhu M, Liu W, Liu H, Liao Y, Wei J, Zhou X, Xing D (2015) Construction of Fe3O4/vancomycin/PEG magnetic nanocarrier for highly efficient pathogen enrichment and gene sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(23):12873–12881
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1602500), Research Foundation from Academic and Technical Leaders of Major Disciplines in Jiangxi Province, China (20194BCJ22004), and Research Foundation from State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University, China (SKLF-ZZA-201912).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
Guanhua Chen declares that there is no conflict of interest. Guotai Yang declares that there is no conflict of interest. Yutong Wang declares that there is no conflict of interest. Mei Deng declares that there is no conflict of interest. Zhengzheng Wang declares that there is no conflict of interest. Zoraida P. Aguilar declares that there is no conflict of interest. Hengyi Xu declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Yang, G., Wang, Y. et al. Antibiotic-Based Magnetic Nanoprobes Combined with mPCR for Simultaneous Detection of Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus. Food Anal. Methods 14, 1964–1976 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-02026-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-02026-z