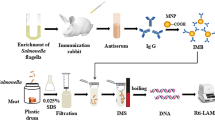
Abstract
In this study, a real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification (Rti-LAMP) combined with immunomagnetic beads separation (IMS) and ethidium bromide monoazide (EMA) treatment was developed for the rapid and ultrasensitive detection of viable Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157:H7 in milk without enrichment. Polyclonal antibodies against E. coli O157:H7 flagellum and specific immunomagnetic beads (IMBs) were prepared. The capture efficiency of target bacteria was more than 95% by adding 50 μL of prepared IMBs into 1 mL of E. coli sample for incubation at 37 °C for 20 min. Then, Gly-HCl buffer (0.2 M, pH 2.2) was a key to the effective eluting and separating of bacteria from IMB-bacterial complexes. The eluted bacteria were resuspended with 20 μL TZ lysing solution and boiled at 99.5 °C for 10 min, as a DNA template of Rti-LAMP. The development of IMS-Rti-LAMP assay could specifically detect viable E. coli O157:H7 as low as 2.7 CFU/mL in pure culture. Furthermore, the optimum volume for detection of E. coli O157:H7 in milk was 1 mL of the sample by IMS-Rti-LAMP assay. Before Gly-HCl elution, 4 μg/mL of EMA was used to treat bacterial cells which significantly inhibited DNA amplification derived from dead cells in Rti-LAMP. The limit of detection (LOD) of viable E. coli O157:H7 in milk was 6 CFU/mL by the IMS-EMA-Rti-LAMP, and the whole assay could be completed in 4 h. The development of IMS-EMA-Rti-LAMP assay was a rapid, ultrasensitive, and specific detection of viable E. coli O157:H7 in milk without enrichment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolmaaty A, Vu C, Oliver J, Levin RE (2000) Development of a new lysis solution for releasing genomic DNA from bacterial cells for DNA amplification by polymerase chain reaction. Microbios 101(400):181–189
Bi Y, Shu M, Zhong C, Li SY, Li YK, Yang HH, Wu GP (2020) A novel SDS rinse and immunomagnetic beads separation combined with real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella in ready-to-eat duck meat. Food Anal Methods 13(5):1166–1175
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:254–261
Bustin SA (2002) Quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR): trends and problems. J Mol Endocrinol 29:23–39
CDC (2019) E. coli and food safety https://www.cdc.gov/features/ecoliinfection/index.html
Chen J, Park B (2018) Effect of immunomagnetic bead size on recovery of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 267:1–8
Chen Q, Li Y, Tao T, Bie X, Lu F, Lu Z (2017) Development and application of a sensitive, rapid, and reliable immunomagnetic separation-PCR detection method for Cronobacter spp. J Dairy Sci 100(2):961–969
Chen H, Zhao YY, Shu M, Zhang TT, Bi Y, Gao YY, Wu GP (2018) Detection and evaluation of viable but non-culturable Escherichia coli O157:H7 induced by low temperature with a BCAC-EMA-Rti-LAMP assay in chicken without enrichment. Food Anal Methods 12(2):458–468
Dai F, Zhang M, Xu D, Yang Y, Wang J, Li M, Du M (2017) The development of methods for the detection of Salmonella in chickens by a combination of immunomagnetic separation and PCRs. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 64(6):888–894
Du M, Li J, Zhao R, Yang Y, Wang Y, Ma K, Cheng X, Wan Y, Wu X (2018) Effective pre-treatment technique based on immune-magnetic separation for rapid detection of trace levels of Salmonella in milk. Food Control 91:92–99
EFSA BIOHAZ Panel (2015) Scientific opinion on the public health risks related to consumption of raw drinking milk. EFSA J 13(1):3940–3995
Gunasekera TS, Sørensen A, Attfield PV, Veal DA (2002) Inducible gene expression by nonculturable bacteria in milk after pasteurization. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):1988–1993
Han J, Zhang L, Hu L, Xing K, Lu X, Huang Y, Zhang J, Lai W, Chen T (2018) Nanozyme-based lateral flow assay for the sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. J Dairy Sci 101(7):5770–5779
Incili GK, Koluman A, Aktüre A, Ataşalan A (2019) Validation and verification of LAMP, ISO, and VIDAS UP methods for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in different food matrices. J Microbiol Methods 165:105697
Kazuya T, Fujisaki R, Yamazaki T, Makimura K (2017) Enhancing melting curve analysis for the discrimination of loop-mediated isothermal amplification products from four pathogenic molds: use of inorganic pyrophosphatase and its effect in reducing the variance in melting temperature values. J Microbiol Methods 132:41–45
Kojima S (2015) Dynamism and regulation of the stator, the energy conversion complex of the bacterial flagellar motor. Curr Opin Microbiol 28:66–71
Li F, Li F, Chen B, Zhou B, Yu P, Yu S, Lai W, Xu H (2016) Sextuplex PCR combined with immunomagnetic separation and PMA treatment for rapid detection and specific identification of viable Salmonella spp., Salmonella enterica serovars Paratyphi B, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Salmonella Enteritidis in raw meat. Food Control 73:587–594
Li B, Liu H, Wang W (2017) Multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and screening for non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing E. coli. BMC Microbiol 17(1):215
Mao Y, Huang X, Xiong S, Xu H, Aguilar ZP, Xiong Y (2016) Large volume immunomagnetic separation combined with multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria ivanovii in lettuce. Food Control 59:601–608
Meng X, Li F, Li F, Xiong Y, Xu H (2017) Vancomycin modified PEGylated-magnetic nanoparticles combined with PCR for efficient enrichment and detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:546–555
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28(12):E63
Ravan H, Amandadi M (2015) Analysis of yeh fimbrial gene cluster in Escherichia coli O157:H7 in order to find a genetic marker for this serotype. Curr Microbiol 71(2):274–282
Ravan H, Amandadi M, Sanadgol N (2016) A highly specific and sensitive loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Microb Pathog 91:161–165
Taban MB, Aytac SA (2019) An evaluation of immunomagnetic separation-real-time PCR (IMS-RtiPCR) combined assay for rapid and specific detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in raw milk and ground beef. Food Sci Tech-Brazil 39(4):955–961
Wagner AO, Praeg N, Reitschuler C, Illmer P (2015) Effect of DNA extraction procedure, repeated extraction and ethidium monoazide (EMA)/propidium monoazide (PMA) treatment on overall DNA yield and impact on microbial fingerprints for bacteria, fungi and archaea in a reference soil. Appl Soil Ecol 93:56–64
Wang L, Li P, Zhang Z, Chen Q, Aguilar ZP, Xu H, Yang L, Xu F, Lai W, Xiong Y, Wei H (2014) Rapid and accurate detection of viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk using a combined IMS, sodium deoxycholate, PMA and real-time quantitative PCR process. Food Control 36(1):119–125
Xin L, Zhang L, Meng Z, Lin K, Zhang S, Han X (2017) Development of a novel loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the detection of lipolytic Pseudomonas fluorescens in raw cow milk from North China. J Dairy Sci 100(10):7802–7811
Xiong Q, Cui X, Saini JK, Liu D, Shan S, Jin Y, Lai W (2014) Development of an immunomagnetic separation method for efficient enrichment of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Food Control 37:41–45
Yan M (2017) PMA-LAMP for rapid detection of Escherichia coli and shiga toxins from viable but non-culturable state. Microb Pathog 105:245–250
Yang Y, Xu F, Xu H, Aguilar ZP, Niu R, Yuan Y, Sun J, You X, Lai W, Xiong Y, Wan C, Wei H (2013) Magnetic nano-beads based separation combined with propidium monoazide treatment and multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of viable Salmonella Typhimurium, Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes in food products. Food Microbiol 34(2):418–424
Ye Y, Li H, Wu Q, Na L, Han Y (2014) Immunocaptured-loop mediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus in seafood. J Food Saf 34(1):21–25
Zhang B, Sun X, Fan H, He K, Zhang X (2018a) The fimbrial gene z3276 in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 contributes to bacterial pathogenicity. other, 9
Zhang L, Wei Q, Han Q, Chen Q, Tai W, Zhang J, Song Y, Xia X (2018b) Detection of Shigella in milk and clinical samples by magnetic immunocaptured-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Front Microbiol 9:94
Zhang TT, Zhong C, Shu M, Wu X, Chen H, Lin LP, Wu GP (2019) Real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays combined with ethidium monoazide bromide and bentonite coated activated carbon for rapid and sensitive detection of viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 from milk without enrichment. J Food Saf 39(5):e12677
Zhao YY, Tang KJ, Zhang TT, Gao YY, Lin LP, Wu GP (2018) Quantification and discrimination of viable and dead Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells from chicken without enrichment by ethidium bromide monoazide real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Food Anal Methods 11(5):1257–1266
Zhi A, Ma B, Wu Y, Fang J, Yu X, Zhang M (2018) Detection of viable Vibrio cholerae cells in seafood using a real-time visual loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with propidium monoazide. Food Anal Methods 11(1):99–110
Zhong Q, Tian J, Wang B, Wang L (2016) PMA based real-time fluorescent LAMP for detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in viable but nonculturable state. Food Control 63:230–238
Zhu F, Rogelj S, Kieft TL (2005) Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 by immunomagnetic separation and real-time PCR. Int J Food Microbiol 99(1):47–57
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31760483); the Special Funds for Collaborative Innovation of Modern Agricultural Science and Research in Jiangxi Province, China (No. JXXTCX201703); and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China (No. 20171ACB20013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Hu Chen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ya-Ke Li declares that he has no conflict of interest. Tian-Tian Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yan Bi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Mei Shu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Chan Zhong declares that he has no conflict of interest. Kai-Jie Tang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Guo-Ping Wu declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Li, YK., Zhang, TT. et al. A Novel Real-Time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Combined with Immunomagnetic Beads Separation and Ethidium Bromide Monoazide Treatment for Rapid and Ultrasensitive Detection of Viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Milk. Food Anal. Methods 14, 944–956 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01932-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01932-y