Abstract
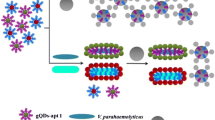
This paper describes a novel strategy based on fluorescence energy transfer (FRET) with green synthesis of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) and gold nanoparticles (GNPs) for the detection of one of the most pathogenic bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). Novel green CQDs with blue color emission and high quantum yield were synthesized from olive leaves via the hydrothermal method. The fluorescence of the CQDs was quenched in the presence of aptamers and GNPs. After addition of specific bacteria, the aptamer–target complex was formed and the emission of the free CQDs returned. The linear range of this aptasensor was 108 to 101 CFU/mL with a detection limit as low as 10 CFU/mL for S. aureus. The proposed aptasensing approach has been successfully used for the assay of S. aureus in human serum, milk, and orange juice. Due to its simplicity and effectiveness, this system exhibits great promise as a practical aptasensor for the detection of other bacteria and biomolecules.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour A, Norouz-Sarvestani F, Noori A, Soltani N (2015) Aptamer-conjugated silver nanoparticles for electrochemical dual-aptamer-based sandwich detection of staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 68:149–155
Abdelhamid HN, Wu HF (2018) Selective biosensing of Staphylococcus aureus using chitosan quantum dots. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 188:50–56
Ahmadian-Fard-Fini S, Salavati-Niasari M, Ghanbari D (2018) Hydrothermal green synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4-carbon dots by lemon and grape fruit extracts and as a photoluminescence sensor for detecting of E. coli bacteria. Spectrochim Acta A 203:481–493
Al-Bahry SN, Mahmoud IY, Al-Musharafi SK, Sivakumar N (2014) Staphylococcus aureus contamination during food preparation, processing and handling. Int J Chem Eng Appl 5(5):388–392
Álvaro Raya Barón DR, Ignacio F (2015) Bioactive compounds in the olive leaf: introducing hands-on HPLCMS and NMR in the undergraduate curricula. Chem Educ 20:321–326
Amiri S, Ahmadi R, Salimi A, Navaee A, Hamd Qaddare S, Amini MK (2018) Ultrasensitive and highly selective FRET aptasensor for Hg2+ measurement in fish samples using carbon dots/AuNPs as donor/acceptor platform. New J Chem 42:16027–16035
Arkan E, Barati A, Rahmanpanah M, Hosseinzadeh L, Moradi S, Hajialyani M (2018) Green synthesis of carbon dots derived from walnut oil and an investigation of their cytotoxic and apoptogenic activities toward cancer cells. Adv Pharm Bull 8:149–155
Baig MMF, Chen YC (2017) Bright carbon dots as fluorescence sensing agents for bacteria and curcumin. J Coll Interf Sci 501:341–349
Baumstummler A, Lehmann D, Janjic N, Ochsner UA (2014) Specific capture and detection of Staphylococcus aureus with high-affinity modified aptamers to cell surface components. Lett Appl Microbiol 59:422–431
Behera BS, Maiti TK, Mohapatra S (2012) Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem Commun 48:8835–8837
Borghei YS, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR (2017) Fluorometric determination of microRNA via FRET between silver nanoclusters and CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184:4713–4721
Borghei YS, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR, Ju H (2018) Colorimetric and energy transfer based fluorometric turn-on method for determination of microRNA using silver nanoclusters and gold nanoparticles. Mikrochim Acta 185:286
Borsa BA, Tuna BG, Hernandez FJ, Hernandez LI, Bayramoglu G, Arica MY, Ozalp VC (2016) Staphylococcus aureus detection in blood samples by silica nanoparticle-oligonucleotides conjugates. Biosens Bioelectron 86:27–32
Davydova A, Vorobjeva M, Pyshnyi D, Altman S, Vlassov V, Venyaminova A (2015) Aptamers against pathogenic microorganisms. Crit Rev Microbiol 42:847–865
Dehghani Z, Hosseini M, Mohammadnejad J, Ganjali MR (2019) New colorimetric DNA sensor for detection of Campylobacter jejuni in milk sample based on peroxidase-like activity of gold/platinium nanocluster. Chemitryselect 4:11687–11692
Dehghani Z, Mohammadnejad J, Hosseini M, Bakhshi B, Rezyan AH (2020) A low-cost and high-efficiency carbazole-based porous organic polymer as a novel sorbent for solid-phase extraction of triazine herbicides in vegetables. Food Chem 309:125618
Duan N, Wu S, Zhu C, Ma X, Wang Z, Yu Y, Jiang Y (2012) Dual-color upconversion fluorescence and aptamer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles-based bioassay for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Anal Chim Acta 723:1–6
Fakhri N, Hosseini M, Tavakoli O (2018) Aptamer-based colorimetric determination of Pb2+ using a paper-based microfluidic platform. Anal Methods 10:4438–4444
Farokhzad OC, Karp JM, Langer R (2006) Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for cancer targeting. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 3:311–324
Jingyi X, Ying Z, Shuxian L, Meiting D, Chaobiao H (2014) Low-cost synthesis of carbon nanodots from natural products used as a fluorescent probe for the detection of ferrum(iii) ions in lake water. R Soc Chem 6:2086–2090
Kadariya J, Smith TC, Thapaliya D (2014) Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal food-borne disease: an ongoing challenge in public health. Biomed Res Int 2014:827965
Lian Y, He F, Wang H, Tong F (2015) A new aptamer/graphene interdigitated gold electrode piezoelectric sensor for rapid and specific detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 15:314–319
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao Z (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:362–381
Lin H, Huang J, Ding L (2019) Preparation of carbon dots with high-fluorescence quantum yield and their application in dopamine fluorescence probe and cellular imaging. J Nanomater:1–9
Liu J, Zhang P, Yang X, Wang K, Guo Q, Huang J, Li W (2014) Aptamer-mediated indirect quantum dot labeling and fluorescent imaging of target proteins in living cells. Nanotechnology 25:505502
Meng X, Yang G, Li F, Liang T, Lai W, Xu H (2017) Sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus with vancomycin-conjugated magnetic beads as enrichment carriers combined with flow cytometry. ACS Appl Mater Interf 9:21464–21472
Motaghi H, Mehrgardi MA, Bouvet P (2017) Carbon dots-AS1411 aptamer nanoconjugate for ultrasensitive spectrofluorometric detection of cancer cells. Sci Rep 7:10513
Naderi M, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR (2018) Naked-eye detection of potassium ions in a novel gold nanoparticle aggregation-based aptasensor. Spectrochim Acta A 195:75–83
Nemati F, Zare-Dorabei R, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR (2018) Fluorescence turn-on sensing of thiamine based on arginine – functionalized graphene quantum dots (Arg-GQDs): central composite design for process optimization. Sensors Actuators B Chem 255:2078–2085
Ramlal S, Mondal B, Lavu PS, Bhavanashri N, Kingston J (2018) Capture and detection of Staphylococcus aureus with dual labeled aptamers to cell surface components. Int J Food Microbiol 265:74–83
Rao H, Ge H, Wang X, Zhang Z, Liu X, Yang Y, Liu Y, Liu W, Zou P, Wang Y (2017) Colorimetric and fluorometric detection of protamine by using a dual-mode probe consisting of carbon quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:3017–3025
Sabet FS, Hosseini M, Khabbaz H, Dadmehr M, Ganjali MR (2017) FRET-based aptamer biosensor for selective and sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 in peanut and rice. Food Chem 220:527–532
Sachdev A, Gopinath P (2015) Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots from coriander leaves and their potential application as antioxidants, sensors and bioimaging agents. Analyst 140:4260–4269
Salehnia F, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR (2017) A fluorometric aptamer based assay for cytochrome C using fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets. Microchim Acta 184:2157–2163
Song KM, Lee S, Ban C (2012) Aptamers and their biological applications. Sensors (Basel) 12:612–631
Sun X, Lei Y (2017) Fluorescent carbon dots and their sensing applications. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 89:163–180
Talhaoui N, Taamalli A, Gómez-Caravaca AM, Fernández-Gutiérrez A, Segura-Carretero A (2015) Phenolic compounds in olive leaves: analytical determination, biotic and abiotic influence, and health benefits. Food Res Int 77:92–108
Templier V, Roupioz Y (2017) On the challenges of detecting whole Staphylococcus aureus cells with biosensors. J Appl Microbiol 123(5):1056–1067
Vasimalai N, Vilas-Boas V, Gallo J, Cerqueira MF, Menéndez-Miranda M, Costa-Fernández JM et al (2018) Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from spices for in vitro imaging and tumor cell growth inhibition. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:530–544
Wang R, Xu Y, Zhang T, Jiang Y (2015) Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using aptamer conjugated carbon dots as fluorescence probe. Anal Methods 7:1701–1706
Wang N, Wang Y, Guo T, Yang T, Chen M, Wang J (2016) Green preparation of carbon dots with papaya as carbon source for effective fluorescent sensing of Iron (III) and Escherichia coli. Biosens Bioelectron 85:68–75
Wang S, Deng W, Yang L, Tan Y, Xie Q, Yao S (2017) Copper-based metal-organic framework nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity for sensitive colorimetric detection of Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(29):24440–24445
Wang T, Wang A, Wang R, Liu Z, Sun Y, Shan G, Chen Y, Liu Y (2019) Carbon dots with molecular fluorescence and their application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for ferricyanide detection. Sci Rep 9:10723
Xu J, Zhou Y, Liu S, Donga M, Huang C (2014) Low-cost synthesis of carbon nanodots from natural products used as a fluo-rescent probe for the detection of ferrum(iii) ions in lake water. Anal Methods 6:2086–2090
Yuan J, Wu S, Duan N, Ma X, Xia Y, Chen J, Ding Z, Wang Z (2014) A sensitive gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric aptasensor for Staphylococcus aureus. Talanta 127:163–168
Zhu L, Yin Y, Wang C-F, Chen S (2013) Plant leaf-derived fluorescent carbon dots for sensing, patterning and coding. J Mater Chem C 1:32
Funding
Financial support was provided by the Faculty of New Sciences and Technologies, Tehran University, Tehran (Iran). This project was funded by the Research Council of University of Tehran and authors gratefully appreciated the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Azam Bagheri Pebdeni·declares that there is no conflict of interest. Morteza Hosseini declares that there is no conflict of interest. Mohammad Reza Ganjali declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 481 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pebdeni, A.B., Hosseini, M. & Ganjali, M.R. Fluorescent Turn-on Aptasensor of Staphylococcus aureus Based on the FRET Between Green Carbon Quantum Dot and Gold Nanoparticle. Food Anal. Methods 13, 2070–2079 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01821-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01821-4