Abstract
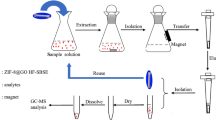
A method of hollow fiber–stir bar sorptive extraction (HF–SBSE) coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry was proposed to explore the migration of eight organochlorine pesticide residues in environmental and biological matrices. HF–SBSE was a configuration for solid–phase microextraction purposes, combining the features of SBSE and hollow fiber membrane extraction technology. Variables affecting the extraction (salt addition, extraction temperature, and time) and desorption (microwave time, eluted solvent) have been evaluated. Under the optimal conditions, good linearity (r > 0.999) of all calibration curves was obtained in validation experiments. The recoveries in different sample matrices were in the range from 69.0 to 114.1% with RSD% less than 10.2%. The bio-accumulation of OCPs was tested in samples of soil, underground water, forage grass, and raw milk. It was indicated that HF-SBSE could be applied in simultaneous extraction of hazardous substances in different matrices without sample clean-up.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur CL, Pawliszyn J (1990) Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal Chem 62:2145–2148
Ballesteros–Gőmez A, Rubio S (2011) Recent advances in environmental analysis. Anal Chem 83:4579–4613
Basheer C, Suresh V, Renu R, Lee HK (2004) Development and application of polymer-coated hollow fiber membrane microextraction to the determination of organochlorine pesticides in water. J Chromatogr A 1033:213–220
Basheer C, Vetrichelvan M, Valiyaveettil S, Lee HK (2007) On-site polymer-coated hollow fiber membrane microextraction and gas chromatography–massspectrometry of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenylethers. J Chromatogr A 1139:157–164
Büchel G, Unger KK, Matsumoto A, Tsutsumi K (1998) A novel pathway for synthesis of submicrometer-size solid core/mesoporous Shell silica spheres. Adv Mater 10:1036–1038
Chiuchiolo AL, Dickhut RM, Cochran MA, Ducklow HW (2004) Persistent organic pollutants at the base of the Antarctic marine food web. Environ Sci Technol 38:3551–3557
De Carvalho PHV, Barreto AS, Rodrigues MO, Prata VD (2009a) Two-dimensional coordination polymer matrix for solid-phase extraction of pesticide residues from plant Cordia salicifolia. J Sep Sci 32:2132–2138
De Carvalho PHV, Prata VD, Alves PB, Navickiene S (2009b) Determination of six pesticides in the medicinal herb Cordia salicifolia by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J AOAC Inter 92:1184–1189
Hwang BH, Lee MR (2000) Solid-phase microextraction for organochlorine pesticide residues analysis in Chinese herbal formulations. J Chromatogr A 898:245–256
Li J, Zhang H–F, Shi Y–P (2011) In-situ synthesis and normal chromatographic properties of nonporous SiO2/ZrO2 core–shell composite microspheres. Anal Sci 27:447–450
Li J, Wang YB, Li KY, Cao YQ, Wu S, Wu L (2015) Advances in different configurations of solid-phase microextraction and their applications in food and environmental analysis. Trend Anal Chem 72:141–152
Nakata H, Hirakawa Y, Kawazoe M, Nakabo T, Arizono K, Abe S–I, Kitano T, Shimada H, Watanabe I, Li W, Ding X (2005) Concentrations and compositions of organochlorine contaminants in sediments, soils, crustaceans, fishes and birds collected from Lake Tai, Hangzhou Bay and Shanghai city region, China. Environ Pollut 133:415–429
Nawrocki J, Rigney MP, McCormick A, Carr PW (1993) Chemistry of zirconia and its use in chromatography. J Chromatogr A 657:229–282
Ochiai N, Ieda T, Sasamoto K, Takazawa Y, Hashimoto S, Fushimi A, Tanabe K (2011) Stir bar sorptive extraction and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry for ultra-trace analysis of organochlorine pesticides in river water. J Chromatogr A 1218:6851–6860
Oh CH (2007) Monitoring of residual pesticides in herbal drug materials of Korea and China. Bull Environ Contam Tox 78:314–318
Ouyang G, Pawliszyn J (2006) Configurations and calibration methods for passive sampling techniques. Trend Anal Chem 25:692–703
Pabby AK, Sastre AM (2013) State-of-the-art review on hollow fibre contactor technology and membrane-based extraction processes. J Membr Sci 430:263–303
Rigney MP, Funkenbusch EF, Carr PW (1990) Physical and chemical characterization of microporous zirconia. J Chromatogr A 499:291–304
Rodil R, Popp P (2006) Development of pressurized subcritical water extraction combined with stir bar sorptive extraction for the analysis of organochlorine pesticides and chlorobenzenes in soils. J Chromatogr A 1124:82–90
Stashenko EE, Martínez JR (2007) Sampling volatile compounds from natural products with headspace/solid-phase micro-extraction. J Biochem Biophys Meth 70:235–242
Tanabe S, Iwata H, Tatsukawa R (1994) Global contamination by persistent organochlorines and their ecotoxicological impact on marine mammals. Sci Total Environ 154:163–177
Tang F, Yue YD, Hua RM, Cao HQ (2006) Matrix solid–phase dispersion microextraction and determination of pesticide residues in medicinal herbs by gas chromatography with a nitrogen-phosphorus detector. J AOAC Inter 89:498–502
Tang S, Zhang H, Lee HK (2016) Advances in sample extraction. Anal Chem 88:228–249
Tsygankov VY, Boyarova MD, Lukyanova ON (2015) Bioaccumulation of persistent organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) by gray whale and Pacific walrus from the western part of the Bering Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 99:235–239
Wania F, Mackay D (1996) Peer reviewed: tracking the distribution of persistent organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 30:390A–396A
Xu L, Lee HK (2007) Zirconia hollow fiber: preparation, characterization, and microextraction application. Anal Chem 79:5241–5248
Xue J, Hao L, Peng F (2008) Residues of 18 organochlorine pesticides in 30 traditional Chinese medicines. Chemosphere 71:1051–1055
Zhao CJ, Hao GM, Li HX, Luo X, Chen YJ (2006) Decontamination of organochlorine pesticides in Radix Codonopsis by supercritical fluid extractions and determination by gas chromatography. Biomed Chromatogr 20:857–863
Acknowledgements
Financial supports from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 21467027 No. 31260500, and No. 51563022) are gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant number 21467027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Hong Li declares that he has no conflict of interest. Wen-Juan Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yan-Bin Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Qiong Su declares that she has no conflict of interest. Lan Wu declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Chinese National Standard, General Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, GB/T 23200.86–2016: National food safety standards–Determination of multiple residue of organochlorine pesticides in milk and dairy products–gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; GB/T5009.146–2008: Determination of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticide multi-residues in vegetable foods; DB22/T 2084–2014: Determination of organochlorine pesticides residues in soil–gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; HJ 699–2014:Water quality– Determination of organochlorine pesticides and chlorobenzenes–Gas chromatography mass spectrometry
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, H., Zhang, WJ. et al. Hollow Fiber–Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry for Determination of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Environmental and Food Matrices. Food Anal. Methods 11, 883–891 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1053-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1053-5