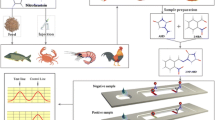
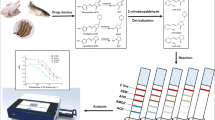
Abstract
Due to their potential adverse effects on human health, the use of carbadox and olaquindox in feedingstuffs was prohibited by the European Union since 1998. In this work, highly luminescent quantum dot beads (QBs) were synthesized by encapsulating CdSe/ZnS and used as novel fluorescent probes in the immunochromatographic assay (ICA) for simultaneous and quantitative determination of metabolites of olaquindox (3-methylquinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid, MQCA) and carbadox (quinoxaline-2-carboxylic, QCA). The fluorescence intensities of the test lines were recorded using a fluorescence strip reader. The 50% of inhibition for MQCA and QCA was shown to be 8.1 and 10.6 μg L−1, respectively. The whole assay process can be accomplished within 10 min. The immunosensor was used to analyze spiked samples, and analyte intra- and inter-assay recovery rates ranged from 78.7 to 92.2% for MQCA and 80.6 to 95.8% for QCA, and coefficients of variation were all below 12%. The incurred tissues samples were assayed using both QB-based ICA and commercial ELISA kit and were further confirmed with LC-MS/MS. The QB-based ICA results exhibited good agreement with both commercial ELISA and LC-MS/MS methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AQSIQ (General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China) (2006) Method for the determination of the residues of carbadox, olaquindox and related metabolites in bovine and porcine liver and muscle tissues: LC-MS/MS method. GBT 20746−2006
Boison JO, Lee SC, Gedir RG (2009) A determinative and confirmatory method for residues of the metabolites of carbadox and olaquindox in porcine tissues. Anal Chim Acta 637:128–134
Commission of the European Communities (2002) Commission Decision (EC) No. 657/2002 of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off J Eur Commun L 221:8–36
Dibai WLS, de Alkimin Filho JF, da Silva Oliveir FA, de Assis DCS, Lara LJC, de Figueiredo TC, de Vasconcelos CS (2015) HPLC-MS/MS method validation for the detection of carbadox and olaquindox in poultry and swine feedingstuffs. Talanta 144:740–744
Duan Z, Yi J, Fang G, Fan L, Wang S (2013) A sensitive and selective imprinted solid phase extraction coupled to HPLC for simultaneous detection of trace quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid and methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in animal muscles. Food Chem 139:274–280
Duan H, Chen X, Xu W, Fu J, Xiong Y, Wang A (2015) Quantum-dot submicrobead-based immunochromatographic assay for quantitative and sensitive detection of zearalenone. Talanta 132:126–131
Huang L, Wang Y, Tao Y, Chen D, Yuan Z (2008) Development of high performance liquid chromatographic methods for the determination of cyadox and its metabolites in plasma and tissues of chicken. J Chromatogr B 874:7–14
Hutchinson M, Young P, Kennedy D (2005) Confirmation of carbadox and olaquindox metabolites in porcine liver using liquid chromatography-electrospray, tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 816:15–20
Jiang WX, Beier RC, Wang ZH, Wu YN, Shen JZ (2013) Simultaneous screening analysis of 3-methyl-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid and quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid residues in edible animal tissues by a competitive indirect immunoassay. J Agric Food Chem 61:10018–10025
Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (1991) Toxicological evaluation of certain veterinary drug residues in food. Food Addit Series 27:175
Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (2003) Carbadox. In: Toxicological evaluation of certain veterinary drug residues in food. Food Addit Series 51:49–59
Kim D, Kim B, Hyung SW, Lee CH, Kim J (2015) An optimized method for the accurate determination of nitrofurans in chicken meat using isotope dilution–liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Food Compos Anal 40:24–31
Kuang H, Xing C, Hao C, Liu L, Wang L, Xu C (2013) Rapid and highly sensitive detection of lead ions in drinking water based on a strip immunosensor. Sensors Mar 28(13):4214–4224
Le T, Xu J, Jia YY, He HQ, Niu XD, Chen Y (2012) Development and validation of an immunochromatographic assay for the rapid detection of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid, the major metabolite of carbadox in the edible tissues of pigs. Food Addit Contam Part A 29:925–934
Le T, Wei S, Niu XD, Liu J (2014) Development of a time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for the rapid detection of methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in porcine tissues. Anal Lett 47:606–615
Le T, Xie Y, Zhu LQ, Zhang L (2016a) Rapid and sensitive detection of 3-amino-2-oxazolidinone using a quantum dot-based immunochromatographic fluorescent biosensor. J Agri Food Chem 64:8678–8683
Le T, Zhu L, Yu H (2016b) Dual-label quantum dot-based immunoassay for simultaneous determination of carbadox and olaquindox metabolites in animal tissues. Food Chem 15(199):70–74
Li GP, Zhao L, Zhou F, Li JY, Xing Y, Wang TG, Zhou XL, Ji BP, Ren WP (2016) Monoclonal antibody production and indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay development of 3-methyl-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid based on novel haptens. Food Chem 209:279–285
Liu ZY, Huang LL, Chen DM, Dai MH, Tao YF, Yuan ZH (2010) The metabolism and N-oxide reduction of olaquindox in liver preparations of rats, pigs and chicken. Toxicol Lett 195:51–59
Lynch MJ, Mosher FR, Schneider RP, Fouda HG, Risk JE (1991) Determination of carbadox-related residues in swine liver by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry with ion trap detection. J AOAC 74:611–618
Peng D, Zhang Z, Chen D, Wang Y, Tao Y, Yuan Z (2011) Development and validation of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for monitoring quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in the edible tissues of animals. Food Addit Contam Part A 28:1524–1533
Peng D, Zhang X, Wang Y, Pan Y, Liu Z, Chen D, Sheng F, Yuan Z (2017) An immunoaffinity column for the selective purification of 3-methyl-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid from swine tissues and its determination by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection and a colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay. Food Chem 237:290–296
Ren M, Xu HY, Huang XL, Kuang M, Xiong Y, Xu H, Xu Y, Chen H, Wang A (2014) Immunochromatographic assay for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 in maize by highly luminescent quantum dot beads. ACS Appl Mater Inter 6:14215–14222
Sin DWM, Chung LPK, Lai MMC, Siu SMP, Tang HPO (2004) Determination of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid, the major metabolite of carbadox, in porcine liver by isotope dilution gas chromatography–electron capture negative ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 508:147–158
Sniegocki T, Gbylik-Sikorska M, Posyniak A, Zmudzki J (2014) Determination of carbadox and olaquindox metabolites in swine muscle by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 944:25–29
Song C, Liu Q, Zhi A, Yang J, Zhi Y, Li Q, Hu X, Deng R, Casas J, Tang L, Zhang G (2011) Development of a lateral flow colloidal gold immunoassay strip for the rapid detection of olaquindox residues. J Agri Food Chem 59:9319–9326
Wu Y, Yu H, Wang Y, Huang L, Tao Y, Chen D, Peng D, Liu Z, Yuan Z (2007) Development of a high-performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous quantification of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid and methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in animal tissues. J Chromatogr A 1146:1–7
Zhang Y, Huang L, Chen D, Fan S, Wang Y, Tao Y, Yuan Z (2005) Development of HPLC methods for the determination of cyadox and its main metabolites in goat tissues. Anal Sci 21:1495–1499
Zhang X, Peng D, Pan Y, Wang Y, Chen D, Zhou Q, Liu Z, Yuan Z (2015) A novel hapten and monoclonal-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for 3-methyl-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in edible animal tissues. Anal Methods 7:6588–6594
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the individuals who helped during the research and would especially like to thank Professor Xudong Cao (Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, University of Ottawa) for his suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments in this study adhered to the Chongqing Normal University animal experiment center guidelines and were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee (number of the using of Laboratory Animal: SYXK(Yu)2012-0006).
Funding
The work was financially supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Project of Chongqing China (Project No. cstc2016shmszx80069), the China Scholarship Council (CSC No. 201608505051), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31671939), and the Chongqing Normal University.
Conflict of Interest
Yong Xie declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lei Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Qi Sun declares that he has no conflict of interest. Zhihao Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Tao Le declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects. All animal experiments that were described in the present study were performed in adherence to Chongqing Normal University animal experiment center guidelines and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Y., Zhang, L., Sun, Q. et al. Immunochromatographic Assay for Simultaneous and Quantitative Detection of 3-Methyl-Quinoxaline-2-Carboxylic Acid and Quinoxaline-2-Carboxylic Acid Residues in Animal Tissues Based on Highly Luminescent Quantum Dot Beads. Food Anal. Methods 11, 334–342 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1003-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1003-2