Abstract
Olaquindox (OLA), used as a medicinal feed additive, has been put under ban due to hazard concerns over animal-derived food security. In this study, a simple, rapid, ultrasensitive, and quantitative gold immunochromatography assay (GICA) was established to analyze OLA in animal feed samples and surface water samples to monitor food security. Various trying has been experimented to improve the sensitivity. The IC50 of the optimized method is 3.35 μg L−1 for feedstuff and 0.35 μg L−1 for environmental water. The recoveries ranged from 77.33 to 86.91 % (CV <23.62 %) for spiked feedstuff and 96.30 to 117.83 % (CV <22.51 %) for spiked water samples. Then, the developed GICA was applied to animal feed and field water, followed by confirmation with ELISA and the consistency of results indicated that the developed GICA could be applied for rapid screening of OLA in real samples. Compared with previous assay, the developed GICA in this study was more sensitive and more rapid, which exhibited broader prospect to supervise the animal products and water rapidly.

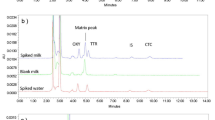
Schematic illustration of the test strip









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belhadjali C, Marguery MC, Journe F, Giordano LF, Lefebvre H (2002) Bazex, J. Allergic and photoallergic contact dermatitis to olaquindox in a pig breeder with prolonged photosensitivity. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 18:52–53
Cheng LL (2013) Studies on residue determination of quinoxalines in animal tissues. China Agricultural University, China, pp 22–24
Cheng LL, Shen JZ, Wang ZH, Zhang QD, Dong XY, Wu C, Zhang SX (2013) Rapid screening of quinoxaline antimicrobial growth promoters and their metabolites in swine liver by indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Food Anal Methods 6(6):1583–1591
Czekalski N, Sigdel N, Birtel J, Matthews M, Bürgmanna H (2015) Does human activity impact the natural antibiotic resistance background? Abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in 21 Swiss lakes. Environ Int 81:45–55
Duan ZJ, Fan LP, Guo ZF, Jiang HY, Shuo W (2011) Novel surface molecularly imprinted sol–gel polymer applied to the online solid phase extraction of methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid and quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid from pork muscle. Anal Bioanal Chem 401(7):2291–2299
Haiss W, Thanh NT, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV–vis spectra. Anal Chem 79:4215–4221
Ihsana A, Wang X, Zhang W, Tu HG, Wang YL, Huang LL, Iqbala Z, Cheng GY, Pan YH, Liu ZL, Tan ZQ, Zhang YY, Yuan ZH (2013) Genotoxicity of quinocetone, cyadox and olaquindox in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem Toxicol 59:207–214
Lee JY, Kim YA, Kim MY, Lee YT, Hammock BD, Lee HS (2012) Importance of membrane selection in the development of immunochromatographic assays for low-molecular weight compound. Anal Chim Acta 757:69–74
Lee WN, Lin AY, Wang XH (2015) The occurrence of quinolone and imidazole antibiotics in rivers in Central Taiwan. Desalin Water Treat 52(4–6):1143–1152
Leung HW, Jin L, Wei S, Mirabelle MP, Zhou BS, Jiao LP, Cheung PC, Chun YK, Murphy MB, Lam PK (2013) Pharmaceuticals in tap water: human health risk assessment and proposed monitoring framework in China. Environ Health Perspect 121(7):839–846
Li K, Zhao DY, Guo MJ (2013) Determination of olaquindox in freshwater fish by HPLC. Occup Health 29(3):322–324
Liu ZY, Huang LL, Chen DM, Dai MH, Tao YF, Yuan ZH (2010) The metabolism and N-oxide reduction of olaquindox in liver preparations of rats, pigs and chicken. Toxicol Lett 195:51–59
Neumann NJ, Blotz A, Wasinska KG, Rosenbruch M, Lehmann P, Ahr HG, Vohr HW (2005) Evaluation of phototoxic and photoallergic potentials of 13 compounds by different in vitro and in vivo methods. Photochem Photobiol B 79:25–34
Sniegocki T, Gbylik-Sikorska M, Posyniak A, Zmudzki J (2014) Determination of carbadox and olaquindox metabolites in swine muscle by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 944:25–29
Song J, Qiao X, Chen H, Zhao D, Zhang Y, Xu Z (2010) Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for analysis of trace olaquindox residues in chick feeds. J Sci Food Agric 91(13):2378–2385
Song CM, Liu QT, Zhi AM, Yang JY, Zhi YB, Li QM, Hu XF, Deng RG, Casas J, Tang L (2011) Development of a lateral flow colloidal gold immunoassay strip for the rapid detection of olaquindox residues. J Agric Food Chem 59:9319–9326
Tong L, Huang SB, Wang YX, Liu H, Li MJ (2014) Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment of Jianghan Plain, central China. Sci Total Environ 497:180–187
Uslu MO, Jasim S, Arvai A, Bewtra J, Biswas N (2013) A survey of occurrence and risk assessment of pharmaceutical substances in the Great Lakes Basin. Ozone: Sci Eng: J Int Ozone Assoc 35(4):249–262
Wang L, Wang S, Zhang JY, Liu JW, Zhang Y (2008) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and colloidal gold immunoassay for sulphamethazine residues in edible animal foods: investigation of the effects of the analytical conditions and the sample matrix on assay performance. Anal Bioanal Chem 390(6):1619–1627
Wang N, Shan ZJ, Ge F, Chen CB, Jiao SJ, Gao SX (2012) Ecological risk assessment of olaquindox based on model prediction. J Ecol Rural Environ 28(6):732–737
Wang D, Tian Z, Zhang J (2013) Rapid detection of Bacillus anthracis spores using a super-paramagnetic lateral-flow immunological detection system. Biosens Bioelectron 42:661–667
Wang L, Zhang JY, Cui DG, Wang XZ, Yang ZQ, Zhang K, Qin Z, Meng JR, Hao GJ, Li JX (2014) A monoclonal antibody-based indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of olaquindox in animal feed. Anal Lett 47(6):1015–1030
Wang X, Zhang HH, Huang LL, Pan YH, Li J, Chen DM, Cheng GY, Hao HH, Tao YY, Liu ZL, Yuan ZH (2015) Deoxidation rates play a critical role in DNA damage mediated by important synthetic drugs, quinoxaline 1,4-dioxides. Chem Res Toxicol 28(3):470–481
Xiao YH, Stuart NI (2012) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and blocking with bovine serum albumin (BSA)-not all BSAs are alike. J Immunol Methods 384(1–2):148–151
Yan DD, He LM, Zhang GJ, Fang BH, Yong Y, Li Y (2012) Simultaneous determination of cyadox and its metabolites in chicken tissues by LC-MS/MS. Food Anal Methods 5(6):1497–1505
Zhang HY, Wei YW, Zhou JH, Xu ZX, Xian S, Huang H, He JX (2013) Preparation and application of a molecular imprinting matrix solid phase dispersion extraction for the determination of olaquindox in chicken by high performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal Methods 6:915–921
Zhao DY, Shi QY, He X, Zhang Z (2014) A novel sorbent for solid-phase extraction coupling to high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of olaquindox in fish feed. Czech J Food Sci 32(5):449–455
Zhou QX, Fang Z (2015) Highly sensitive determination of sulfonamides in environmental water samples by sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate enhanced micro-solid phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 141:170–174
Zhou T, Wei LJ, Chen XL (2013) Development of colloidal gold immunochromatographic strip for rapid detection of olaquindox residues (in Chinese). Chin J Health Lab Tech 23(17):3322–3324
Zhou J, Zhu K, Xu F, Jun WJ, Jiang HY, Wang ZH, Ding SY (2014) Development of a microsphere-based fluorescence immunochromatographic assay for monitoring lincomycin in milk, honey, beef, and swine urine. J Agric Food Chem 62(49):12061–12066
Zou JJ, Chen Q, Jin X, Tang SS, Chen KP, Zhang T, Xiao XL (2011) Olaquindox induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in HepG2 cells. Toxicology 285:104–113
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Special Research Project of Public Welfare Quality Testing Industry (2012104003) and the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the 12th 5-year Plan Period (2015BAK36B03). And the authors appreciate the cooperation of other faculty members in the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology of the College of Veterinary Medicine at China Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
Xingyao Pei declares that she has no conflict of interest. Qi Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Xiangmei Li declares that she has no conflict of interest. Jie Xie declares that she has no conflict of interest. Sanlei Xie declares that he has no conflict of interest. Tao Peng declares that he has no conflict of interest. Cheng Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yuanze Sun declares that she has no conflict of interest. Haiyang Jiang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Not applicable (It is not applicable on the study).
Funding
This study was funded by the Special Research Project of Public Welfare Quality Testing Industry (2012104003) and the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the 12th 5-year Plan Period (2015BAK36B03).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, X., Wang, Q., Li, X. et al. Provision of Ultrasensitive Quantitative Gold Immunochromatography for Rapid Monitoring of Olaquindox in Animal Feed and Water Samples. Food Anal. Methods 9, 1919–1927 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0360-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0360-y