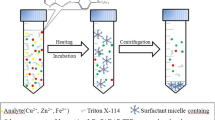
Abstract
A new indirect ultrasonic-assisted cloud point extraction (UA-CPE) method has been developed for the determination of trace sulfite species by means of spectrophotometry. The method is based on either directly imide–bisulfite adducts formation or ion-pairing complexation of enolate–bisulfite adducts produced by the oxidation of pyrogallol with sulfite at pH 10 with 3-amino-7-diethylamino-8,9-benzo-2-phenoxazine chloride (Nile blue A) and CPE of ion-pairing complex formed from aqueous solution using Triton X-114. Under the optimized conditions, the calibration graphs with and without bromide were highly linear in the ranges of 6–180 and 7.5–180 μg L−1 with changing sensitivity. The limits of detection and quantification (LOD and LOQ) (3σ blank/m and 10σ blank/m) with bromide was 1.75 and 5.83 μg L−1 (n = 6) and the precision, the relative standard deviations (RSDs), for determination of 25, 75, and 150 μg L−1 of sulfite was in range of 2.40–5.20 % (n = 10). The method showed good selectivity, and was successfully applied to the speciative determination of trace sulfite in selected beverages with and without alcohol. The results were compared with those of the standard 5,5′-dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic acid (DTNB) method, and the two paired t test was used to determine whether the results obtained by the two methods differ significantly.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonov L, Gergov G, Petrov V, Kubista M, Nygren J (1999) UV–Vis spectroscopic and chemometric study on the aggregation of ionic dyes in water. Talanta 49:99–106
Armstrong JK, Chowdhry BZ, Snowden MJ, Leharne SA (1998) Effect of sodium chloride upon micellization and phase separation transitions in aqueous solutions of triblock copolymers: a high-sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry study. Langmuir 14:2004–2010
Claudia RC, Francisco JC (2009) Application of flow injection analysis for determining sulphites in food and beverages: a review. Food Chem 112(2):487–493
Cmelík J, Machát J, Otruba V, Kanický V (2010) Contribution to vapor generation-inductively coupled plasma spectrometric techniques for determination of sulfide in water samples. Talanta 80:1777–1781
Colon M, Todoli JL, Hidalgo M, Iglesias M (2008) Development of novel and sensitive methods for the determination of sulfide in aqueous samples by hydrogen sulfide generation-inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta 609:160–168
Degui T, Santschi PH (2000) Sensitive determination of dissolved sulfide in estuarine water by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography of methylene blue. J Chromatogr A 883:305–309
Filik H, Çetintaş G (2012) Determination of sulfite in water and dried fruit samples by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with uv–vis fiber optic linear array spectrophotometry. Food Anal Methods 5:1362–1367
Filik H, Giray D, Ceylan B, Apak R (2011) A novel fiber optic spectrophotometric determination of nitrite using Safranin O and cloud point extraction. Talanta 85:1818–1824
Fulda B, Voegelin A, Ehlert K, Kretzschmar R (2013) Redox transformation, solid phase speciation and solution dynamics of copper during soil reduction and reoxidation as affected by sulfate availability. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 123:385–402
Garcia T, Casero E, Lorenzo E, Pariente F (2005) Electrochemical sensor for sulfite determination based on iron hexacyanoferrate film modified electrodes. Sensors Actuators B 106:803–809
Gómez-Otero E, Costas M, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2014) Ultrasensitive, simple and solvent-free micro-assay for determining sulphite preservatives (E220–228) in foods by HS-SDME and UV–vis micro-spectrophotometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:2133–2140
Gu T, Galera-Gomez PA (1995) Clouding of Triton X-114: the effect of added electrolytes on the cloud point of Triton X-114 in the presence of ionic surfactants. Colloid Surf A 104:307–312
Gürkan R, Yılmaz Ö (2013) Indirect quantification of trace levels cyanide in environmental waters through flame atomic absorption spectrometry coupled with cloud point extraction. J Iran Chem Soc 10:631–642
Gürkan R, Yılmaz Ö (2013) Cloud point extraction of trace cyanide from environmental waters for indirect flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Toxicol Environ Chem 95:1455–1469
Hassan SSM, Mohamed SA, Ayman HKM (2006) A novel spectrophotometric method for batch and flow injection determination of sulfite in beverages. Anal Chim Acta 570:232–239
Isaac A, Livingstone C, Wain AJ, Compton RG, Davis J (2006) Electroanalytical methods for the determination of sulfite in food and beverages. Trends Anal Chem 25(6):589–598
Komaromy-Hiller G, Calkins N, Wandruszka R (1996) Changes in polarity and aggregation number upon clouding of a nonionic detergent: effect of ionic surfactants and sodium chloride. Langmuir 12:916–920
Li Y, Zhao M (2006) Simple methods for rapid determination of sulfite in food products. Food Control 17:975–980
Liao BS, Jacqueline CS, Darin JF (2013) Determination of free sulfites (SO3 –2) in dried fruits processed with sulfur dioxide by ion chromatography through anion exchange column and conductivity detection. J AOAC Int 96:1103–1108
Machado RMD, Toledo MCF, Almeida CAS, Vicente E (2008) Analytical determination of sulphites in fruit juices available on the Brazilian market. Braz J Food Technol 11(3):226–233
Madsen J, Canton I, Warren NJ, Themistou E, Blanazs A, Ustbas B, Tian X, Pearson R, Battaglia G, Lewis AL, Steven AL, Armes P (2013) Nile blue-based nanosized pH sensors for simultaneous far-red and near-infrared live bioimaging. J Am Chem Soc 135:14863–14870
Matthias K, Köppen R, Siegel D, Witt A, Nehls I (2010) Determination of total sulfite in wine by ion chromatography after in-sample oxidation. J Agric Food Chem 58:9463–9467
McFeeters RF, Barish AO (2003) Sulfite analysis of fruits and vegetables by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with ultraviolet spectrophotometric detection. J Agric Food Chem 51:1513–1517
Nascentes CC, Arruda MAZ (2003) Cloud point formation based on mixed micelles in the presence of electrolytes for cobalt extraction and preconcentration. Talanta 61:759–768
Niazi A, Yazdanipour A, Ghasemi J, Kubista M (2006) Spectrophotometric and thermodynamic study on the dimerization equilibrium of ionic dyes in water by chemometrics method. Spectrochim Acta A 65(1):73–78
Pérez EL, Ríos A, Valcárcel M (1998) Flow-injection spectrophotometric determination of citric acid in beverages based on a photochemical reaction. Anal Chim Acta 366:231–240
Safizadeh F, Larachi F (2014) Speciation of sulfides and cyanicides in the cyanidation of precious metal bearing ores using capillary electrophoresis—a review. Instrum Sci Technol 42:215–229
Sakchai S, Phongdong P, Liawruangrath S (2010) Pervaporation flow injection analysis for the determination of sulphite in food samples utilising potassium permanganate—rhodamine B chemiluminescence detection. Food Chem 121:893–898
Santosh KV, Manas KD (2007) Single-drop and nanogram level determination of sulfite (SO3 2−) in alcoholic and nonalcoholic beverage samples based on diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic (DRS-FTIR) analysis on KBr matrix. .J. Agri. Food Chem 21:8319–8324
Sarudi I, Kelemen J (1998) Determination of sulphur and total sulphur dioxide in wines by an ICP-AES method. Talanta 45:1281–1284
Segundo MA, Rangel AOSS (2001) A gas diffusion sequential injection system for the determination of sulphur dioxide in wines. Anal Chim Acta 427:279–286
Vally HK, Thompson N (2000) Alcoholic drinks: important triggers for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105:462–467
Wang L, Xu L (2014) Cyclic voltammetric determination of free and total sulfite in muscle foods using an acetyl ferrocene–carbon black–poly(vinyl butyral) modified glassy carbon electrode. J Agric Food Chem 62:10248–10253
Wang T, Gao X, Tong J, Chen L (2012) Determination of formaldehyde in beer based on cloud point extraction using 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine as derivative reagent. Food Chem 131:1577–1582
Wen X, Zhang Y, Li C, Fang X, Zhang X (2014) Comparison of rapidly synergistic cloud point extraction and ultrasound-assisted cloud point extraction for trace selenium coupled with spectrophotometric determination. Spectrochim Acta A 123:200–205
Wu F, Tong B, Wei X, Chen L (2012) Chemiluminescence determination of sulphite using a cyclometalated iridium complex as chemiluminescence reagent. Luminescence 27:519–523
Yang XF, Guo XQ, Zhao YB (2002) Novel spectrofluorimetric method for the determination of sulfite with rhodamine B hydrazide in a micellar medium. Anal Chim Acta 456:121–128
Zarei AR (2009) Sequential spectrophotometric determination of trace amounts of periodate and iodate in water samples after micelle-mediated extraction. J Anal Chem 64:896–902
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Cumhuriyet University Scientific Research Projects Commission (CUBAP), Sivas in Turkey, for their financial assistance. Thanks are also due to Prof. Dr. Mehmet Akçay for his meaningful help and contributions in the critical evaluation and publication step of the presented research article.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
► A simple method is proposed to determine sulfite species in selected beverages.
► The method is based on interaction of bisulfite with Nile blue A in presence of pyrogallol at pH 10.
► Then, it was successfully used in separation/preconcentration of sulfite from matrix with CPE.
► The UA-CPE was coupled to UV-VIS for reliable monitoring of free and total sulfite in beverages.
► The analytical variables affecting UA-CPE efficiency were optimized.
► The method is simple, inexpensive, and eco-friendly.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altunay, N., Gürkan, R. & Sertakan, K. Indirect Determination of Free, Total, and Reversibly Bound Sulfite in Selected Beverages by Spectrophotometry Using Ultrasonic-Assisted Cloud Point Extraction as a Preconcentration Step. Food Anal. Methods 8, 2094–2106 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0094-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0094-x