Abstract
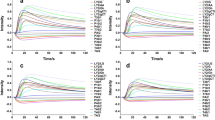
The potential of a gas chromatography (GC)-based electronic nose (E-nose) combined with chemometrics to classify Chinese rice wine by wine age was investigated. Olfactive fingerprints of 1-, 3-, and 5-year Chinese rice wine samples collected by the E-nose were analyzed by principal component analysis (PCA) and discriminant analysis (DA). Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was used for wine age validation purpose. The results indicated that the percentage of samples correctly classified by the E-nose was 96.88 %. It was concluded that the GC-based E-nose together with DA was a reliable method for wine age discrimination.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcalde-Eon C, Escribano-Bailon MT, Santos-Buelga C, Rivas-Gonzalo JC (2006) Changes in the detailed pigment composition of red wine during maturity and ageing. A comprehensive study. Anal Chim Acta 563(1–2):238–254
Aleixandre M, Lozano J, Gutierrez J, Sayago I, Fernandez MJ, Horrillo MC (2008) Portable e-nose to classify different kinds of wine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 131(1):71–76
Bartlett PN, Elliot JE, Gardner JW (1997) Electronic noses and their application in the food industry. Food Technol 51(12):44–48
Bellomarino SA, Parker RM, Conlan XA, Barnett NW, Adams MJ (2010) Partial least squares and principal components analysis of wine vintage by high performance liquid chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 678(1):34–38
Berna AZ, Trowell S, Cynkar W, Cozzolino D (2008) Comparison of metal oxide-based electronic nose and mass spectrometry-based electronic nose for the prediction of red wine spoilage. Sensors Actuators B Chem 56(9):3238–3244
Berna AZ, Trowell S, Clifford D, Cynkar W, Cozzolino D (2009) Geographical origin of Sauvignon Blanc wines predicted by mass spectrometry and metal oxide based electronic nose. Anal Chim Acta 648(2):146–152
Boido E, Alcalde-Eon C, Carrau F, Dellacassa E, Rivas-Gonzalo JC (2006) Aging effect on the pigment composition and color of Vitis vinifera L. Cv. Tannat wines. Contribution of the main pigment families to wine color. J Agric Food Chem 54(18):6692–6704
Capone S, Tufariello M, Francioso L, Montagna G, Casino F, Leone A, Sicilian P (2013) Aroma analysis by GC/MS and electronic nose dedicated to Negroamaro and Primitivo typical Italian Apulian wines. Sensors Actuators B Chem 179:259–269
Chen S, Xu Y (2010) The influence of yeast strain on the volatile flavor compounds of Chinese rice wine. J Inst Brew 116:190–196
Cozzolino D, Smyth HE, Cynkar W, Dambergs RG, Gishen M (2005) Usefulness of chemometrics and mass spectrometry-based electronic nose to classify Australian white wines by their varietal origin. Talanta 68(2):382–387
Cynkar W, Dambergs R, Smith P, Cozzolino D (2009) Classification of Tempranillo wines according to geographic origin: Combination of mass spectrometry based electronic nose and chemometrics. Anal Chim Acta 660(1–2):227–231
Ebeler SE, Spaulding RS (1999) Characterization and measurement of aldehydes in wine. In: Waterhouse AL, Ebeler SE (eds) Chemistry of Wine Flavor. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 166–179
Fan W, Qian MC (2005) Headspace solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography–olfactometry dilution analysis of young and aged Chinese “Yanghe Daqu” liquors. J Agric Food Chem 53(20):7931–7938
Fang F, Li JM, Pan QH, Huang WD (2007) Determination of red wine flavonoids by HPLC and effect of aging. Food Chem 101(1):428–433
Garcia M, Aleixandre M, Gutierrez J, Horrillo MC (2006a) Electronic nose for wine discrimination. Sensors Actuators B Chem 113(2):911–916
Garcia M, Fernandez MJ, Fontecha JL, Lozano J, Santos JP, Aleixandre M, Sayago I, Gutierrez J, Horrillo MC (2006b) Differentiation of red wines using an electronic nose based on surface acoustic wave devices. Talanta 68(4):1162–1165
Hernandez T, Estrella I, Carlavilla D, Martin-Alvarez PJ, Moreno-Arribas MV (2006) Phenolic compounds in red wine subjected to industrial malolactic fermentation and ageing on lees. Anal Chim Acta 563(1–2):116–125
Hernanz D, Gallo V, Recamales AF, Melendez-Martínez AJ, Gonzalez-Miret ML, Heredia FJ (2009) Effect of storage on the phenolic content, volatile composition and colour of white wines from the varieties Zalema and Colombard. Food Chem 113(2):530–537
Jaitz L, Siegl K, Eder R, Rak G, Abranko L, Koellensperger G, Hann S (2010) LC–MS/MS analysis of phenols for classification of red wine according to geographic origin, grape variety and vintage. Food Chem 122(1):366–372
Jelen HH, Majcher M, Dziadas M, Zawirska-Wojtasiak R, Czaczyk K, Wasowicz E (2011) Volatile compounds responsible for aroma of Jutrzenka liquer wine. J Chromatogr A 1218(42):7566–7573
Johnsson L, Dutta PC (2005) Separation of phytosterol oxidation products by combination of different polarity gas chromatography capillary columns. J Chromatogr A 1064(2):213–217
Legin A, Rudnitskaya A, Lvovaa L, Vlaso Y, Natale CD, D’Amico A (2003) Evaluation of Italian wine by the electronic tongue: recognition, quantitative analysis and correlation with human sensory perception. Anal Chim Acta 484(1):33–44
Li J (2001) Sources of color components, aroma components and taste components in yellow rice wine. Liquor Mak Sci Technol 105:48–50
Li M, Zhao Y, Zhou S, Xing W (2010) Clarification of raw rice wine by ceramic microfiltration membranes and membrane fouling analysis. Desalination 256(1–3):166–173
Liu F, He Y, Wang L, Pan H (2007) Feasibility of the use of visible and near infrared spectroscopy to assess soluble solids content and pH of rice wines. J Food Eng 83(3):430–435
Lozano J, Santos JP, Horrillo MC (2005) Classification of white wine aromas with an electronic nose. Talanta 67(3):610–616
Lozano J, Santos JP, Gutierrez J, Horrillo MC (2007) Comparative study of sampling systems combined with gas sensors for wine discrimination. Sensors Actuators B Chem 126(2):616–623
Lozano J, Arroyo T, Santos JP, Cabellos JM, Horrillo MC (2008) Electronic nose for wine ageing detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 133(1):180–186
Luo T, Fan W, Xu Y (2008) Characterization of volatile and semi-volatile compounds in chinese rice wines by headspace solid phase microextraction followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Inst Brew 114(2):172–179
Pereira AC, Reis MS, Saraiva PM, Marques JC (2010a) Aroma ageing trends in GC/MS profiles of liqueur wines. Anal Chim Acta 659(1–2):93–101
Pereira AC, Reis MS, Saraiva PM, Marques JC (2010b) Analysis and assessment of Madeira wine ageing over an extended time period through GC–MS and chemome tric analysis. Anal Chim Acta 660(1–2):8–21
Pereira AC, Reis MS, Saraiva PM, Marques JC (2011) Madeira wine ageing prediction based on different analytical techniques: UV–vis, GC-MS, HPLC-DAD. Chemometr Intell Lab 105(1):43–55
Peris M, Escuder-Gilabert L (2009) A 21st century technique for food control: Electronic noses. Anal Chim Acta 638(1):1–15
Ragazzo-Sanchez JA, Chalier P, Chevalier D, Ghommidh C (2006) Electronic nose discrimination of aroma compounds in alcoholised solutions. Sensors Actuators B Chem 114(2):665–673
Ragazzo-Sanchez JA, Chalier P, Chevalier D, Calderon-Santoyo M, Ghommidh C (2008) Identification of different alcoholic beverages by electronic nose coupled to GC. Sensors Actuators B Chem 134(1):43–48
Ragazzo-Sanchez JA, Chalier P, Chevalier-Lucia D, Calderon-Santoyo M, Ghommidh C (2009) Off-flavours detection in alcoholic beverages by electronic nose coupled to GC. Sensors Actuators B Chem 140(1):29–34
Rock F, Barsan N, Weimar U (2008) Electronic nose: current status and future trends. Chem Rev 108(2):705–725
Shen F, Ying Y, Li B, Zheng Y, Zhuge Q (2011) Multivariate classification of rice wines according to ageing time and brand based on amino acid profiles. Food Chem 129(2):565–569
Shen F, Li F, Liu D, Xu H, Ying Y, Li B (2012) Ageing status characterization of Chinese rice wines using chemical descriptors combined with multivariate data analysis. Food Control 25(2):458–463
Wang B, Xu S, Sun DW (2010) Application of the electronic nose to the identification of different milk flavorings. Food Res Int 43(1):255–262
Xu R, Bao Z, Pan X, Hu P (2003) Maurtization of Chinese rice wine. Liquor Mak 30:50–52
Yu H, Lin H, Xu H, Ying Y, Li B, Pan X (2008) Prediction of enological parameters and discrimination of rice wine age using least-squares support vector machines and near infrared spectroscopy. J Agric Food Chem 56(2):307–313
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21105065), Special Funds for National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of China (No.201059), and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 10ZR1429600).
Conflict of Interest
Haiyan Yu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Xin Dai declares that she has no conflict of interest. Guiyan Yao declares that she has no conflict of interest. Zuobing Xiao declares that he has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Dai, X., Yao, G. et al. Application of Gas Chromatography-Based Electronic Nose for Classification of Chinese Rice Wine by Wine Age. Food Anal. Methods 7, 1489–1497 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9778-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9778-2