Abstract
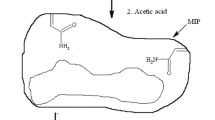
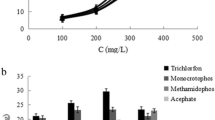
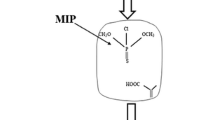
How to determine the pesticide residues in vegetable is an urgent problem. In this study, we reported a new method of solid-phase extraction coupled to capillary electrophoresis (SPE–CE) based on a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for determination of trace trichlorfon. The electrophoretic conditions and factors which affected the molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction were optimized. Under optimal conditions, the linear ranges of the calibration graph were 0.1 μg/L to 10 mg/L. The limit of detection (LOD) and method quantitation limit (MQL) were 4.9 and 16.2 μg/kg, respectively. With a flow rate of 2.5 mL/min for 50 mL loading, an enrichment factor of 160 was obtained. The relative standard deviation (RSD) for five replicate extractions of 0.01 mg/L trichlorfon standard solution was 4.5 %. The blank cucumber, lettuce, and radish samples spiked with trichlorfon at three levels were extracted and determined by this presented method with recoveries ranging from 77.6 to 93.2 %. Moreover, this proposed methodology was successfully applied to the quantitative detection of the trichlorfon residues in the leek samples, and the results were in good agreement with that obtained by the gas chromatography method.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berijani S, Assadi Y, Anbia M, Hosseini MM, Aghaee E (2006) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with gas chromatography-flame photometric detection: Very simple, rapid and sensitive method for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water. J Chromatogr A 1123:1–9
Bui BTS, Haupt K (2010) Molecularly imprinted polymers: synthetic receptors in bioanalysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:2481–2492
Chen XM, Lin ZJ, Cai ZM, Chen X, Wang XR (2008) Electrochemiluminescence detection of dichlorvos pesticide in luminal-CTAB medium. Talanta 76:1083–1087
Gallart-Ayala H, Nunez O, Moyano E, Galceran MT (2010) Field-amplified sample injection-micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography for the analysis of bisphenol A, bisphenol F, and their diglycidyl ethers and derivatives in canned soft drinks. Electrophoresis 31:1550–1557
Gong SL, Yu ZJ, Meng LZ, Hu L, He YB (2004) Dye-molecular-imprinted polysiloxanes. II. Preparation, characterization, and recognition behavior. J Appl Polym Sci 93:637–643
Haginaka J (2004) Non-covalent molecular imprinting with emphasis on its application in separation and drug development. Anal Bioanal Chem 379:332–334
He Y, Lee HK (2006) Continuous flow microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for the analysis of pesticides in natural waters. J Chromatogr A 1122:7–12
He LJ, Luo XL, Xie HX, Wang CJ, Jiang XM, Lu K (2009) Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water sample. Anal Chim Acta 655:52–59
Lee EK, Kim YJ, Park WC, Chung T, Lee YT (2006) Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of the organophosphorus insecticide isofenphos. Anal Chim Acta 557:169–178
Li X, Chu S, Fu S, Ma L, Liu X, Xu X (2005) Off-line concentration of bisphenol A and three alkylphenols by SPE then on-line concentration and rapid separation by reverse-migration micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Chromatographia 61:161–166
Li L, Zhou SS, Jin LX, Zhang C, Liu WP (2010) Enantiomeric separation of organophosphorus pesticides by high-performance liquid chromatography, gas chromatography and capillary electrophoresis and their applications to environmental fate and toxicity assays. J Chromatogr B 878:1264–1276
Martin-Esteban A (2004) Molecular imprinting technology: a simple way of synthesizing biomimetic polymeric receptors. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1875
Mei S, Wu D, Jiang M et al (2011) Determination of trace bisphenol A in complex samples using selective molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with capillary electrophoresis. Microchem J 98:150–155
Meng L, Qiao XG, Song JM, Xu ZX, Xin JH, Zhang Y (2011) Study of an online molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction coupled to chemiluminescence sensor for the determination of trichlorfon in vegetables. J Agric Food Chem 59:12745–12751
Pang GF, Liu YM, Fan CL et al (2006) Simultaneous determination of 405 pesticide residues in grain by accelerated solvent extraction then gas chromatography-mass spectrometry or liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 384:1366–1408
Peter JV, Prabhakar AT, Pichamuthu K (2008) Delayed-onset encephalopathy and coma in acute organophosphate poisoning in humans. Neurotoxicology 29:335–342
Shen X, Su QD (2007) Determination of pesticide residues in soil by modified matrix solid‐phase dispersion and gas chromatography. Anal Chem 97:647–653
Sun X, Wang XY (2010) Acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on prussian blue-modified electrode for detecting organophosphorous pesticides. Biosens Bioelectron 25:2611–2614
Sun F, Betzendahl I, Van Wemmel K et al (2008) Trichlorfon-induced polyploidy and nondisjunction in mouse oocytes from preantral follicle culture. Mutat Res 651:114–124
Takeda S, Omura A, Chayama K et al (2003) Separation and on-line concentration of bisphenol A and alkylphenols by micellar electrokinetic chromatography with anionic surfactant. J Chromatogr A 1014:103–107
Turiel E, Martin-Esteban A (2004) Molecularly imprinted polymers: towards highly selective stationary phases in liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1876–1886
Xu ZX, Fang GZ, Wang S (2010) Molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography for determination of trace dichlorvos residues in vegetables. Food Chem 119:845–850
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31171699), the Post-doctoral Innovation Foundation of Shandong Province, China (no. 200902012) and Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (no. J11LC30).
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
We have no financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research. Dr. Zhixiang Xu has received research grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Department of Human Resources and Social Security of Shandong Province, and the Department of Education of Shandong Province.
Conflict of Interest
Tao Zhao has no conflict of interest. Huiju Gao has no conflict of interest. Xilong Wang has no conflict of interest. Limin Zhang has no conflict of interest. Xuguang Qiao has no conflict of interest. Zhixiang Xu has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Huiju Gao and Tao Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, T., Gao, H., Wang, X. et al. Study on a Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled to Capillary Electrophoresis Method for the Determination of Trace Trichlorfon in Vegetables. Food Anal. Methods 7, 1159–1165 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9729-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9729-y