Abstract
Objective
To improve the spatial resolution of brain single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), we propose a new brain SPECT system in which the detector heads are tilted towards the rotation axis so that they are closer to the brain. In addition, parallel detector heads are used to obtain the complete projection data set. We evaluated this parallel and tilted detector head system (PT-SPECT) in simulations.
Methods
In the simulation study, the tilt angle of the detector heads relative to the axis was 45°. The distance from the collimator surface of the parallel detector heads to the axis was 130 mm. The distance from the collimator surface of the tilted detector heads to the origin on the axis was 110 mm. A CdTe semiconductor panel with a 1.4 mm detector pitch and a parallel-hole collimator were employed in both types of detector head. A line source phantom, cold-rod brain-shaped phantom, and cerebral blood flow phantom were evaluated. The projection data were generated by forward-projection of the phantom images using physics models, and Poisson noise at clinical levels was applied to the projection data. The ordered-subsets expectation maximization algorithm with physics models was used. We also evaluated conventional SPECT using four parallel detector heads for the sake of comparison.
Results
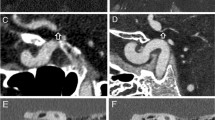
The evaluation of the line source phantom showed that the transaxial FWHM in the central slice for conventional SPECT ranged from 6.1 to 8.5 mm, while that for PT-SPECT ranged from 5.3 to 6.9 mm. The cold-rod brain-shaped phantom image showed that conventional SPECT could visualize up to 8-mm-diameter rods. By contrast, PT-SPECT could visualize up to 6-mm-diameter rods in upper slices of a cerebrum. The cerebral blood flow phantom image showed that the PT-SPECT system provided higher resolution at the thalamus and caudate nucleus as well as at the longitudinal fissure of the cerebrum compared with conventional SPECT.
Conclusion
PT-SPECT provides improved image resolution at not only upper but also at central slices of the cerebrum.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsuchiya K, Takahashi I, Kawaguchi T, Yokoi K, Morimoto Y, Ishitsu T, et al. Basic performance and stability of a CdTe solid-state detector panel. Ann Nucl Med. 2010;24:301–11.
Kouris K, Clarke GA, Jarritt PH, Townsend CE, Thomas SN. Physical performance evaluation of the Toshiba GCA-9300A triple-head system. J Nucl Med. 1993;34:1778–89.
Laere KV, Koole M, Kauppinen T, Monsieurs M, Bouwens L, Dierck R. Nonuniform transmission in brain SPECT using 201Tl, 153Gd, and 99mTc static line sources: anthropomorphic dosimetry studies and influence on brain quantification. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:2051–62.
Suzuki A, Takeuchi W, Ishitsu T, Tsuchiya K, Ueno Y, Kobashi K. A four-pixel matched collimator for high-sensitivity SPECT imaging. Phys Med Biol. 2013;58:2199–217.
Suzuki A, Takeuchi W, Ishitsu T, Tsuchiya K, Morimoto Y, Ueno Y, et al. High-sensitivity brain SPECT system using cadmium telluride (CdTe) semiconductor detector and 4-pixel matched collimator. Phys Med Biol. 2013;58:7715–31.
Esser PD, Alderson PO, Mitnick RJ, Arliss JJ. Angled-collimator SPECT (A-SPECT): an improved approach to cranial single photon emission tomography. J Nucl Med. 1984;25:805–9.
Polak JF, Holman BL, Moretti JL, Eisner RL, Lister-James J, English RJ. I-123 HIPDM brain imaging with rotating gamma camera and slant-hole collimator. J Nucl Med. 1984;25:495–8.
Agostinelli S, Allisonas J, Amakoe K, Apostolakisa J, Araujoaj H, Arcel P, et al. Geant4—a simulation toolkit. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 2003;506:250–303.
The Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine. http://www.jsnm.org.
Wallis JW, Miller TR. An optimal rotator for iterative reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 1997;16:118–23.
Hudson HM, Larkin RS. Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 1994;13:601–9.
de Jong H, Slijpen E, Beekman F. Acceleration of Monte Carlo SPECT simulation using convolution-based forced detection. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2001;48:58–64.
Hirao K, Ohnishi T, Hirata Y, Yamashita F, Mori T, Moriguchi Y, et al. The prediction of rapid conversion to Alzheimer’s disease in mild cognitive impairment using regional cerebral blood flow SPECT. Neuroimage. 2005;28:1014–21.
Matsuda H, Mizumura S, Nagao T, Ota T, Iizuka T, Nemoto K, et al. Automated discrimination between very early Alzheimer disease and controls using an easy Z-score imaging system for multicenter brain perfusion single-photon emission tomography. Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:731–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, A., Takeuchi, W., Ishitsu, T. et al. High-resolution brain SPECT imaging by combination of parallel and tilted detector heads. Ann Nucl Med 29, 682–696 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-015-0992-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-015-0992-4