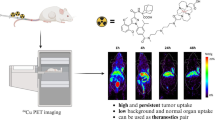
Abstract
Objective
3-[18F]Fluoro-α-methyl-l-tyrosine (l-[18F]FAMT) is a useful amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of malignant tumors. Because d-amino acids are not well distributed in non-target organs and are rapidly excreted in urine, the d-isomer of [18F]FAMT could allow clear PET imaging of tumors early after administration. In this study, we prepared 3-[18F]fluoro-α-methyl-d-tyrosine (d-[18F]FAMT) and evaluated its usefulness.
Methods
d-[18F]FAMT was synthesized according to the method for preparation of l-[18F]FAMT. The in vitro and in vivo stability of [18F]FAMT were evaluated by high-performance liquid chromatography. Cellular uptake of [18F]FAMT was evaluated using LS180 colon adenocarcinoma cells. Biodistribution studies were performed in LS180 tumor-bearing mice, and the tumors were imaged using a small-animal PET scanner.
Results
The radiolabeling yield of d-[18F]FAMT was approximately 10 %, similar to that of l-[18F]FAMT. Over 95 % of d-[18F]FAMT remained intact in mice until 60 min after administration. d-[18F]FAMT was gradually taken up by the LS180 cells. Tumor uptake of d-[18F]FAMT was competitively inhibited by pretreatment with α-methyl-l-tyrosine, a selective substrate for the system l-amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1), suggesting the involvement of LAT1 in tumor uptake of d-[18F]FAMT. In biodistribution studies, d-[18F]FAMT showed rapid clearance from the blood, marked accumulation and retention in the tumor, and lower accumulation in non-target organs, especially kidney and pancreas, compared to l-[18F]FAMT. The amount of d-[18F]FAMT in the tumor was also reduced, and tumor-to-blood ratio and tumor-to-muscle ratio of d-[18F]FAMT were similar to those of l-[18F]FAMT at every time point. PET imaging with d-[18F]FAMT did not provide a clear image of the tumor early after administration. However, d-[18F]FAMT provided higher tumor-to-background contrast than l-[18F]FAMT.
Conclusions
d-[18F]FAMT showed rapid blood clearance, low accumulation in non-target organs, and tumor-selective imaging compared with l-[18F]FAMT. Thus, d-[18F]FAMT could potentially serve as a novel PET tracer for imaging malignant tumors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plathow C, Weber WA. Tumor cell metabolism imaging. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(Suppl 2):43S–63S.
Zhu A, Shim H. Current molecular imaging positron emitting radiotracers in oncology. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;45:1–14.
Jager PL, Vaalburg W, Pruim J, de Vries EG, Langen KJ, Piers DA. Radiolabeled amino acids: basic aspects and clinical applications in oncology. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:432–45.
Långström B, Antoni G, Gullberg P, Halldin C, Malmborg P, Någren K, et al. Synthesis of l- and d-[methyl-11C]methionine. J Nucl Med. 1987;28:1037–40.
Wester HJ, Herz M, Weber W, Heiss P, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R, Schwaiger M, et al. Synthesis and radiopharmacology of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine for tumor imaging. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:205–12.
Tomiyoshi K, Amed K, Muhammad S, Higuchi T, Inoue T, Endo K, et al. Synthesis of isomers of 18F-labelled amino acid radiopharmaceutical: position 2- and 3-l-18F-alpha-methyltyrosine using a separation and purification system. Nucl Med Commun. 1997;18:169–75.
Inoue T, Tomiyoshi K, Higuichi T, Ahmed K, Sarwar M, Aoyagi K, et al. Biodistribution studies on l-3-[fluorine-18]fluoro-alpha-methyl tyrosine: a potential tumor-detecting agent. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:663–7.
Inoue T, Shibasaki T, Oriuchi N, Aoyagi K, Tomiyoshi K, Amano S, et al. 18F Alpha-methyl tyrosine PET studies in patients with brain tumors. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:399–405.
Inoue T, Koyama K, Oriuchi N, Alyafei S, Yuan Z, Suzuki H, et al. Detection of malignant tumors: whole-body PET with fluorine 18 alpha-methyl tyrosine versus FDG—preliminary study. Radiology. 2001;220:54–62.
Kaira K, Oriuchi N, Otani Y, Shimizu K, Tanaka S, Imai H, et al. Fluorine-18-alpha-methyltyrosine positron emission tomography for diagnosis and staging of lung cancer: a clinicopathologic study. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:6369–78.
Miyakubo M, Oriuchi N, Tsushima Y, Higuchi T, Koyama K, Arai K, et al. Diagnosis of maxillofacial tumor with l-3-[18F]-fluoro-alpha-methyltyrosine (FMT) PET: a comparative study with FDG-PET. Ann Nucl Med. 2007;21:129–35.
Kaira K, Oriuchi N, Shimizu K, Ishikita T, Higuchi T, Imai H, et al. Evaluation of thoracic tumors with 18F-FMT and 18F-FDG PET-CT: a clinicopathological study. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:1152–60.
Kaira K, Oriuchi N, Imai H, Shimizu K, Yanagitani N, Sunaga N, et al. Prognostic significance of l-type amino acid transporter 1 expression in resectable stage I–III nonsmall cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:742–8.
Kaira K, Oriuchi N, Shimizu K, Imai H, Tominaga H, Yanagitani N, et al. Comparison of l-type amino acid transporter 1 expression and l-[3-18F]-α-methyl tyrosine uptake in outcome of non-small cell lung cancer. Nucl Med Biol. 2010;37:911–6.
Wiriyasermkul P, Nagamori S, Tominaga H, Oriuchi N, Kaira K, Nakao H, et al. Transport of 3-fluoro-l-α-methyl-tyrosine by tumor-upregulated l-type amino acid transporter 1: a cause of the tumor uptake in PET. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:1253–61.
Kanai Y, Segawa H, Miyamoto K, Uchino H, Takeda E, Endou H. Expression cloning and characterization of a transporter for large neutral amino acids activated by the heavy chain of 4F2 antigen (CD98). J Biol Chem. 1998;273:23629–32.
Yanagida O, Kanai Y, Chairoungdua A, Kim DK, Segawa H, Nii T, et al. Human l-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): characterization of function and expression in tumor cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1514:291–302.
Uchino H, Kanai Y, Kim DK, Wempe MF, Chairoungdua A, Morimoto E, et al. Transport of amino acid-related compounds mediated by l-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): insights into the mechanisms of substrate recognition. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;61:729–37.
Imai H, Kaira K, Oriuchi N, Shimizu K, Tominaga H, Yanagitani N, et al. Inhibition of l-type amino acid transporter 1 has antitumor activity in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:4819–28.
Crampton RF, Smyth DH. The excretion of the enantiomorphs of aminoacids. J Physiol. 1953;122:1–10.
Doolan PD, Harper HA, Hutchin ME, Shreeve WW. Renal clearance of eighteen individual amino acids in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1955;34:1247–55.
Tsukada H, Sato K, Fukumoto D, Nishiyama S, Harada N, Kakiuchi T. Evaluation of d-isomers of O-11C-methyl tyrosine and O-18F-fluoromethyl tyrosine as tumor-imaging agents in tumor-bearing mice: comparison with l- and d-11C-methionine. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:679–88.
Ohshima Y, Hanaoka H, Watanabe Sh, Sugo Y, Watanabe Sa, Tominaga H, et al. Preparation and biological evaluation of 3-[76Br]bromo-α-methyl-l-tyrosine, a novel tyrosine analog for positron emission tomography imaging of tumors. Nucl Med Biol. 2011;38:857–65.
Morimoto E, Kanai Y, Kim do K, Chairoungdua A, Choi HW, Wempe MF, et al. Establishment and characterization of mammalian cell lines stably expressing human l-type amino acid transporters. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008;108:505–16.
Kaira K, Oriuchi N, Sunaga N, Ishizuka T, Shimizu K, Yamamoto N. A systemic review of PET and biology in lung cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2011;3:383–91.
Ishiwata K, Kasahara C, Hatano K, Ishii S, Senda M. Carbon-11 labeled ethionine and propionine as tumor detecting agents. Ann Nucl Med. 1997;11:115–22.
Ishiwata K, Ido T, Vaalburg W. Increased amounts of d-enantiomer dependent on alkaline concentration in the synthesis of l-[methyl-11C]methionine. Int J Rad Appl Instrum A. 1988;39:311–4.
Bröer S. Amino acid transport across mammalian intestinal and renal epithelia. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:249–86.
Friedman M, Levin CE. Nutritional and medicinal aspects of D:-amino acids. Amino Acids. 2011. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-0915-1.
Young JA, Freedman BS. Renal tubular transport of amino acids. Clin Chem. 1971;17:245–66.
Engelman K, Jéquier E, Udenfriend S, Sjoerdsma A. Metabolism of alpha-methyltyrosine in man: relationship to its potency as an inhibitor of catecholamine biosynthesis. J Clin Invest. 1968;47:568–76.
Shikano N, Kawai K, Nakajima S, Nishii R, Flores LG 2nd, Kubodera A, et al. Renal accumulation and excretion of radioiodinated 3-iodo-alpha-methyl-l-tyrosine. Ann Nucl Med. 2004;18:263–70.
Shikano N, Kawai K, Nakajima S, Kubodera A, Kubota N, Ishikawa N, et al. Transcellular transport of radioiodinated 3-iodo-alpha-methyl-l-tyrosine across monolayers of kidney epithelial cell line LLC-PK1. Ann Nucl Med. 2004;18:227–34.
Kaira K, Sunose Y, Arakawa K, Ogawa T, Sunaga N, Shimizu K, et al. Prognostic significance of l-type amino-acid transporter 1 expression in surgically resected pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:632–8.
Shnitsar V, Eckardt R, Gupta S, Grottker J, Muller GA, Koepsell H, et al. Expression of human organic cation transporter 3 in kidney carcinoma cell lines increases chemosensitivity to melphalan, irinotecan, and vincristine. Cancer Res. 2009;69:1494–501.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Funding Program for Next Generation World-Leading Researchers (NEXT program) from Cabinet Office, Government of Japan. We are grateful to Mr. Takashi OGASAWARA for operation of the biomedical cyclotron. We also would like to thank the staff of the Medical Radioisotope Application Group at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency as well as the Departments of Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine at Gunma University Graduate School of Medicine for their cooperation and helpful input.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohshima, Y., Hanaoka, H., Tominaga, H. et al. Biological evaluation of 3-[18F]fluoro-α-methyl-d-tyrosine (d-[18F]FAMT) as a novel amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med 27, 314–324 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-013-0687-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-013-0687-7