Abstract
Objective
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR), also known as stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT), is now a standard treatment option for patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer or oligometastatic lung tumor who are medically inoperable or medically operable but refuse surgery. When mass-like consolidation is observed on follow-up CT after SABR, it is sometimes difficult to differentiate tumor recurrence from SABR-induced pulmonary fibrosis. In this study, we evaluated the role of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography combined with computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) in differentiating tumor recurrence from radiation fibrosis after SABR.
Methods
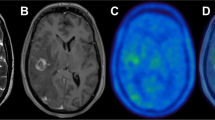
Between June 2006 and June 2009, 130 patients received SABR for stage I non-small cell lung cancer or metastatic lung cancer at our institution. Fifty-nine patients of them were imaged with FDG-PET/CT after SABR. There were a total of 137 FDG-PET/CT scans for retrospective analysis. The FDG uptake in the pulmonary region was assessed qualitatively using a 3-point scale (0, none or faint; 1, mild; or 2, moderate to intense), and the shape (mass-like or non mass-like) was evaluated. For semi-quantitative analysis, the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) was calculated.
Results
Sixteen of 59 patients had local failure. In recurrent tumor, the combination of intensity grade 2 and mass-like shape was most common (21/23; 91 %). By contrast, in cases of radiation fibrosis, the combination of intensity grade 0 or 1 and non mass-like shape was most common (48/59; 81 %). The SUVmax of tumor recurrence after 12 months was significantly higher than that of radiation fibrosis (8.0 ± 3.2 vs. 2.1 ± 0.9, p < 0.001), and all tumor recurrence showed the SUVmax > 4.5 at diagnosis of local failure. At ≥12 months after SABR, these two variables, the combination of intensity 2 and mass-like FDG uptake or SUVmax > 4.5 acquired a significant high predictive value of local recurrence, finding sensitivity 100 % and specificity 100 % for both of them.
Conclusions
The combination of FDG uptake patterns and SUVmax was useful for distinguishing tumor recurrence from radiation fibrosis after SABR.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoyer M, Roed H, Hansen A. Prospective study on stereotactic radiotherapy of limited-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:S128–35.
Louie AV, Rodrigues G, Hannouf M, Zaric GS, Palma DA, Cao JQ, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy versus surgery for medically operable Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a Markov model-based decision analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:964–73.
Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, Gomi K, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:1352–8.
Aoki T, Nagata Y, Negoro Y, Takayama K, Mizowaki T, Kokubo M, et al. Evaluation of lung injury after three-dimensional conformal stereotactic radiation therapy for solitary lung tumors: CT appearance. Radiology. 2004;230:101–8.
Koenig TR, Munden RF, Erasmus JJ, Sabloff BS, Gladish GW, Komaki R, et al. Radiation injury of the lung after three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178:1383–8.
Linda A, Trovo M, Bradley JD. Radiation injury of the lung after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancer: a timeline and pattern of CT changes. Eur J Radiol. 2011;79:147–54.
Huang K, Dahele M, Senan S, Guckenberger M, Rodrigues GB, Ward A, et al. Radiographic changes after lung stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR)—can we distinguish recurrence from fibrosis? A systematic review of the literature. Radiother Oncol. 2012;102:335–42.
Inoue T, Kim EE, Komaki R, Wong FC, Bassa P, Wong WH, et al. Detecting recurrent or residual lung cancer with FDG-PET. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:788–93.
Takeda A, Kunieda E, Takeda T, Tanaka M, Sanuki N, Fujii H, et al. Possible misinterpretation of demarcated solid patterns of radiation fibrosis on CT scans as tumor recurrence in patients receiving hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:1057–65.
Bollineni VR, Widder J, Pruim J, Langendijk JA, Wiegman EM. Residual (18)F-FDG-PET uptake 12 weeks after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer predicts local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:e551–5.
Rusthoven KE, Kavanagh BD, Burri SH, Chen C, Cardenes H, Chidel MA, et al. Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1579–84.
Matsuo Y, Nakamoto Y, Nagata Y, Shibuya K, Takayama K, Norihisa Y, et al. Characterization of FDG-PET images after stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2010;97:200–4.
Raz DJ, Zell JA, Ou SH, Gandara DR, Anton-Culver H, Jablons DM. Natural history of stage I non-small cell lung cancer: implications for early detection. Chest. 2007;132:193–9.
Matsuo Y, Nagata Y, Mizowaki T, Takayama K, Sakamoto T, Sakamoto M, et al. Evaluation of mass-like consolidation after stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung tumors. Int J Clin Oncol. 2007;12:356–62.
Bury T, Corhay JL, Duysinx B, Daenen F, Ghaye B, Barthelemy N, et al. Value of FDG-PET in detecting residual or recurrent nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir J. 1999;14:1376–80.
Frank A, Lefkowitz D, Jaeger S, Gobar L, Sunderland J, Gupta N, et al. Decision logic for retreatment of asymptomatic lung cancer recurrence based on positron emission tomography findings. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;32:1495–512.
van Loon J, Grutters J, Wanders R, Boersma L, Oellers M, Dingemans AM, et al. Follow-up with 18FDG-PET-CT after radical radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy allows the detection of potentially curable progressive disease in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a prospective study. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:588–95.
Hoopes DJ, Tann M, Fletcher JW, Forquer JA, Lin PF, Lo SS, et al. FDG-PET and stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2007;56:229–34.
Chen F, Matsuo Y, Yoshizawa A, Sato T, Sakai H, Bando T, et al. Salvage lung resection for non-small cell lung cancer after stereotactic body radiotherapy in initially operable patients. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:1999–2002.
Neri S, Takahashi Y, Terashi T, Hamakawa H, Tomii K, Katakami N, et al. Surgical treatment of local recurrence after stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary and metastatic lung cancers. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:2003–7.
Taremi M, Hope A, Dahele M, Pearson S, Fung S, Purdie T, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for medically inoperable lung cancer: prospective, single-center study of 108 consecutive patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:967–73.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (Program for Enhancing Systematic Education in Graduate School).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakajima, N., Sugawara, Y., Kataoka, M. et al. Differentiation of tumor recurrence from radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for lung cancer: characterization of 18F-FDG PET/CT findings. Ann Nucl Med 27, 261–270 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-012-0682-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-012-0682-4