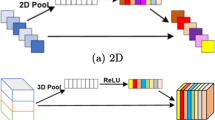
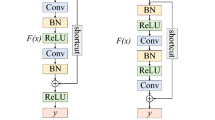
Abstract
3D convolution can fully utilize the spectral-spatial characteristics of hyperspectral image (HSI), and stacked blocks with deep layers are capable of extracting hidden features and utilizing discriminant information for classification. Naturally, a 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) based on stacked blocks named SB-3D-CNN is presented for HSI classification. Moreover, the proposed network introduces the attention mechanism before the fully connected layer, which can filter out interfering information effectively. Then we optimized the architecture to obtain optimal results on three commonly used datasets of Indian Pines, Salinas and Pavia University. Experimental results demonstrate that the optimized architecture achieves better classification rates than related recent works. Because the classification accuracies on the three datasets have reached saturation, we transferred the optimized architecture to a more complex dataset adopting the airborne hyperspectral data, which obtains from Guangxi province in south China. The results show that the optimized architecture achieves superior classification accuracies compared with other state-of-the-art methods. These results also demonstrate the optimized SB-3D-CNN has the advantages of validity and portability to more complex data.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ba JL, Kiros JR, Hinton GE (2016) Layer normalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.06450
Chen YS, Lin ZH, Zhao X et al (2014) Deep learning-based classification of Hyperspectral data. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing 7(6):2094–2107
Chen YS, Zhao X, Jia XP (2015) Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral data based on deep belief network. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing 8(6):2381–2392
Chen YS, Jiang HL, Li CY et al (2016) Deep feature extraction and classification of Hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(10):6232–6251
Cheng G, Li ZP, Han JW et al (2018) Exploring hierarchical convolutional features for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(11):6712–6722
Fauvel M, Benediktsson JA, Chanussot J et al (2008) Spectral and spatial classification of hyperspectral data using SVMs and morphological profiles. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 46(11):3804–3814
Geng J, Wang HY, Fan JC et al (2017) Deep supervised and contractive neural network for SAR image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(4):2442–2459
Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y (2011) Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. J Mach Learn Res 15:315–323
Hamida AB, Benoit A, Lambert P et al (2018) 3-D deep learning approach for remote sensing image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(8):4420–4434
He M, Li B, Chen H (2018) Multi-scale 3D deep convolutional neural network for hyperspectral image classification. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)
Huang X, Serge B (2017) Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)
Kang XD, Li ST, Fang LY et al (2014) Extended random Walker-based classification of Hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(1):144–153
Kang XD, Xiang XL, Li ST et al (2017) PCA-based edge-preserving features for Hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(12):7140–7151
Khan MJ, Khan HS, Yousaf A et al (2018) Modern trends in Hyperspectral image analysis: a review. IEEE Access 6:14118–14129
Khurshid H, Khan MF (2015) Segmentation and classification using logistic regression in remote sensing imagery. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 8(1):224–232
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. International Conference on Learning Representations
Lee H, Kwon H (2017) Going deeper with contextual CNN for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(10):4843–4855
Leng J, Li T, Bai G et al (2017) Cube-CNN-SVM: a novel Hyperspectral image classification method. In: 2016 IEEE 28th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), pp. 1027–1034
Léon B (2010) Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. Proc of COMPSTAT:177–186
Li XH, Lee WS, Li MZ et al (2012) Spectral difference analysis and airborne imaging classification for citrus greening infected trees. Computers & Electronics in Agriculture 83:32–46
Li Y, Zhang H, Shen Q (2017) Spectral-spatial classification of Hyperspectral imagery with 3D convolutional neural network. Remote Sens 9(1):67
Li CM, Wang YC, Zhang XK et al (2019) Deep Belief Network for Spectral–Spatial Classification of Hyperspectral Remote Sensor Data. Sensors 19(1)
Loffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.03167
Makantasis K, Karantzalos K, Doulamis A et al (2015) Deep supervised learning for hyperspectral data classification through convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, pp. 4959–4962
Nesterov Y (2012) Efficiency of coordinate descent methods on huge-scale optimization problems. SIAM J Optim 22(2):341–362
Qi K, Wu H, Shen C et al (2015) Land-use scene classification in high-resolution remote sensing images using improved Correlatons. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(12):2403–2407
Rodarmel C, Shan J (2017) Principal component analysis for Hyperspectral image classification. Engineering of Surveying & Mapping
Samiappan S, Prasad S, Bruce LM (2013) Non-uniform random feature selection and kernel density scoring with SVM based ensemble classification for Hyperspectral image analysis. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing 6(2):792–800
Song WW, Li ST, Fang LY et al (2018) Hyperspectral image classification with deep feature fusion network. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(6):3173–3184
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S et al (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. Computer vision and pattern recognition, In, pp 2818–2826
Wei W, Zhang JY, Zhang L et al (2018) Deep cube-pair network for Hyperspectral imagery classification. Remote Sens 10(5)
Wu Y, He KM (2018) Group normalization. Int J Comput Vis 742–755
Yang LX, Yang SY, Jin PL e al (2014) Semi-supervised Hyperspectral image classification using Spatio-spectral Laplacian support vector machine. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters 11(3):651–655
Yan L, Zhu RX, Liu Y et al (2018) Color-boosted saliency-guided rotation invariant bag of visual words representation with parameter transfer for cross-domain scene-level classification. Remote Sens 10(4)
Zhao WZ, Du SH (2016) Spectral–spatial feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification: a dimension reduction and deep learning approach. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(8):4544–4554
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Guo, Y. & Zhang, X. Hyperspectral image classification based on optimized convolutional neural networks with 3D stacked blocks. Earth Sci Inform 15, 383–395 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00731-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00731-1