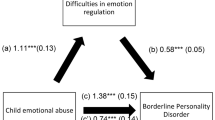Abstract
Among college students, Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) features are prevalent and impairing. Different types of childhood maltreatment (CM) are associated with BPD features, though the type(s) of CM that is most robustly associated with BPD features and the mechanism by which CM leads to BPD features are not well-studied. Thus, the purpose of this study was to investigate which type(s) of CM was most robustly associated with BPD features and to test whether empathy, which is negatively correlated with CM, mediated the relationship between CM and BPD features in college students. Two thousand five hundred fifty-one undergraduate college students completed online self-report questionnaires measuring CM, empathy, and BPD features. A series of regression models were tested to explore relationships between types of CM and BPD features and CM, empathy and BPD features. Childhood physical abuse, but neither sexual abuse nor neglect, significantly predicted BPD features. Cognitive empathy partially mediated the relationship between childhood physical abuse and BPD features. These findings suggest childhood physical abuse is negatively associated with cognitive empathy, which in turn, is negatively associated with BPD features. Implications for treating BPD features in college students based on these findings are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen-Walker, L., & Beaton, A. A. (2015). Empathy and perception of emotion in eyes from the FEEST/ekman and friesen faces. Personality and Individual Differences, 72, 150–154. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2014.08.037.
Ansell, E. B., Sanislow, C. A., McGlashan, T. H., & Grilo, C. M. (2007). Psychosocial impairment and treatment utilization by patients with borderline personality disorder, other personality disorders, mood and anxiety disorders, and a healthy comparison group. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 48(4), 329–336.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51(6), 1173.
Baron-Cohen, S., Wheelwright, S., Hill, J., Raste, Y., & Plumb, I. (2001). The "reading the mind in the eyes" test revised version: A study with normal adults, and adults with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 42(2), 241–251.
Battle, C. L., Shea, M. T., Johnson, D. M., Zlotnick, C., Zanarini, M. C., Sainslow, C. A., & McGlashan, T. H. (2004). Childhood maltreatment associated with adult personality disorders: Findings from the collaborative longitudinal personality disorders study. Journal of Personality Disorders, 18(2), 193–211.
Bernstein, D., Fink, L., Handelsman, L., Foote, J., Lovejoy, M., Wenzel, K., Sapareto, E., & Ruggiero, J. (1994). Initial reliability and validity of a new measure of child abuse and neglect. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 151(8), 1132.
Black, D. W., Blum, N., Pfohl, B., & Hale, N. (2004). Suicidal behavior in borderline personality disorder: Prevalence, risk factors, prediction, and prevention. Journal of Personality Disorders, 18(3), 226.
Bradley, R., Jenei, J., & Westen, D. (2005). Etiology of borderline personality disorder: Disentangling the contributions of intercorrelated antecedents. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 193(1), 24–31.
Brune, M., Walden, S., Edel, M. A., & Dimaggio, G. (2016). Mentalization of complex emotions in borderline personality disorder: The impact of parenting and exposure to trauma on the performance in a novel cartoon-based task. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 64, 29–37.
Chesin, M., Fertuck, E., Goodman, J., Lichenstein, S., & Stanley, B. (2015). The interaction between rejection sensitivity and emotional maltreatment in borderline personality disorder. Psychopathology, 48(1), 31–35. doi:10.1159/000365196.
Clarkin, J. F., Levy, K. N., Lenzenweger, M. F., & Kernberg, O. F. (2007). Evaluating three treatments for borderline personality disorder: A multiwave study. American Journal of Psychiatry, 164(6), 922–928.
Davis, M. H. (1983). Measuring individual differences in empathy: Evidence for a multidimensional approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44(1). doi:10.1037/0022-3514.44.1.113.
van Dijke, A., Ford, J. D., van Son, M., Frank, L., & van der Hart, O. (2013). Association of childhood-trauma-by-primary caregiver and affect dysregulation with borderline personality disorder symptoms in adulthood. Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy, 5(3), 217–224.
Dinsdale, N., & Crespi, B. J. (2013). The borderline empathy paradox: Evidence and conceptual models for empathic enhancements in borderline personality disorder. Journal of Personality Disorders, 27(2), 172–195.
Dong, M., Anda, R. F., Felitti, V. J., Dube, S. R., Williamson, D. F., Thompson, T. J., & Giles, W. H. (2004). The interrelatedness of multiple forms of childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. Child Abuse & Neglect, 28(7), 771–784. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2004.01.008.
Dziobek, I., Preibler, S., Grozdanovic, Z., Heuser, I., Heekeren, H. R., & Roepke, S. (2011). Neuronal correlates of altered empathy and social cognition in borderline personality disorder. NeuroImage, 57(2), 539–548.
Fertuck, E. A., Jekal, A., Song, I., Wyman, B., Morris, M. C., Wilson, S. T., et al. (2009). Enhanced ‘reading the mind in the eyes’ in borderline personality disorder compared to healthy controls. Psychological Medicine, 39(12), 1979–1988. doi:10.1017/S003329170900600X.
First, M. B., Spitzer, R. L., Gibbons, M., Williams, J. B. W., & Benjamin, L. (1997). User's guide for the structured clinical interview for for DSM-IV Axis II personality disorders (SCID-II). New York State Psychiatric Institute: New York.
Fossati, A., Madeddu, F., & Maffei, C. (1999). Borderline personality disorder and childhood sexual abuse: A meta-analytic study. Journal of Personality Disorders, 13(3), 268–280.
Fossati, A., Gratz, K. L., Somma, A., Maffei, C., & Borroni, S. (2015). The mediating role of emotion dysregulation in the relations between childhood trauma history and adult attachment and borderline personality disorder features: A study of italian nonclinical participants. Journal of Personality Disorders, 29, 1–24.
Frick, C., Lang, S., Kotchoubey, B., Sieswerda, S., Dinu-Biringer, R., Berger, M., et al. (2012). Hypersensitivity in borderline personality disorder during mindreading. PloS One, 7(8), e41650.
Gardner, K. J., Qualter, P., Stylianou, M., & Robinson, A. J. (2010). Facial affect recognition in non-clinical adults with borderline personality features: The role of effortful control and rejection sensitivity. Personality and Individual Differences, 49(7), 799–804.
Gibb, B. E., Wheeler, R., Alloy, L. B., & Abramson, L. Y. (2001). Emotional, physical, and sexual maltreatment in childhood versus adolescence and personality dysfunction in young adulthood. Journal of Personality Disorders, 15(6), 505–511.
Glaser, D. (2002). Emotional abuse and neglect (psychological maltreatment): A conceptual framework. Child Abuse & Neglect, 26(6), 697–714.
Goodman, J., Fertuck, E., Chesin, M., Lichenstein, S., & Stanley, B. (2014). The moderating role of rejection sensitivity in the relationship between emotional maltreatment and borderline symptoms. Personality and Individual Differences, 71, 146–150.
Gratz, K. L., Tull, M. T., Baruch, D. E., Bornovalova, M. A., & Lejuez, C. (2008). Factors associated with co-occurring borderline personality disorder among inner-city substance users: The roles of childhood maltreatment, negative affect intensity/reactivity, and emotion dysregulation. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 49(6), 603–615.
Gross, J. J., & Barrett, L. F. (2011). Emotion generation and emotion regulation: One or two depends on your point of view. Emotion Review, 3(1), 8–16.
Harari, H., Shamay-Tsoory, S. G., Ravid, M., & Levkovitz, Y. (2010). Double dissociation between cognitive and affective empathy in borderline personality disorder. Psychiatry Research, 175(3), 277–279.
Higgins, D. J., & McCabe, M. P. (2001). The development of the comprehensive child maltreatment scale. Journal of Family Studies, 7(1), 7–28.
Igarashi, H., Hasui, C., Uji, M., Shono, M., Nagata, T., & Kitamura, T. (2010). Effects of child abuse history on borderline personality traits, negative life events, and depression: A study among a university student population in Japan. Psychiatry Research, 180(2–3), 120–125.
Kuo, J. R., Khoury, J. E., Metcalfe, R., Fitzpatrick, S., & Goodwill, A. (2015). An examination of the relationship between childhood emotional abuse and borderline personality disorder features: The role of difficulties with emotion regulation. Child Abuse & Neglect, 39, 147–155. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2014.08.008.
Lazarus, S. A., Cheavens, J. S., Festa, F., & Rosenthal, M. Z. (2014). Interpersonal functioning in borderline personality disorder: A systematic review of behavioral and laboratory-based assessments. Clinical Psychology Review, 34(3), 193–205.
Levy, K. N., Meehan, K. B., Kelly, K. M., Reynoso, J. S., Weber, M., Clarkin, J. F., & Kernberg, O. F. (2006). Change in attachment patterns and reflective function in a randomized control trial of transference-focused psychotherapy for borderline personality disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 74(6), 1027–1040.
Linehan, M. (1993). Cognitive–behavioral treatment of borderline personality disorder. New York: Guilford Press.
Lobbestael, J., Arntz, A., & Bernstein, D. P. (2010). Disentangling the relationship between different types of childhood maltreatment and personality disorders. Journal of Personality Disorders, 24(3), 285–295.
Locher, S. C., Barenblatt, L., Fourie, M. M., & Gobodo-Madikizela, P. (2014). Empathy and childhood maltreatment: A mixed-methods investigation. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 26(2), 97–110.
MacIntosh, H. B., Godbout, N., & Dubash, N. (2015). Borderline personality disorder: Disorder of trauma or personality, a review of the empirical literature. Canadian Psychology/Psychologie Canadienne, 56(2), 227–241.
Mancke, F., Herpertz, S. C., & Bertsch, K. (2015). Aggression in borderline personality disorder: A multidimensional model. Personality Disorders: Theory, Research, and Treatment, 6(3), 278.
Meaney, R., Hasking, P., & Reupert, A. (2016). Prevalance of borderline personality disorder in university samples: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. PloS One, 11(5). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0155439.
Merza, K., Papp, G., & Kuritárné Szabó, I. (2015). The role of childhood traumatization in the development of borderline personality disorder in hungary. The European Journal of Psychiatry, 29(2), 105–118.
New, A. S., Aan Het Rot, M., Ripoll, L. H., Perez-Rodriguez, M. M., Lazarus, S., Zipursky, E., & Goodman, M. (2012). Empathy and alexithymia in borderline personality disorder: Clinical and laboratory measures. Journal of Personality Disorders, 26(5), 660–675.
Nisbett, R. E., & Wilson, T. D. (1977). Telling more than we can know: Verbal reports on mental processes. Psychological Review, 84(3), 231–259.
Pistorello, J., Fruzzetti, A. E., Maclane, C., Gallop, R., & Iverson, K. M. (2012). Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) applied to college students: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 80(6), 982–994.
Preti, E., Richetin, J., Suttora, C., & Pisani, A. (2016). Individual differences in components of impulsivity and effortful control moderate the relation between borderline personality disorder traits and emotion recognition in a sample of university students. Psychiatry Research, 238, 109–115. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2016.02.037.
Richman, M. J., & Unoka, Z. (2015). Mental state decoding impairment in major depression and borderline personality disorder: Meta-analysis. The British Journal of Psychiatry: the Journal of Mental Science, 207(6), 483–489. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.114.152108.
Rosenbach, C., & Renneberg, B. (2014). Rejection sensitivity as a mediator of the relationship between experienced rejection and borderline characteristics. Personality and Individual Differences, 69, 176–181.
Tomko, R. L., Trull, T. J., Wood, P. K., & Sher, K. J. (2014). Characteristics of borderline personality disorder in a community sample: Comorbidity, treatment utilization, and general functioning. Journal of Personality Disorders, 28(5), 734–750. doi:10.1521/pedi_2012_26_093.
Tonmyr, L., Draca, J., Crain, J., & MacMillan, H. L. (2011). Measurement of emotional/psychological child maltreatment: A review. Child Abuse & Neglect, 35(10), 767–782. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2011.04.011.
Trull, T. J., Useda, D., Conforti, K., & Doan, B. (1997). Borderline personality disorder features in nonclinical young adults: 2. Two-year outcome. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 106(2), 307.
Wagner, A. W., & Linehan, M. M. (1999). Facial expression recognition ability among women with borderline personality disorder: Implications for emotin regulation? Journal of Personality Disorders, 13(4), 329–344.
Weinstein, S. R., Meehan, K. B., Cain, N. M., Ripoll, L. H., Boussi, A. R., Papouchis, N., & New, A. S. (2016). Mental state identification, borderline pathology, and the neglected role of childhood trauma. Personality Disorders: Theory, Research, and Treatment, 7(1), 61–71.
Widom, C. S., & Shepard, R. L. (1996). Accuracy of adult recollections of childhood victimization: Part 1. Childhood physical abuse. Psychological Assessment, 8(4), 412–421.
Young, J. C., & Widom, C. S. (2014). Long-term effects of child abuse and neglect on emotion processing in adulthood. Child Abuse & Neglect, 38(8), 1369–1381. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2014.03.008.
Zanarini, M. C., Williams, A. A., Lewis, R. E., & Reich, R. B. (1997). Reported pathological childhood experiences associated with the development of borderline personality disorder. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 154(8), 1101–1106.
Zimmerman, M., Rothschild, L., & Chelminski, I. (2005). The prevalence of DSM-IV personality disorders in psychiatric outpatients. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(10), 1911–1918.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, by funds from a Summer Stipend from the Research Center for the Humanities and Social Sciences at William Paterson University (WPU). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of WPU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported, in part, by funds from a Summer Stipend from the Research Center for the Humanities and Social Sciences at William Paterson University (WPU). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of WPU.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the studies.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bujalski, A.S., Chesin, M.S. & Jeglic, E.L. Cognitive Empathy Partially Mediates the Relationship between Childhood Physical Abuse and Borderline Personality Disorder Features in College Students. Curr Psychol 38, 121–127 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-017-9597-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-017-9597-5