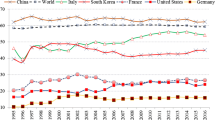
Abstract
Henley Passport Index (HPI) is a rank on the number of countries a passport holder of a country can travel VISA-free. Countries with high HPI ranking enjoy certain passport privileges. Little is known about the relationship between HPI and other global indices. This paper investigates the relationship between HPI and the trio of Corruption Perception Index (CPI), Global Peace Index (GPI), and World Happiness Report (WHR). The data of the country ranks of the 4 indices were obtained from the respective websites of the publishers of the indices. A final sample of 150 countries was analyzed after the cases of missing values were discarded. The result showed positive correlation between HPI and CPI (r = 0.768, p < 0.0005), GPI (r = 0.671, p < 0.005), and WHR (r = 0.775, p < 0.005), respectively. Regression analysis yielded an equation that showed that a unit increase in the country ranking of CPI, GPI, and WHR of countries increases the ranking of HPI by 0.196, 0.149, and 0.352, respectively. The coefficients of the independent variables are all significant at p value equals 0.05 and the model validation showed the absence of multicollinearity and the presence of small non-significant autocorrelation. The research concluded that countries with high passport privileges also have low corruption instances and conflicts and are perceived to be happy. The implications of this research were discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, S. W., & Kroløkke, C. (2018). Passport to parenthood: reproductive pathways in and out of Denmark. NORA - Nordic Journal of Feminist and Gender Research, 26(2), 112–128.
Ageeva, O. N., Anoschenkova, S. V., Petrikova, S. V., & Pomnina, S. N. (2016). The ability of civil society to act against corruption. European Research Studies Journal, 19(3), 151–169.
Albayrak, T., Herstein, R., Caber, M., Drori, N., Bideci, M., & Berger, R. (2018). Exploring religious tourist experiences in Jerusalem: the intersection of Abrahamic religions. Tourism Management, 69, 285–296.
Al-Rimmawi, H., & Butcher, S. (2015). Trends of tourism in Bethlehem, Palestine: 1994-2015. Tourism, 63(3), 317–335.
Armeanu, D. S., Vintilă, G., & Gherghina, S. C. (2017). Empirical study towards the drivers of sustainable economic growth in EU-28 countries. Sustainability, 10(1), 4.
Asongu, S., Tchamyou, V., Asongu, N., & Tchamyou, N. (2018). The comparative African economics of governance in fighting terrorism. African Security, 11(4), 296–338.
Asongu, S. A., Nnanna, J., Biekpe, N., & Acha-Anyi, P. N. (2019). Contemporary drivers of global tourism: evidence from terrorism and peace factors. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 36(3), 345–357.
Bazurto-Gomez, N., Torres, J. C., Gutierrez, R., Chamorro, M., Bulger, C., Hernandez, T., & Guerra-Gomez, J. A. (2019). An information visualization application case to understand the world happiness report. Communications in Computer and Information Science, 847, 44–56.
Bhattacharyya, S., Burman, R. R., & Paul, S. (2019). The concept of measuring happiness and how India can go the Nordic Way. Current Science, 116(1), 26–28.
Boulton, F., & Louise, N. (2016). Can the health of a nation be correlated to its state of internal peace? Medicine, Conflict and Survival, 32(1), 70–79.
Chand, M. (2019). Brain drain, brain circulation, and the African diaspora in the United States. Journal of African Business, 20(1), 6–19.
Chang, F., Prytherch, H., Nesbitt, R. C., & Wilder-Smith, A. (2013). HIV-related travel restrictions: trends and country characteristics. Global Health Action, 6, 1–8.
Chen, W. (2012). How education enhances happiness: comparison of mediating factors in four East Asian countries. Social Indicators Research, 106(1), 117–131.
Chim-Miki, A. F., & Domareski-Ruiz, T. C. (2018). Business environment and tourism competitiveness. Journal of Globalization, Competitiveness and Government, 12(2), 79–96.
Corbet, S., O’Connell, J. F., Efthymiou, M., Guiomard, C., & Lucey, B. (2019). The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Ann. Tourism Research, 75, 1–17.
CPI (2019). https://www.transparency.org/research/cpi/overview. Accessed 24 Feb 2019.
Cristina, B., Emilia, T. and Daniela, T. 2007. International migration-challenges to European Union. Romania Within the EU: Opportunities, Requirements and Perspectives, Vol I, pp 46–52.
Czaika, M., & de Haas, H. (2017). The effect of visas on migration processes. International Migration Review, 51(4), 893–926.
d’Agostino, G., & Pieroni, L. (2019). Modelling corruption perceptions: evidence from Eastern Europe and Central Asian countries. Social Indicators Research, 142(1), 311–341.
Das, J., & Dirienzo, C. (2010). Tourism competitiveness and corruption: a cross-country analysis. Tourism Economics, 16(3), 477–492.
Dickenson-Jones, G., Hyslop, D., & Vaira-Lucero, M. (2014). Estimating the global costs of violence. Business, Peace and Sustainable Development, 2014(2), 6–27.
Drehmer, J. E. (2018). Sex differences in the association between countries’ smoking prevalence and happiness ratings. Public Health, 160, 41–48.
Du, H., & Chi, P. (2016). War, worries, and religiousness. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 7(5), 444–451.
Efobi, U., Asongu, S., & Beecroft, I. (2018). Aid, terrorism, and foreign direct investment: empirical insight conditioned on corruption control. International Economic Journal. https://doi.org/10.1080/10168737.2018.1549089.
Fatmawati, I., Suman, A., & Syafitri, W. (2018). The impact of FDI, human capital, and corruption on growth in Asian developed and developing countries. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 7(12), 216–221.
Fourie, J., Rosselló-Nadal, J., & Santana-Gallego, M. (2019). Fatal attraction: how security threats hurt tourism. Journal of Travel Research. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287519826208.
Frey, B. S. (2019). What are the opportunities for future happiness research? International Review of Economics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12232-019-00318-9.
Ghosh, S. (2014). A passage to Canada: the differential migrations of South Asian skilled workers to Toronto. Journal of International Migration and Integration, 15(4), 715–735.
Giménez-Gómez, J.-M., Walle, Y. M., & Zergawu, Y. Z. (2019). Trends in African migration to Europe: drivers beyond economic motivations. Journal of Conflict Resolution. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022002718823907.
GPI (2019). Institute for Economics and Peace. http://visionofhumanity.org/. Accessed 21 Feb 2019.
Harpaz, Y. (2013). Rooted cosmopolitans: Israelis with a European passport–history, property, identity. International Migration Review, 47(1), 166–206.
Harpaz, Y. 2018. Compensatory citizenship: dual nationality as a strategy of global upward mobility. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369183X.2018.1440486.
Hercog, M., & van de Laar, M. (2017). Motivations and constraints of moving abroad for Indian students. Journal of International Migration and Integration, 18(3), 749–770.
HPI (2019). Henley and Passport Partners Holding Limited. henleypassportindex.com/passport. Accessed 20 Feb 2019.
Ivanov, S., & Ivanova, M. (2016). Do hotel chains improve destination’s competitiveness? Tourism Management Perspectives, 19, 74–79.
Joshanloo, M., & Weijers, D. (2016). Religiosity moderates the relationship between income inequality and life satisfaction across the globe. Social Indicators Research, 128(2), 731–750.
Kafashpor, A., Ghasempour Ganji, S. F., Sadeghian, S., & Johnson, L. W. (2018). Perception of tourism development and subjective happiness of residents in Mashhad, Iran. Asia Pacific J. Tourism Research, 23(6), 521–531.
Kang, S., Vogt, C. A., & Lee, S. (2018). Does taking vacations make people happy? A regional disparity perspective. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 23(11), 1021–1033.
Kang’ethe, S. M., & Wotshela, N. (2016). An autopsy of xenophobia and xenophobic attitudes inherent in institutions of higher learning in South Africa. Journal of Social Sciences, 49(1–2), 158–164.
Knezackova, R. and Linhartova, V. 2013. The economic openness and its influence on the level of corruption in the Czech Republic. In Proceedings of The 11th International Conference: Economic Policy In The European Union Member Countries, Selected Papers. pp 114–125.
Kollias, C., & Paleologou, S.-M. (2017). The globalization and peace nexus: findings using two composite indices. Social Indicators Research, 131(3), 871–885.
Kollias, C., & Papadamou, S. (2017). Peace and tourism: a nexus? Evidence from developed and developing countries. Singapore Economic Review. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217590817470038.
Kuzey, C., Karaman, A. S., & Akman, E. (2019). Elucidating the impact of visa regimes: a decision tree analysis. Tourism Management Perspectives, 29, 148–156.
Li, R. Y. M., Tang, E. C. H., & Leung, T. H. (2019). Democracy and economic growth. International Journal of Data Analysis Techniques and Strategies, 11(1), 58–80.
Lieven, A. (2017). Against: limiting migration to preserve European social peace. Debating Migration to Europe: Welfare vs Identity, pp. 35–54.
Lundy, B. D., & Darkwah, K. (2018). Measuring community integration of Lusophone West African immigrant populations through needs assessment, human security, and realistic conflict theory. Journal of International Migration and Integration, 19(2), 513–526.
Maridal, J. H. (2017). A worldwide measure of societal quality of life. Social Indicators Research, 134, 1–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-016-1418-y.
Markina, I., Safonov, Y., Zhylinska, O., Diachkov, D., & Varaksina, E. (2018). Defining the dimensions of national security, financial security and food supply chain in Ukraine. International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 7(6), 608–620.
Mashika, H. V. (2018). Impact of institutional factors on formation of economic development and potential of Carpathian region. Journal of Geology, Geography and Geoecology, 24(1), 82–89. https://doi.org/10.15421/111612.
May, M., & Smilde, D. (2016). Minority participation and well-being in majority Catholic nations: what does it mean to be a religious minority? Journal of Religion and Health, 55(3), 874–894.
Meisenberg, G., & Woodley, M. A. (2015). Gender differences in subjective well-being and their relationships with gender equality. Journal of Happiness Studies, 16(6), 1539–1555.
Melotti, M., Ruspini, E., & Marra, E. (2018). Migration, tourism and peace: Lampedusa as a social laboratory. Anatolia, 29(2), 215–224.
Nair, S. (2017). Passport privilege entrenches inequality. Eureka Street, 27(24), 33.
Okagbue, H. I., Iroham, C. O., Peter, N. J., Owolabi, J. D., Adamu, P. I., & Opanuga, A. A. (2018). Systematic review of building failure and collapse in Nigeria. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 9(10), 1391–1401.
Olanrewaju, F. O., Omotoso, F., & Alabi, J. O. (2018). Datasets on the challenges of forced displacement and coping strategies among displaced women in selected Internally Displaced Persons’ (IDPs) camps in Nigeria. Data in Brief, 20, 152–158.
Olgiati, A., Calvo, R., & Berkman, L. (2013). Are migrants going up a blind alley? Economic migration and life satisfaction around the world: cross-national evidence from Europe, North America and Australia. Social Indicators Research, 114(2), 383–404.
Ortega, B., Casquero, A., & Sanjuán, J. (2016). Corruption and convergence in human development: evidence from 69 countries during 1990–2012. Social Indicators Research, 127(2), 691–719.
Ozaltin, D., Shakir, F., & Loizides, N. (2019). Why do people flee? Revisiting forced migration in post-Saddam Baghdad. Journal of International Migration and Integration. Article in Press.
Paparusso, A. (2019). Studying immigrant integration through self-reported life satisfaction in the country of residence. Applied Research in Quality of Life, 14(2), 479–505.
Park, P. C. (2017). Chile’s limited passport into the global literary market. Symplokē, 25(1-2), 97–112.
Podobnik, B., Shao, J., Njavro, D., Ivanov, P. C., & Stanley, H. E. (2008). Influence of corruption on economic growth rate and foreign investment. European Physical Journal B, 63(4), 547.
Policardo, L., Sanchez Carrera, E. J., & Risso, W. A. (2019). Causality between income inequality and corruption in OECD countries. World Development Perspectives. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wdp.2019.02.013.
Poprawe, M. (2016). A panel data analysis of the effect of corruption on tourism. Applied Economics, 47(23), 2399–2412. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2015.1005874.
Pratt, S., & Liu, A. (2016). Does tourism really lead to peace? A global view. International Journal of Tourism Research, 18(1), 82–90.
Richmond, O. P., & Mac Ginty, R. (2018). Mobilities and peace. Globalizations. https://doi.org/10.1080/14747731.2018.1557586.
Rinzin, C. (2006). On the middle path: the social basis for sustainable development in Bhutan. Nederlandse Geografische Studies, 352, 1–204.
Sanz, M. T., Caselles, A., Micó, J. C., & Soler, D. (2018). A stochastic dynamical social model involving a human happiness index. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 340, 231–246.
Seabra, C., Kastenholz, E., Abrantes, J. L., & Reis, M. (2018). Peacefulness at home: impacts on international travel. International Journal of Tourism Cities, 4(4), 413–428.
Shao, J., Ivanov, P. C., Podobnik, B., & Stanley, H. E. (2007). Quantitative relations between corruption and economic factors. European Physical Journal B, 56(2), 157.
Sriyana, J., Prabowo, H. Y., & Syamsudin, M. (2017). Preventing corruption in the Indonesian public sector. European Research Studies Journal, 20(3), 538–553.
Suzuki, T. (2018). Corruption, interest rates and business cycles: comparison of emerging economies. Economic Change and Restructuring, 51(4), 303–316.
Tajaddini, R., & Gholipour, H. F. (2018). Control of corruption and luxury goods consumption. Kyklos, 71(4), 613–641.
Tang, C. F. (2018). The impacts of governance and institutions on inbound tourism demand: evidence from a dynamic panel data study. Asia Pacific J. Tourism Research, 23(10), 1000–1007.
Tang, Y. (2019). Immigration status and adolescent life satisfaction: an international comparative analysis based on PISA 2015. Journal of Happiness Studies, 20(5), 1499–1518.
Vilkova, A. V., & Timofeeva, E. A. (2018). Socio-economic stratification and the penitentiary system. European Research Studies Journal, 21(4), 186–194.
Viveros, M. (2016). Correlation between peace and development. International Journal of Interdisciplinary Global Studies, 11(4), 13–27.
Webster, C., & Ivanov, S. (2016). The ideologies of national security and tourist visa restrictions. International Journal of Tourism Policy, 6(3–4), 171–190.
WHR (2019). http://worldhappiness.report/. Accessed 23 Feb 2019.
Wilhem, P. G. (2002). International validation of the corruption perceptions index: implications for business ethics and entrepreneurship education. Journal of Business Ethics, 35(3), 177–189.
Yoon, J., & Klasen, S. (2018). An application of partial least squares to the construction of the Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI) and the Corruption Perception Index (CPI). Social Indicators Research, 138(1), 61–88.
Yunusa, I. A. M., Zerihun, A., & Gibberd, M. R. (2018). Analysis of the nexus between population, water resources and Global Food Security highlights significance of governance and research investments and policy priorities. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 98(15), 5764–5775.
Zabelina, M. I., Nikishkin, V. V., Arefyeva, N. T., Mudrova, S. V., & Cherednichenko, L. G. (2017). Theoretical approaches towards global social development. European Research Studies Journal, 20(2), 338–345.
Zhang, L., & Zhang, J. (2018). Impacts of leisure and tourism on the elderly’s quality of life in intimacy: a comparative study in Japan. Sustainability, 10(12), 4861.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okagbue, H.I., Oguntunde, P.E., Bishop, S.A. et al. Significant Predictors of Henley Passport Index. Int. Migration & Integration 22, 21–32 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12134-019-00726-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12134-019-00726-4