Abstract
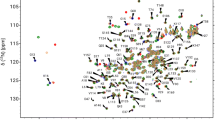
Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) plays a pivotal role in modulating multiple signaling networks. Here we report backbone and side chain resonance assignments of uniformly 15N, 13C labeled human RKIP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banfield MJ, Barker JJ et al (1998) Function from structure? The crystal structure of human phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein suggests a role in membrane signal transduction. Structure 6(10):1245–1254
Corbit KC, Trakul N et al (2003) Activation of Raf-1 signaling by protein kinase C through a mechanism involving Raf kinase inhibitory protein. J Biol Chem 278(15):13061–13068
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S et al (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6(3):277–293
Dhillon AS, Hagan S et al (2007) MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 26(22):3279–3290
Frayne J, McMillen A et al (1998) Expression of phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein in the male reproductive tract: immunolocalisation and expression in prepubertal and adult rat testes and epididymides. Mol Reprod Dev 49(4):454–460
Frayne J, Ingram C et al (1999) Localisation of phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein in the brain and other tissues of the rat. Cell Tissue Res 298(3):415–423
Kroslak T, Koch T et al (2001) Human phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein facilitates heterotrimeric G protein-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem 276(43):39772–39778
Lorenz K, Lohse MJ et al (2003) Protein kinase C switches the Raf kinase inhibitor from Raf-1 to GRK-2. Nature 426(6966):574–579
Pearson G, Robinson F et al (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22(2):153–183
Roberts PJ, Der CJ (2007) Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 26(22):3291–3310
Schoentgen F, Seddiqi N et al (1992) Main structural and functional features of the basic cytosolic bovine 21 kDa protein delineated through hydrophobic cluster analysis and molecular modelling. Protein Eng 5(4):295–303
Trakul N, Rosner MR (2005) Modulation of the MAP kinase signaling cascade by Raf kinase inhibitory protein. Cell Res 15(1):19–23
Wellbrock C, Karasarides M et al (2004) The RAF proteins take centre stage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(11):875–885
Wishart DS, Sykes BD (1994) The 13C chemical-shift index: a simple method for the identification of protein secondary structure using 13C chemical-shift data. J Biomol NMR 4(2):171–180
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30900233, 30730026) and the Program of Shanghai Subject Chief Scientist (No. 09XD1405100). We would like to thank Prof. J. Y. Li for providing the human RKIP gene.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, C., Peng, Y., Guo, C. et al. 1H, 13C, 15N backbone and side-chain resonance assignments of the human Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein. Biomol NMR Assign 5, 63–66 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-010-9268-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-010-9268-z