Abstract
Objective
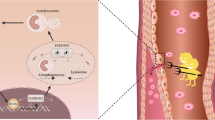
To evaluate ITPKC and NLRP3 expression in children with Kawasaki disease (KD) and investigate the relationship between serum pro-inflammatory cytokines triggered by NLRP3 and inflammatory indices. Simultaneously, the methylation level in the ITPKC promoter was evaluated in children with KD.
Methods
Children who satisfied the American Heart Association diagnostic criteria for KD were enrolled in the study from August 2018 to January 2019. The levels of ITPKC, NLRP3, IL-1β, and IL-18 were measured. The effect of DNA methylation on the activity of the ITPKC promoter was observed. Methylation-specific PCR was used to verify methylation modification of the ITPKC promoter region in children with KD.
Results
ITPKC expression was downregulated in patients with KD, whereas NLRP3 was upregulated. Expression of the downstream cytokine, IL-18, was significantly upregulated in children with KD and correlated positively with inflammatory indices. Modifying DNA methylation significantly decreased the luciferase activity of the plasmid containing the ITPKC promoter region and thus, may inhibit ITPKC gene promoter activity. Furthermore, methylation modification was observed in the ITPKC promoter region of children with KD.
Conclusion
Modification of DNA methylation inhibits ITPKC promoter activity and is involved in NLRP3 inflammasome activation in children with KD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
On reasonable request.
References
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American heart association. Circulation. 2017;135:e927–99.
Singh S, Vignesh P, Burgner D. The epidemiology of Kawasaki disease: a globalupdate. Arch Dis Child. 2015;100:1084–8.
Kato H, Koike S, Yamamoto M, Ito Y, Yano E. Coronary aneurysms in infants and young children with acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. J Pediatr. 1975;86:892–8.
Onouchi Y, Gunji T, Burns JC, et al. ITPKC functional polymorphism associated with Kawasaki disease susceptibility and formation of coronary artery aneurysms. Nat Genet. 2008;40:35–42.
Alphonse MP, Duong TT, Shumitzu C, et al. Inositol-triphosphate 3-kinase C mediates inflammasome activation and treatment response in Kawasaki disease. J Immunol. 2016;197:3481–9.
Yeung RS. Kawasaki disease: update on pathogenesis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010;22:551–60.
Fukushige S, Horii A. DNA methylation in cancer: a gene silencing mechanism and the clinical potential of its biomarkers. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2013;229:173–85.
Noval Rivas M, Arditi M. Kawasaki disease: pathophysiology and insights from mouse models. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16:391–405.
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH. Improving coronary artery outcomes for children with Kawasaki disease. Lancet. 2019;393:1077–8.
Ammirati E, Burns JC, Moreo A, Daniels LB, Oliva F. Extreme giant aneurysms of three coronary arteries causing heart failure as late sequelae of Kawasaki disease. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:759–60.
Kuo HC, Chang WC. Genetic polymorphisms in Kawasaki disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011;32:1193–8.
Rowley AH. Kawasaki disease: novel insights into etiology and genetic susceptibility. Annu Rev Med. 2011;62:69–77.
Kelley N, Jeltema D, DuanY, He Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:3328.
Moretti J, Blander JM. Increasing complexity of NLRP3 inflammasome regulation. J Leukoc Biol. 2020;109:561–71.
Liu LP, Yuan YH, He XH, et al. Expression of nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of children with Kawasaki disease in the acute stage. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019;21:992–7.
Anzai F, Watanabe S, Kimura H, et al. Crucial role of NLRP3 inflammasome in a murine model of Kawasaki disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020;138:185–96.
Stock AT, Jama HA, Hansen JA, Wicks IP. TNF and IL–1 play essential but temporally distinct roles in driving cardiac inflammation in a murine model of Kawasaki disease. J Immunol. 2019;202:3151–60.
Tirelli F, Marrani E, Giani T, Cimaz R. One year in review: Kawasaki disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020;32:15–20.
Abe M, Rastelli DD, Gomez AC, et al. IL-1-dependent electrophysiological changes and cardiac neural remodeling in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020;199:303–13.
Kone-Paut I, Cimaz R, Herberg J, et al. The use of interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) in Kawasaki disease: a retrospective cases series. Autoimmun Rev. 2018;17:768–74.
Dusser P, Koné-Paut I. IL–1 Inhibition may have an important role in treating refractory Kawasaki disease. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:163.
Nakanishi K. Unique action of interleukin-18 on T cells and other immune cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:763.
Chen SY, Wan L, Huang YC, et al. Interleukin-18 gene 105A/C genetic polymorphism is associated with the susceptibility of kawasaki disease. J Clin Lab Anal. 2009;23:71–6.
Weng KP, Hsieh KS, Huang SH, et al. Interleukin-18 and coronary artery lesions in patients with kawasaki disease. J Chin Med Assoc. 2013;76:438–45.
Chang D, Qian C, Li H, Feng H. Comprehensive analyses of DNA methylation and gene expression profiles of Kawasaki disease. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:13001–11.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81202345, 81771762).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J-ML, F-ZD, and Y-HG contributed to the conceptualization and study design; D-JY, XY, and P-YT interpreted and statistically analyzed the data; F-ZD and Y-HG were responsible for monitoring and data management, as well as reviewing and editing the manuscript; All authors were involved in drafting the article or revising it critically, and all authors approved the final version to be published. Y-HG will act as the guarantor for this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All study protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Hospital.
Consent to Participate
All patients and healthy controls were informed about the study aim, and informed consent was obtained from their legal guardians.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, ML., Dong, JY., Xu, Y. et al. Inositol-Triphosphate 3-Kinase C and DNA Methylation Involvement in NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Kawasaki Disease. Indian J Pediatr 90, 22–28 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-022-04126-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-022-04126-y