Abstract
Objectives
To study the effectiveness, tolerability, and safety of oral nitrazepam in children with resistant West syndrome (WS).
Methods
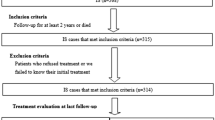
This prospective observational study was conducted at a tertiary care hospital in North India from January 2019 to October 2020. Children with WS resistant to standard therapy were enrolled within 7 d of initiation of nitrazepam and prospectively followed-up for cessation of spasms and adverse events.
Results
Forty-one children with resistant WS initiated on nitrazepam therapy were evaluated. The median age at onset of spasms was 6 mo (Q1, Q3: 4, 8). There was a preponderance of male gender (71%) and structural causes (78%). More than half of the enrolled children had failed four or more antiseizure medications (ASM) for epileptic spasms. The study participants had a long lead-time-to-treatment (LTTT) for the initial standard therapy (median: 2 mo; Q1, Q3: 1, 5) and nitrazepam (median: 11 mo; Q1, Q3: 8, 16). Nitrazepam was instituted as monotherapy in 7 (17%) children and as an adjunct in the rest. Twenty-one (51%) children achieved persistent cessation of epileptic spasms. However, the electroclinical response was observed in 17 (42%) children. Drowsiness, sialorrhea, and decreased appetite were the most commonly observed adverse events. Most adverse events were mild to moderate in severity and did not require dose reduction or change of medication. There was no significant difference between the responders and nonresponders in terms of LTTT, age at onset, or etiology.
Conclusions
Nitrazepam is a safe and feasible treatment alternative in children with resistant WS resulting in persistent cessation of spasms and electroclinical response in nearly half of patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lux AL, Osborne JP. A proposal for case definitions and outcome measures in studies of infantile spasms and West syndrome: consensus statement of the West Delphi group. Epilepsia. 2004;45:1416–28.
Sahu JK. Infantile spasms--evidence based medical management.Indian J Pediatr. 2014;81:1052–5.
Go CY, Mackay MT, Weiss SK, et al. Evidence-based guideline update: medical treatment of infantile spasms. report of the guideline development subcommittee of the American academy of neurology and the practice committee of the child neurology society. Neurology. 2012;78:1974–80.
Chang Y, Chen C, Chen S, Shen Y, Kuo Y. Effectiveness of corticosteroids versus adrenocorticotropic hormone for infantile spasms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019;6:2270–81.
Song JM, Hahn J, Kim SH, Chang MJ. Efficacy of treatments for infantile spasms: a systematic review.Clin Neuropharmacol. 2017;40:63–84.
Rajpurohit M, Gupta A, Madaan P, Sahu JK, Singhi P. Safety, Feasibility and Effectiveness of Pulse Methylprednisolone Therapy in Comparison with Intramuscular Adrenocorticotropic Hormone in Children with West Syndrome. Indian J Pediatr. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-020-03521-7.
Angappan D, Sahu JK, Malhi P, Singhi P. Safety, tolerability, and effectiveness of oral zonisamide therapy in comparison with intramuscular adrenocorticotropic hormone therapy in infants with West syndrome. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2019;23:136–42.
Glauser TA, Clark PO, Strawsburg R. A pilot study of topiramate in the treatment of infantile spasms. Epilepsia. 2005;39:1324–8.
Hsieh MY, Lin KL, Wang HS, Chou ML, Hung PC, Chang MY. Low-dose topiramate is effective in the treatment of infantile spasms. Chang Gung Med J. 2006;29:291–6.
Zou LP, Lin Q, Qin J, Cai FC, Liu ZS, Mix E; Tapirisat study group. Evaluation of open-label topiramate as primary or adjunctive therapy in infantile spasms. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2008;31:86–92.
Hussain SA, Dlugos DJ, Cilio MR, Parikh N, Oh A, Sankar R. Synthetic pharmaceutical grade cannabidiol for treatment of refractory infantile spasms: A multicenter phase-2 study. Epilepsy Behav. 2020;102:106826.
Herlopian A, Hess EJ, Barnett J, Geffrey AL, et al. Cannabidiol in treatment of refractory epileptic spasms: An open-label study. Epilepsy Behav. 2020;106:106988.
Syed RA. Dexamathasone pulse therapy in refractory childhood seizure disorders. J. Neurosci. 2017;1:12.
Jan JE, Riegl JA, Crichton JU, Dunn HG. Nitrazepam in the treatment of epilepsy in childhood. Can Med Assoc J. 1971;104:571–5.
Fallah R, Salor F, Akhavan Karbasi S, Motaghipisheh H. Randomised clinical efficacy trial of topiramate and nitrazepam in treatment of infantile spasms, Iran. J Child Neurol. 2014;8:12–9.
Auvichayapat N, Tassniyom S, Treerotphon S, Auvichayapat P. Treatment of infantile spasms with sodium valproate followed by benzodiazepines. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007;90:1809–14.
Dreifuss F, Farwell J, Holmes G, et al. Infantile spasms. Comparative trial of nitrazepam and corticotropin. Arch Neurol. 1986;43:1107–10.
Baloch A. Goodman and Gilman’s Pharmacology.13th Edition. Medicos Republic; 2018. Available at: https://www.medicosrepublic.com/goodman-and-gilmans-the-pharmacological-basis-of-therapeutics-13th-edition-pdf-free-download/. Accessed on 27 Nov 2020
Vinkers CH, Olivier B. Mechanisms Underlying Tolerance after Long-Term Benzodiazepine Use: A Future for Subtype-Selective GABAA Receptor Modulators? Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2012;2012:416864.
Chamberlain MC. Nitrazepam for refractory infantile spasms and the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. J Child Neurol. 1996;11:31–4.
Antoniuk SA, Bruck I, Spessatto A, et al. West syndrome: clinical and electroencephalographic evolution of 70 patients and response to treatment with adrenocorticotrophic hormone, prednisone, vigabatrin, nitrazepam and valproic acid. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2000;58:683–90.
Capovilla G, Beccaria F, Montagnini A, et al. Short-term nonhormonal and nonsteroid treatment in West syndrome. Epilepsia. 2003;44:1085–8.
Madaan P, Chand P, Linn K, et al. Management practices for West syndrome in South Asia: a survey study and meta-analysis. Epilepsia Open. 2020;5:461–74.
Mytinger JR, Hussain SA, Islam MP, et al. Improving the inter-rater agreement of hypsarrhythmia using a simplified EEG grading scale for children with infantile spasms. Epilepsy Res. 2015;116:93–8.
Sehgal R, Gulati S, Sapra S, Tripathi M, Kabra M, Pandey RM. Neurodevelopmental and epilepsy outcome in children aged one to five years with infantile spasms–a North Indian cohort. Epilepsy Res. 2014;108:526–34.
Singhi P, Ray M. Profile of West syndrome in North Indian children. Brain Dev. 2005;27:135–40.
O’Callaghan FJK, Lux AL, Darke K, et al. The effect of lead time to treatment and of age of onset on developmental outcome at 4 years in infantile spasms: evidence from the United Kingdom infantile spasms study. Epilepsia. 2011;52:1359–64.
Millichap J. Toxicity of Nitrazepam (Mogadon). Pediatr Neurol Briefs. 1987;1:18–9.
Murphy JV, Sawasky F, Marquardt KM, Harris DJ. Deaths in young children receiving nitrazepam. J Pediatr. 1987;111:145–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the families of all children with West syndrome who participated in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ, JKS: Planning and conduct of the study, data collection, data analysis, literature search, and preparation of the initial draft; PM: EEG interpretation, data collection, data interpretation, preparation of the initial draft and critical review of manuscript; RS, SP, AGS, LS, NS: Planning and conduct of the study, data collection, data interpretation and critical review of the manuscript; AK: Data analysis, literature search, and critical review of the manuscript; SZ, AK: Statistical analysis. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. JKS is the guarantor of this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Committee Approval
Was obtained from IEC at PGIMER, Chandigarh vide INT/IEC/2019/000245 dated 11/02/2019.
Informed Consent
Was obtained from parents of each subject before enrolment.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahan, S., Sahu, J.K., Madaan, P. et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Nitrazepam in Children with Resistant West Syndrome. Indian J Pediatr 89, 37–44 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-021-03823-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-021-03823-4