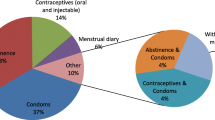
Abstract
Objective
To compare the knowledge, attitude and practice of boys and girls on reproductive sexual health and their perspective on the needs of adolescents on this aspect.
Methods
This comparative study was conducted among boys and girls between 10 and 24 y in three districts of Kerala; through a cross sectional community survey using a pretested structured schedule with additional sexuality related questions for 15–24 y age group.
Results
Higher percentage of boys knew about condoms (95.1 %, p 0.001) whereas higher percentage of girls (56.5 %, p 0.001) knew about copper-T. Girls had a better knowledge on legal age of marriage (91 %, p 0.001), that both the partners are equally responsible for the problem of infertility (89.7 %, p 0.009) and that the gender of the baby is determined by male sperm (60.4 %, p 0.001). Above 90 % of boys and girls demanded adolescent care services and facilities for counseling.
Conclusions
This comparative study on knowledge, attitude and practice of boys and girls between 10 and 24 y has shown that greater proportion of girls had correct knowledge on the legal age of marriage, ideal age of pregnancy, preferred an arranged marriage and felt the need for premarital counseling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO. Promoting and safeguarding the sexual and reproductive health of adolescents. Implementing the Global Reproductive Health Strategy. Policy brief – 4. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2006. Available from URL: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2006/RHR_policybrief4_eng.pdf. Accessed on 31 December 2012. pp.1–3.
WHO. The sexual and reproductive health of young adolescents in developing countries: Reviewing the evidence, identifying research gaps, and moving the agenda. Geneva: Report of a WHO technical consultation; 2010. pp. 5.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the cooperation and support received from UNFPA through Directorate of Health Services, Kerala, Adolescents and their parents, all community stakeholders of Kollam, Alappuzha and Wayanad district, Dr. G. Suresh Kumar, Registrar, Ms. Deepa NR, PS to Director, Prasanna GL and other staff of ARSH Project, CDC Kerala, especially Mr. Asokan N, PA to Director, Ms. Suja S, Junior Programmer in helping the study.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Role of Funding Source
UNFPA through Directorate of Health Services, Kerala.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, M.K.C., Leena, M.L., George, B. et al. ARSH 2: Reproductive and Sexual Health Knowledge, Attitude and Practices: Comparison Among Boys and Girls (10–24 y). Indian J Pediatr 80 (Suppl 2), 199–202 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1139-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1139-z